C2.3 Key Words
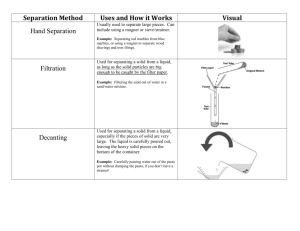
advertisement

Atoms Fraction The smallest part of an element that can take part in chemical reactions. A component of a mixture that has been separated by fractional distillation. Chromatogram Fractional distillation The piece of paper showing the results of carrying out chromatography on a substance. A method a separating a mixture of liquids with different boiling points into individual components (fractions). Chromatography Fractionating column A technique for separating the components of a mixture, for example different food colouring agents. It works because dissolved substances move at different rates through a piece of paper soaked in a solvent. A long column used to separate a mixture of liquids into different fractions with different boiling points. The column is warmer at the top than at the bottom. Covalent bond A bond between two non-metal atoms made up pf a shared pair of electrons- one from the outermost shell of each atom. Diamond A form of carbon that is very hard and doesn’t conduct electricity. It is used in cutting tools. Giant molecular covalent substance Substances containing millions of atoms all held together by covalent bonds. Graphite A form of carbon that is soft and conducts electricity. It is used as a lubricant as the layers slip over each other easily. Immiscible Liquids that do not form a solution but separate into two layers. Dissolve This occurs when a solute splits up and mixes with a solvent to make a solution. Liquefy Convert a substance into a liquid by heating or cooling. Dot and cross diagram A way of showing electronic structures in covalent substances, using dots and crosses to represent the electrons from different atoms. Lubricant Double bond Miscible When two bonds join a pair of the same atoms (usually two carbon atoms). Liquids that completely mix together to form a solution. A substance placed between two moving surfaces to reduce the friction between them. Molecule Two or more atoms joined together by covalent bonds. Rf value The ratio of the distance travelled by a solute on a chromatogram (measured from the centre of the spot) to the distance travelled by the solvent under the same conditions. Also called retardation factor. The Rf value for a substance can be used to identify compounds. Simple molecular covalent substance A substance made of individual small molecules, with strong covalent bonds holding the atoms together in the molecules but only weak forces between neighbouring molecules. Soluble A substance which dissolves in a given solvent. Solution Separating funnel The clear mixture that forms when a solute dissolves in a given solvent. A funnel with a tap on the bottom that is used for separating immiscible liquids. Solvent The liquid that dissolves the solute. Solute + Solvent = Solution