Blood Pressure
advertisement

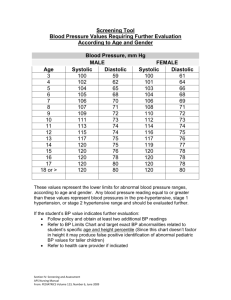
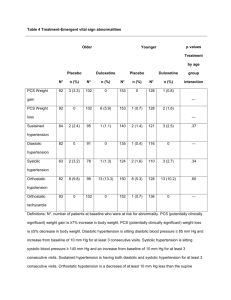
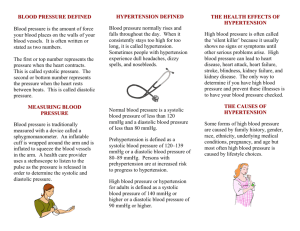
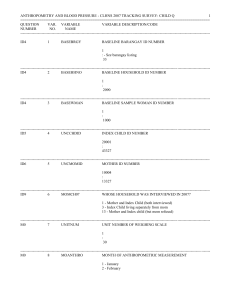
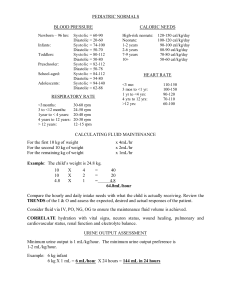
BLOOD PRESSURE Blood Pressure Definition: The measurement of the force exerted by the heart against the arterial walls when the heart contracts and relaxes. 1. Force comes from the pumping of the heart 2. If arteries are hardened or narrowed, this force might be increased to pump the blood throughout the body How do we measure Done by listening for two sounds with a stethoscope First: sound = systolic Second: change in sound = diastolic Units Millimeters of mercury Top number = systolic Bottom number = diastolic Systolic/diastolic 120/80 mm Hg Blood Pressure Values Hypotensive: less than 100/60 mm Hg Dizziness, light-headedness, faint No signs and symptoms Factors: Rx, level of physical fitness, illness, injury Hypertensive: greater than 140/90 mm Hg Silent killer – no symptoms Signs: headache, pressure in head, ringing in ears, general feeling of malaise Continued increase – Cerebral Vascular Accident (stroke) Factors: overweight, emotional upset, family history, high NaCl diet, pain, illness, Rx AHA Recommendation High blood pressure >140/90 mm Hg Blood Pressure (mm Hg) Normal Prehypertension Hypertension Systolic Less than 120 120-139 140+ Diastolic Less than 80 80-89 90+ Blood Pressure Category Normal Systolic mm Hg (upper #) Diastolic mm Hg (lower #) less than 120 and less than 80 Prehypertension 120 – 139 or 80 – 89 High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Stage 1 140 – 159 or 90 – 99 High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Stage 2 160 or higher or 100 or higher Hypertensive Crisis (Emergency care needed) Higher than 180 or Higher than 110 Risk High Blood pressure directly increases the risk of coronary heart disease lead to ________________ and _______________. Occurs in children or adults Prevalent in AA, middle-aged, elderly, obese, heavy drinkers Diabetes, gout or kidney disease more often