Diet and Hypertension
advertisement

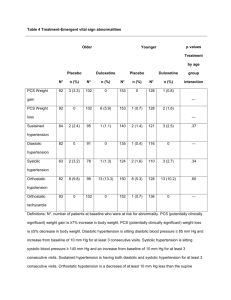
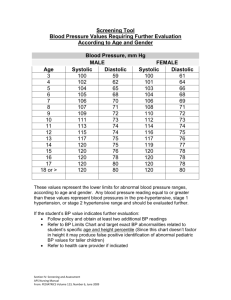
Diet and Hypertension Created by: Tricia Fleming, University of Kansas Dietetic Intern Tammy Beason, MS, Nutrition Education Specialist, Family Nutrition Education Program December 2001 What is Blood Pressure? The force of blood against the wall of the arteries. Systolic- as the heart beats Diastolic - as the heart relaxes Written as systolic over diastolic. Normal Blood pressure is less than 130 mm Hg systolic and less than 85 mm Hg diastolic. High Blood Pressure A consistent blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or higher is considered high blood pressure. It increases chance for heart disease, kidney disease, and for having a stroke. 1 out of 4 Americans have High Bp. Has no warning signs or symptoms. Why is High Blood Pressure Important? Makes the Heart work too hard. Makes the walls of arteries hard. Increases risk for heart disease and stroke. Can cause heart failure, kidney disease, and blindness. How Does It Effect the Body? The Brain High blood pressure is the most important risk factor for stroke. Can cause a break in a weakened blood vessel which then bleeds in the brain. The Heart High Blood Pressure is a major risk factor for heart attack. Is the number one risk factor for Congestive Heart Failure. The Kidneys Kidneys act as filters to rid the body of wastes. High blood pressure can narrow and thicken the blood vessels. Waste builds up in the blood, can result in kidney damage. The Eyes Can eventually cause blood vessels to break and bleed in the eye. Can result in blurred vision or even blindness. The Arteries Causes arteries to harden. This in turn causes the kidneys and heart to work harder. Contributes to a number of problems. What causes High Blood Pressure? Causes vary Narrowing of the arteries Greater than normal volume of blood Heart beating faster or more forcefully than it should Another medical problem The exact cause is not known. Who can develop High Blood Pressure? Anyone, but it is more common in: African Americans- get it earlier and more often then Caucasians. As we get older. 60% of Americans over 60 have hypertension. Overweight, family history High normal bp:135-139/85-89 mm Hg. Detection Dr.’s will diagnose a person with 2 or more readings of 140/90mm Hg or higher taken on more than one occasion. White-Coat Hypertension Measured using a spygmomameter. Tips for Having your blood pressure taken. Don’t drink coffee or smoke cigarettes for 30 minutes before. Before test sit for five minutes with back supported and feet flat on the ground. Test your arm on a table even with your heart. Wear short sleeves so your arm is exposed. Tips for having blood pressure taken. Go to the bathroom before test. A full bladder can affect bp reading. Get 2 readings and average the two of them. Ask the Dr. or nurse to tell you the result in numbers. Categories of High Blood Pressure Ages 18 Years and Older) Blood Pressure Level (mm Hg) Category Systolic Diastolic Optimal** < 120 < 80 Normal < 130 < 85 High Normal 130–139 85–89 Categories of High Blood Pressure High Blood Pressure Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 140–159 /90–99 160–179 /100–109 180 /110 Preventing Hypertension Adopt a healthy lifestyle by: Following a healthy eating pattern. Maintaining a healthy weight. Being Physically Active. Limiting Alcohol. Quitting Smoking. DASH diet Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension. Was an 11 week trial. Differences from the food pyramid: an increase of 1 daily serving of veggies. and increase of 1-2 servings of fruit. inclusion of 4-5 servings of nuts,seeds, and beans. Tips for Reducing Sodium Buy fresh, plain frozen or canned “no added salt” veggies. Use fresh poultry, lean meat, and fish. Use herbs, spices, and salt-free seasonings at the table and while cooking. Choose convenience foods low in salt. Rinse canned foods to reduce sodium. Maintain Healthy Weight Blood pressure rises as weight rises. Obesity is also a risk factor for heart disease. Even a 10# weight loss can reduce blood pressure. Be Physically Active Helps lower blood pressure and lose/ maintain weight. 30 minutes of moderate level activity on most days of week. Can even break it up into 10 minute sessions. Use stairs instead of elevator, get off bus 2 stops early, Park your car at the far end of the lot and walk! Limit Alcohol Intake Alcohol raises blood pressure and can harm liver, brain, and heart What counts as a drink? 12 oz beer 5 oz of wine 1.5 oz of 80 proof whiskey Quit Smoking Injures blood vessel walls Speeds up process of hardening of the arteries. Other Treatment If Lifestyle Modification is not working, blood pressure medication may be needed, there are several types: Diuretics-work on the kidney to remove access water and fluid from body to lower bp. Beta blockers-reduce impulses to the heart and blood vessels. Other Treatment ACE inhibitors- cause blood vessels to relax and blood to flow freely. Angiotensin antagonists- work the same as ACE inhibitors. Calcium Channel Blockers- causes the blood vessel to relax and widen. Alpha Blocker- blocks an impulse to the heart causing blood to flow more freely. Other Treatment Alpha-beta blockers- work the same as beta blockers, also slow the heart down. Nervous system inhibitors- slow nerve impulses to the heart. Vasodilators- cause blood vessel to widen, allowing blood to flow more freely. Conclusion Hypertension is a very controllable disease, with drastic consequences if left uncontrolled. Great Resource: www.nhlbi.nih.gov