First Grade Unit Alphabet Books
advertisement

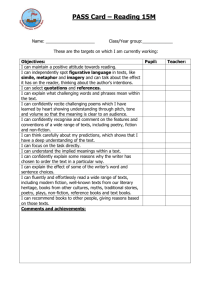
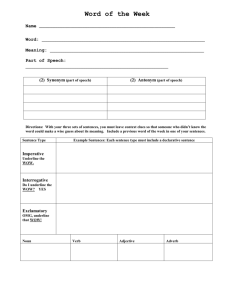
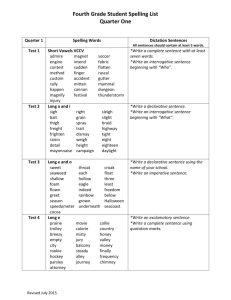
Grade: First Unit: Alphabet Books and Children Who Read Them Pacing: First Six Weeks Subject(s): ELA Objective(s): Students will be able, on Vocabulary: their own to: Standard(s): Note: this unit does not author Ask and answer questions about address the first grade target skills of illustrator key information in non fiction phonics, sight word recognition, or capitalization texts decoding. Those are on going throughout periods the year and should be included in all units Recognize what a question is stories of work. Reading/Phonics skills are a Distinguish how a question is key details progression within the essential different from a telling question standards. Explain how to answer a question questions topic using text as support Common Core Standards: RL 1.1, SL 1.2 Ask and answer questions about key details and fiction Produce and expand complete events in a text. non-fiction and compound declarative, RL 1.5 Explain major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information, drawing on a wide reading of a sort interrogative, imperative and range of text types. poems exclamatory sentences RL 1.10 With prompting and support read and prose poetry of appropriate complexity for grade 1. RI 1.1 Ask and answer questions about key details in a text. RF 1.1 Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print. RF1.1a Recognize the distinguishing features of a sentence (first word, capitalization, ending punctuation) RF 1.4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. W 1.2 Write informative/explanatory texts in which they name a topic, supply some facts about the topic, and provide some sense of closure. W 1.5 With guidance and support from adults, focus on a topic, respond to questions and suggestions from peers, and add details to strengthen writing as needed. W 1.7 Participate in shared research and writing projects(explore a number of how-to books on a given topic and use them to Standards (Cont.) Write a sequence of instructions. W 1.8 With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. SL 1.6 Produce complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation. L 1.1 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. L 1.1a Print all upper and lowercase letters. L 1.1b Use common, proper and possessive nouns. L 1.1j Produce and expand complete simple and compound declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences In response to prompts. L 1.2 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation and spelling when writing. L 1.2a Capitalize dates and names of people. L 1.2b Use end punctuation for sentences. L 1.4a Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. Understanding: Students will understand that: There is a difference between texts that give information and texts that tell a story. Essential Questions: Why is it important to ask questions while you are reading? What makes up a complete sentence? What types of sentences are there? How do we determine what is fact or opinion (fiction/non-fiction) How do we research more about a topic? Literary Texts: (Resources) Houghton Mifflin Text: Mac the Cat, Counting on in the Words, Cats, My Cat, Cat and Dog, Supper for Cal, A Day at School, At School, Nat, Nan, and Pat, Fun, Fun, Fun, Meet the Feet, Pigs in a Rig, Sit, Pig, Pat and Pig, Gram’s Hat, Kit Finds a Mitt, National Geographic Series: Units 3, 4,7 Journeys: Chicka Chicka Boom Boom by: Bill Martin Dr. Suess’s ABC An Amazing Alphabet Book by: Dr. Suess Eating the Alphabet: Fruits and Vegetables from A to Z by: Lois Ehlert How to Eat a Poem by: Eve Merriam Online Story Books: http://magickeys.com/books Evidence: (Evaluation and Assessments) Science/Social Studies Tie: Class ABC Book Suggestions: Create a “How To” Book Health and Fitness (our bodies) Informative writing about exercising How we fit into a group Observable Student Behaviors: Small Group Research Work- Students will research an Animals/Life Cycles author and discuss findings. Living and Non Living Acquisition: Students will know that: Fiction stories are for entertaining and non-fiction stories are for information. It is a good practice to ask questions while you are reading for better comprehension. (understanding) Common Core bridging Standards from previous grades: RL 1.1 with prompting and support, ask and answer questions about key details in a text. RI 1.4 with prompting and support, identify basic similarities in and differences between two texts on the same topic. Pre-Assessment: Students will choose a book based on interest and identify placed information about author and illustrator. Learning Targets: (Tasks) Introduce the writing of declarative and interrogative sentences by focusing on an informational ABC book. Chart answers to the question, “what is your favorite fruit?” Sort letters based on if they are small, tall, or if they fall. Have students sort sentences by type: declarative (telling), interrogative (asking), imperative (bossy/command), and exclamatory (excited). Create a Venn diagram comparing fiction and non-fiction books. Write about hand washing from using a story web. Claim #1 Depth of Knowledge 1 2 3 4 Claim #2 Depth of Knowledge 1 2 3 4 Claim #3 Depth of Knowledge 1 2 3 4 Claim #4 Depth of Knowledge 1 2 3 4 Progress Monitoring: Meaning: How does this relate to me? Students will write/match upper and lower case letters. Students will identify missing letters in a sequence. Students will count words in a sentence. Students will identify sentence structure. (Capital, punctuation) I know what kinds of books I like to read. I know what topics interest me. I can tell about the difference between fact and opinion and reality and fantasy. I can write in a complete sentence. I know what an author and an illustrator do. Teacher Notes: