Chapter 10 Reading Guide
advertisement

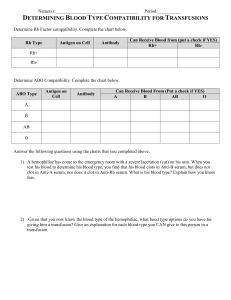
Chapter 10: Blood Name_______________________ Anatomy Blood is a(n) ___________ tissue. Living blood cells are referred to as _________________________. The non-living fluid portion in which the cells are suspended is the ________________________. If the blood is spun down in a ____________________, the red portion that will settle to the bottom includes the red blood cells or the _____________________________. The thin white layer that will appear between this and the plasma is the ______________________________. It includes the white blood cells or the _________________________ and the _________________________. On the average, the formed elements make up about ________ % of blood and the plasma makes up about ________%. Blood can appear scarlet to dull red depending on how much ________________ it is carrying. It is slightly alkaline (basic) with a pH ranging from ________ to _________. Its temperature is about __________ degrees F. It accounts for about ______ % of our body weight. In healthy men, that is about _________ liters. Plasma is mostly made of ______________ (about 90%). Over 100 different substances are dissolved into it, including: 1)_______________________________________ 2)____________________________________________ 3)_______________________________________ 4)____________________________________________ 5)_______________________________________ 6)____________________________________________ Plasma proteins are the most abundant and made by the ______________________. They serve a variety of functions including shuttling molecules (hemoglobin and albumin) and as clotting factors. When blood protein levels drop to undesirable levels, the liver is stimulated to produce more. Formed Elements Read through the sections on each of the types of blood cells. Take notes and identify the homeostatic imbalances associated with each. Red blood cells or Notes Homeostatic Imbalances _______________________ Chapter 10: Blood Name_______________________ White Blood Cells or ______________________ Anatomy Homeostatic Imbalances Notes Platelets or Notes Quiz 1 Blood Cell Formation or ______________________________ This process takes place in the __________________________ or _______________ tissue. On the average, the red marrow turns out each and everyday an ___________________ of new blood containing ____________________ new cells. All the formed elements arise from a common type of stem cell known as a ____________________________. Complete the flow chart showing the different types of cell that can be made. How long do most erythrocytes live?___________________________________________________________ Chapter 10: Blood Name_______________________ Anatomy How is the rate of red blood cell production regulated? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ What stimulates the production of white blood cells? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ What hormones stimulates the production of platelets? _____________________________________________ What is hemostasis? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ What are the three major phases? (brief summary) 1)________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2)________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3)________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Disorders of Hemostasis Undesirable Clotting Thrombus Embolus Bleeding Disorders Thrombocytopenia Liver unable to synthesize clotting factors Hemophilia Blood Groups A loss of 15 to 30 % of your blood can lead to ______________________, whereas loss of more than 30% causes ____________________________ and can be fatal. Blood collected at a blood bank can be stored up to __________ days if refrigerated and stopped from coagulating. The plasma membranes of red blood cells have genetically determined proteins called ____________________. Each of bodies, depending on our blood type, recognize self (type A blood recognizes A antigens). We produce _____________________ that recognize what is not self (A blood would recognize B as not self and produce anti-B antibodies against it.) Be familiar with the types of blood, what antigens they produce, and what antibodies they produce. Know which is the universal donor and universal recipient. BE ABLE TO EXPLAIN how this works. What is Rh factor related to blood? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Discuss the Rh factor problem that can occur when a Rh – woman is pregnant and carrying a Rh + baby. __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ How do we deal with this to protect them? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ How does blood typing work? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Chapter 10: Blood Name_______________________ Anatomy Discuss what is happening in each of the pictures: Developmental Where is blood cell formation before birth?______________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ What is physiologic jaundice? __________________________________________________________________________________________ Quiz 2 AT THE CLINIC QUESTIONS: 1. A patient on renal dialysis has a low RBC count. What hormone, secreted by the kidney, can be assumed to be deficient? 2. A woman comes to the clinic complaining of fatigue, shortness of breath, and chills. Blood tests show anemia, and a bleeding ulcer is diagnosed. What type of anemia is this? 3. A patient is diagnosed with bone marrow cancer and has a hematocrit of 70 percent. What is this condition called? 4. A middle-aged college professor from Boston is in the Swiss Alps studying astronomy. He arrived two days ago and plans to stay the entire year. However, he notices that he is short of breath when he walks up steps and that he tires easily with any physical activity. His symptoms gradually disappear; after two months, he feels fine. Upon returning to the United States, he has a complete physical exam and is told that his erythrocyte count is higher than normal. (a) Attempt to explain this finding. (b) Will his RBC count remain at this higher-than-normal level? Why or why not? 5. Why is someone more likely to bleed to death when an artery is cleanly severed than when it is crushed and torn? 6. When testing for blood type an individuals blood agglutinates in both anti-A and anti-B serum. What can you predict about their blood type? 7. When testing for blood type an individuals blood doesn’t agglutinate with either anti-A and anti-B serum. What can you predict about their blood type? 8. In a blood test, a sample was found to only clump or agglutinate with anti-A serum. The blood sample is type ________.