Obesity and Hypertension: Vulnerable Population Care Plan
advertisement

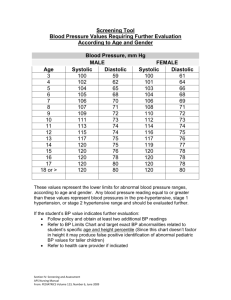
Obesity and Hypertension: Vulnerable Population Care Plan Nicole Chan GNRS 587 July 16, 2015 Vulnerability ● ● ● ● In California, 25.4% of adults and 15.8% of adolescents are obese o Obesity rates are significantly higher in lowincome children Studies show that the relative risk (RR) for hypertension increases sharply for those who are obese o Strongest relative risk seen in younger individuals o Hispanics and Blacks are the most likely to be obese Hypertension is the leading cause of death in the US and California o HTN also increases the risk for heart disease and stroke, the two other leading causes of death The cost of obesity, and obesity-related diseases to the state of California is estimated at $15.2 billion Vulnerable Population Model Flaskerud and Winslow Resource Availability: Lack of Education, Poor Diet, Minimal to Low Exercise, and Lack of Support Ethics: Beneficence and Nonmaleficence Practice: Reduce risk for obesity and hypertension Research Practice, Ethical, & Policy Analysis Health Status: Hypertension, Heart Disease, Stroke, Morbidity and Mortality Relative Risk: Low income, young, Black, Hispanic Policy: Legislative Advocacy & Nursing Influence Patient Profile ● ● The obese and hypertensive patient Priority health needs: reduce risk for obesity and hypertension ○ Primary Level of Prevention: Education ■ Prevent obesity and reduce the risk of hypertension by teaching vulnerable populations (low-income, Hispanic and Black, younger age) about diet, exercise, medication compliance ○ Secondary Level of Prevention: Screening ■ Make sure the patient is seen by PCP regularly and evaluate weight, monitor BP, check blood levels, etc. ○ Tertiary Level of Prevention: Health Maintenance/Treatment ■ Weight loss programs, BP medications, change in diet, exercise plan Interventions and Outcome Measures Interventions ● Primary - Education o Encourage a healthy lifestyle from infant through adulthood o Educate regarding risks associated with obesity and HTN o Educate regarding healthy lifestyle diet exercise ● Secondary - Screening o Regular PCP visits to monitor weight and BP ● Tertiary - Treatment and Maintenance o Weight loss programs o BP Medications Interventions and Outcome Measures Outcome Measures ● BMI ○ ○ ○ Normal or healthy weight: 18.524.9 Overweight: 35.0-29.9 Obese: 30.0 and above ● BP Levels ○ ○ ○ ○ Normal: Systolic ≤ 120 and Diastolic ≤ 80 Prehypertension: Systolic 120-139 or Diastolic 80-90 HTN Stage 1: Systolic 140-159 or Diastolic 90-99 HTN Stage 2: Systolic 160+ or Diastolic 100+ Resources UCSD Weight Management Program CDC.gov NCLEX Question A patient inquires if his blood pressure is normal. The nurse responds that normal blood pressure is defined as less than: A. B. C. D. 160/70 mm Hg 128/60 mm Hg 139/89 mm Hg 130/85 mm Hg NCLEX Question Answer B.128/60 mm Hg Rationale: Normal BP is defined as Systolic ≤ 120 and Diastolic ≤ 80 References https://www.cdph.ca.gov/programs/cpns/Documents/ObesityinCaliforniaReport.pdf https://www.cdph.ca.gov/pubsforms/Pubs/OHIRhypertensionDeaths2004.pdf http://health.ucsd.edu/specialties/surgery/bariatric/non-surgical/Pages/default.aspx Institute of Medicine. Evaluating obesity prevention efforts. http://www.iom.edu/About-IOM/Leadership-Staff/Boards/Food-and-Nutrition-Board/ObesityReports.aspx. Accessed March 28, 2015 Koebnick, C., Smith, N., Huang, K., Martinez, M. P., Clancy, H. A., & Kushi, L. H. (2012). The prevalence of obesity and obesity-related health conditions in a large, multiethnic cohort of young adults in California. Annals Of Epidemiology,22609-616. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2012.05.006 http://www.sandiegocounty.gov/hhsa/programs/phs/documents/CHS-EconomicBurdenofChronicDisease2010.pdf.