Marine and Freshwater Guided Reading
advertisement

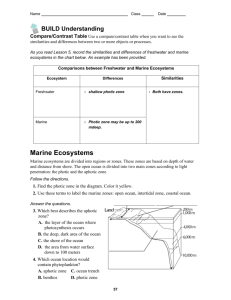
Guided Reading: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems Marine Ecosystems 1. The Earth’s oceans and seas contain about half of the Earth’s water supply. True or False? 2. A marine ecosystem contains a. Acidic water b. Salty water c. Sour water d. Bitter water Abiotic Factors Rule (pg. 481) 3. Which of the following abiotic factors determine what different areas of the ocean are like? (Circle all that apply). a. Temperature b. Amount of sunlight penetrating the water c. Distance from land d. Depth of water 4. Producers are found only to a depth of about __________________ m below the ocean’s surface. 5. How are phytoplankton and zooplankton different? Wonderful Watery Biomes (pg. 482) 6. Suppose you could walk into an ocean and swim to the center of it, in what order would you pass through the following zones? ____ intertidal ____ oceanic ____ neritic ____ benthic 7. Where does the food for animals living in ocean waters too dep for light to penetrate come from? A Closer Look (pg. 484) 8. Which of the following are ways that marine environments affect us? (Circle all that apply). a. They provide most of the water for rainfall on our planet. b. They supply us with food. c. Their temperatures affect climates and wind patterns. d. None of the above. 9. Explain the symbiotic relationship between corals and algae. 10. In the __________________________ most of the animals have adapted to living with huge floating rafts of algae. 11. The ocean water around Antarctica is rich in nutrients. Where did these nutrients come from? 12. Most life in the Arctic Ocean feeds off the large aquatic mammals. True or False? 13. An estuary is a special type of river. True or False? 14. The rise and fall of the tide affects the amount of ___________________________ in an estuary. 15. How do sear stars avoid being washed out to sea? ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------Freshwater Ecosystems 1. One of the most important characteristics of freshwater ecosystems is the ____________________ the water is moving. Water on the Move (pg. 486) 2. How have producers adapted to living in moving freshwater? a. They do not need as much sunlight b. They can float. c. They are strong and can withstand wave action. d. They cling to rocks. 3. Some consumers that live in moving water have adapted to their environment by using suction _____________________ to their hold onto rocks. (disks or cups) 4. All moving water eventually empties into a lake or an ocean. True or False? Still Waters (pg. 487) 5. The largest freshwater lake in the world is Lake ____________________. 6. The most abundant producers in the open-water littoral zone of a lake are a. Bacteria b. Long-leafed plants c. Phytoplankton d. Carp 7. What determines the depth of an open-water zone? 8. Deep-water zone must hunt their food. True or False? 9. Which of the following is NOT true about wetlands? a. b. c. d. For most of the year, the water level is above or near the ground. They are important in flood control. They replenish underground water supplies. They support very few species of plant and animal life. 10. Freshwater marshes occur beside rivers and ocean. True or False? 11. How have trees adapted to living in swamps? From Lake to Forest (pg. 489) 12. How can a pond or lake become a forest?