Outline topic # 7 MLT 310-Urinalysis & OBF URINALYSIS
advertisement

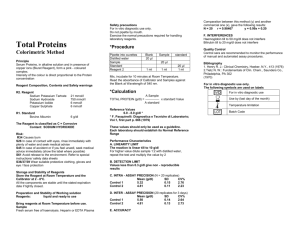
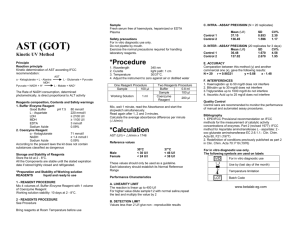
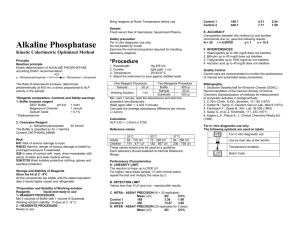
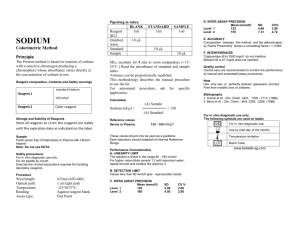
Outline topic # 7 URINALYSIS- Reagent Strip,( Chemical ) MLT 310-Urinalysis & OBF Dr. Bernard C. Silvala/Dr. Ernesto Ramirez URINALYSIS: Reagent Strips: Chemical Analysis of Urine Most common abnormalities Increased amounts of: Sugars Protein RBCs WBCs Bilirubin Ketones urobilinogen Sample reagent strips Multistix Chemstrip Rapignost Comstix SG N-multistix Reagent Strips: Chemical principles employed on all reagent strips are essentially the same Reporting of Results: a. in concentration (mg/dL) b. small, mod., large c. 1+, 2+, 3+, 4+ d. as positive, negative, or normal * exceptions: pH and sp.gr. Procedure Dip into urine specimen (briefly) Remove excess urine Read at specified time Compare color rxn Note Reading time Highly pigmented specimens Interfering substances Proper storage of dipsticks Specimen used Analytes - pH - Specific gravity - Blood - Nitrite - Protein Outline topic # 7 URINALYSIS- Reagent Strip,( Chemical ) MLT 310-Urinalysis & OBF Dr. Bernard C. Silvala/Dr. Ernesto Ramirez - glucose - Ketones - Bilirubin - Urobilinogen - Leukocytes pH: – Indicators: methyl red, bromthymol blue – Sensitivity: 5 – 9 – Affecting factors: bacterial growth & metabolism may cause marked increase; test is not affected by CHON or other endogenous substances; leaching/run-over Specific Gravity: Reagents: polyelectrolyte, bromthymol blue, buffer Sensitivity: 1.000 – 1.030 Affecting factors: o LOW: pH (add 0.005 for ph >6.5), glucose o HIGH: protein, urea, ketones, lactic acids Blood: Reagents: H2O2, tetramethylbenzidine, or orthotoluidine Sensitivity: 5-20 RBCs; 0.05-0.3 mg/dL Hgb Affecting factors: oxidizing contaminants (FP), ≥5 mg/dL ascorbic acid (FN), myoglobin should be ruled out (via dilution 1:40), high nitrite (FN), Protein: Reagents: citrate buffer at pH 3 Sensitivity: 5-20 mg/dL albumin Affecting factors: highly buffered alkaline urine may cause a false-positive result Glucose: Reagents: glucose oxidase, peroxidase, orthotoluidine, KI, aminopropylcarbazol Sensitivity: 0.1 g/dL Affecting factors: ≥50 mg/dL ascorbic acid may inhibit the reaction Ketones: Reagents: sodium nitroprusside Affecting factors: highly volatile; bacteria can degrade Bilirubin: Reagents: dichloroaniline dichlorobenzene diazonium tetrafluoroborate Sensitivity: 0.4-0.8 mg/dL Affecting factors: unstable in light; large amounts of ascorbic acid or nitrite lower results, FP due to abnormal urine color Outline topic # 7 URINALYSIS- Reagent Strip,( Chemical ) MLT 310-Urinalysis & OBF Dr. Bernard C. Silvala/Dr. Ernesto Ramirez Urobilinogen: Reagents: dimethylaminobenzaldehyde Sensitivity: 0.2-8 Erlich units Affecting factors: unstable; fresh specimen required; FN – formalin Leukocytes/LE: Reagents: indoxylcarbonic acid ester, diazonium salt Sensitivity: 5-15/hpf intact or lysed leukocytes w/ esterases Affecting factors: FP w/ histiocytes & trichomonads, vaginal contamination FN high sp. Gr, drugs, oxidizing agents, high glu & CHON Agranulocytes are not detected Detects WBC even when they have been lysed Nitrite: Reagents: para-arsanilic acid, tetrahydrobenzoquinolin-3-ol Sensitivity: ≥105 bacteria/mL Affecting factors: bacteria w/o reductase do not react ≥25 mg/dL ascorbic acid may inhibit reaction <4H retention of urine in bladder Lack of dietary nitrate Contamination doesn’t cause FP