Matter Powerpoint Notes
advertisement

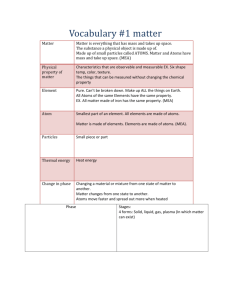
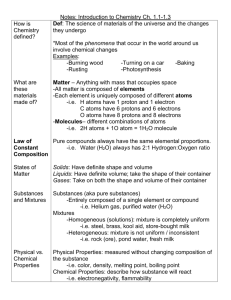
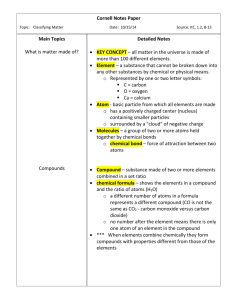
Matter Powerpoint Notes Name_____________________________________ Period: 1 4 6 7 Slide 1: Matter is anything that has mass (you measure this on a balance) and volume (if it’s a regular shaped obj you measure this L x W x H….it it’s a irregular shaped object use displacement method…if it’s a liquid use a graduated cylinder. Illustration: . Slide 2: Solid States of matter. and label each one. Liquid Gas Plasma Slide 3: Physical VRS Chemical Change A physical change is when a substance changes from one state of matter to another. S—>L-->-G A chemical change is when a ____________ ______________is formed. The new substance is totally different from the original one. It has different properties Example: Physical change Ice melts into water Chemical change: Cooking something Slide 4. Atoms and Elements ATOMS: Atoms are the building blocks of MATTER. There are about 118 known substances that make up all of the substances on Earth. You can find all the different types of atoms on the periodic table. Atoms consists of: Protons ( ) charge Neutrons ( ) charge and Electrons ( ). ELEMENTS: Consist of only 1 type of and these are on the periodic chart. The elements are the names of the various different atoms on the periodic chart Cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either chemical changes or physical changes. Can exist as either atoms or molecules (when two or more atoms are combined chemically) Slide 5: MOLECULES: A molecule consists of two or MORE atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are chemically bound together. Draw the illustration here: In the animation above, two nitrogen atoms ( ______ + ______= __________ ) this makes one NITROGEN molecule. Slide 6: Compounds Atoms of two or more different elements bonded together. Can be separated into elements chemically, but not physically. Slide 7: Slide 8: In the animation above, water (H 0) is a compound made of Hydrogen and Oxygen. Solutions and Homogeneous Solutions are groups of molecules that are mixed up in a completely even distribution. Homogeneous uniform distribution: Example: Sugar and water Solute and solvent: Solvent: The substance to be dissolved The one doing the dissolving. EX: Saltwater: in a solution of Saltwater the salt is the solvent and water is the solvent. Slide 9: Making a solution: 1st Solute enters system 2nd Begins dissolving in the solvent 3rd Solute spreads evenly in the solvent Slide 10: Colloids Particle sizes are in between the size of particles found in solutions and suspensions Can be mixed and remain evenly distributed without settling out. Examples: Milk Cheese Jello Slide 11: Mixtures and Heterogeneous MIXTURES: They are substances held together by physical forces, not chemical. Can be separated physically. Solutions are also mixtures EXAMPLE: The ingredients in oil and vinegar salad dressing. Matter Mixtures Pure Substances Homogeneous Heterogeneous Solutions Colliods Suspensions Solvent Solutions Elements Molecules Compounds