2-3 Chapter 2 Review WKST
advertisement

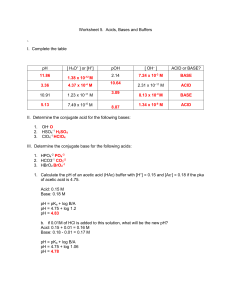
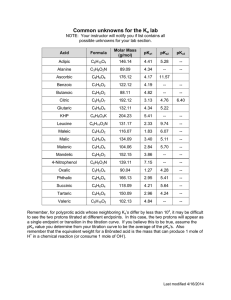
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW SHEET 1. What percent of living things depend on water? 2. Water accounts for between 60% and 90% of a cell’s __________. Identify two exceptions. How is water still important to them? 3. What four macromolecules assume their characteristic shape because of water? 4. Much of the _______________ machinery of cells operates in an _______________ environment because water is an essential _______________ and a _______________ for many cellular reactions. 5. Draw a 3D Lewis structure for water, and apply its net dipole. This makes water _______________. 6. Label the parts of the given diagram. H H O O _______________ __________ (Hf° = –460 kJ/mol) H H _______________ __________ (Hf° = –20 kJ/mol) 7. When water is heated, which of the above breaks first? 8. H-bonding is a type of _______________ force; specifically, a ______________________________ force. 9. Provide an example as to the importance of H-bonding in biochemistry. 10. How does water’s specific heat compare to other liquids? _______________ Therefore, a rather __________ amount of heat is required to change the temperature of water. Therefore, since 60%-90% of a cell’s mass is water, this allows temperature fluctuations to be _______________. This is a critical biological feature due to the fact that reaction __________ is sensitive to temperature changes. 11. How does water’s heat of vaporization compare to other liquids? Why is this biologically important? 12. The _______________ polar groups on a molecule, the more soluble it will be. 13. The _______________ the hydrocarbon chain on a molecule, the less soluble it will be. 14. Decide whether or not these molecules will dissolve in water. a. OH b. NH2 15. Briefly cite three reasons why the behavior of solutes in cytoplasm is different than how they behave in water. 16. _______________ is the process by which a solvent will pass from a lower-concentrated solution to a higher-concentrated solution. 17. What prevents the flow of solvent when a solvent-permeable membrane separates compartments that have drastically different concentrations of dissolved particles? 18. What can cells do to avoid bursting due to osmosis? 19. What two critical processes result from the hydrophobic effect? 20. What does it mean to be amphipathic? Draw an example. 21. Draw a simple micelle. How do micelles work to remove greases and oils from substances? 22. Identify two chaotropes, and describe what they do to nonpolar compounds in water. 23. Draw the hydrogen bonds likely to form between water and the following amino acid side chains: a. R SH O b. R NH2 24. Are the following compounds polar or amphipathic? Will they dissolve in water? a. CH3(CH2)11COO– b. CH3CH2NH3+ 25. Water is _______________ because its __________ pairs attack _______________ during substitution or addition. It is a __________ nucleophile, but it’s concentration in cells is so __________ that it could attack macromolecules, causing them to be _______________. 26. Write an equation for the hydrolysis of the given dipeptide. H H O C C C H + NH3 COO N C H H - CH2 27. Provide four reasons why all proteins are not destroyed by hydrolysis in the cell. 28. Write a mechanism for the self-ionization of water. 29. Calculate the concentration of pure water in 1 L of water. Use this and the ionization constant for water (1.8 x 10–16 M) to calculate Kw. 30. Provide three examples of when the concentration of protons (_____) affects biochemical processes. 31. What is physiological pH? What is the difference between acidosis and alkalosis? 32. Recalling that a strong acid completely _______________, calculate the concentration of perchloric acid if the pH of the solution is 1.025. 33. Recalling that weak acids do not completely _______________, calculate the pKa of carbonic acid if its Ka is 4 x 10–7. 34. Calculate the pH of 0.0500 M lactic acid (CH3CH(OH)COOH) if its pKa = 3.9. 35. Using the Henderson-Hasslebalch equation, explain the half-volume method of determining pKa using titration. 36. Draw a generic titration curve of pH vs. volume of titrant for the titration of sulfurous acid with potassium hydroxide. Sulfurous acid’s pKa values are 1.85 and 7.2. 37. When creating a buffer, the most effective buffering occurs when what two things are equal? 38. Draw the equation for the buffer system that is responsible for regulating the pH of blood. a. Explain how the buffer works when the pH of blood drops. b. Explain how the buffer works when the pH of blood rises. 39. What two things help to buffer cells against pH changes? Other than the bicarbonate system, what else helps to buffer the blood? 40. The pKa of 2-methoxybenzoic acid is 4.08. If 0.125 M of the acid and 0.125 M of the conjugate base are available, calculate the volume of each required to make 250. mL of buffer at a pH of 4.50.