Year 7 Particles Topic 3 Summary Sheets Solids, liquids and gases
advertisement
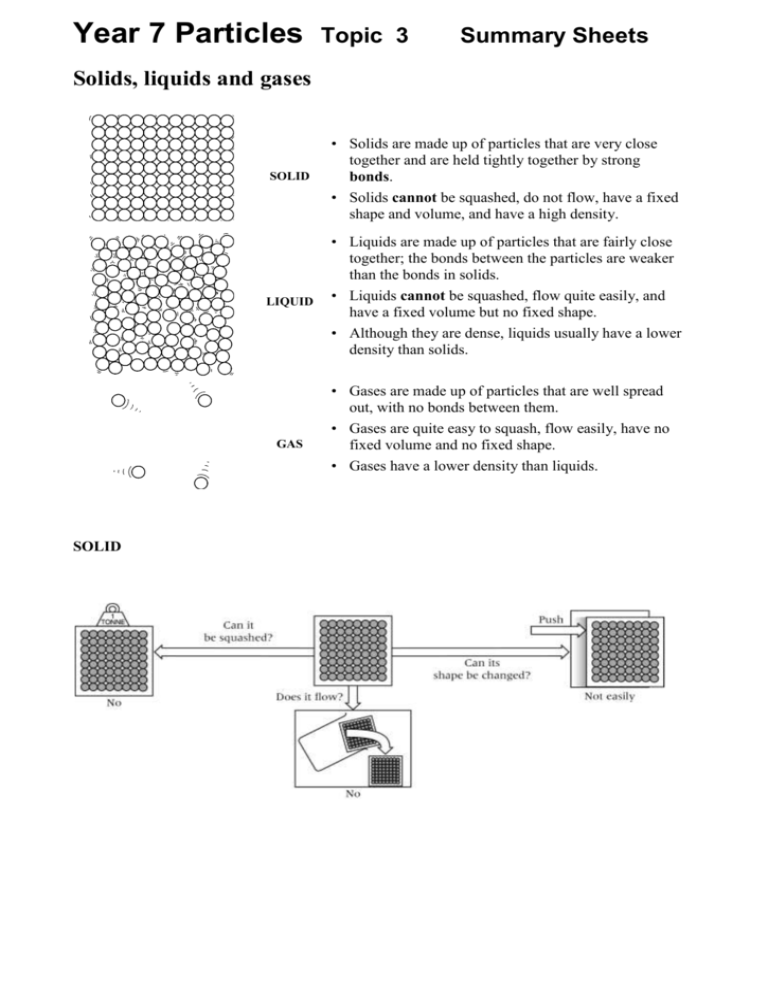
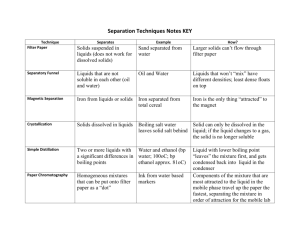
Year 7 Particles Topic 3 Summary Sheets Solids, liquids and gases SOLID LIQUID GAS SOLID • Solids are made up of particles that are very close together and are held tightly together by strong bonds. • Solids cannot be squashed, do not flow, have a fixed shape and volume, and have a high density. • Liquids are made up of particles that are fairly close together; the bonds between the particles are weaker than the bonds in solids. • Liquids cannot be squashed, flow quite easily, and have a fixed volume but no fixed shape. • Although they are dense, liquids usually have a lower density than solids. • Gases are made up of particles that are well spread out, with no bonds between them. • Gases are quite easy to squash, flow easily, have no fixed volume and no fixed shape. • Gases have a lower density than liquids. LIQUID GAS How solids liquids and gases interact: Mixture: Filtering: Insoluble: Solution: Soluble: Solvent: Solute: Evaporation: Solubility: A lot of different things jumbled up together. Separating things that have not dissolved in a liquid. Will not dissolve. When a solid (solute) is dissolved in a liquid (solvent). A solid that can dissolve in a liquid. The liquid that dissolves a solid (solute) to make a solution. When a solid split up and mixes with a liquid to make a solution. A liquid turning into a gas ( leaving behind the chemicals dissolved in it). A measure of how much of a solid will dissolve in a liquid, Dissolving Solids that do not dissolve are insoluble. When an insoluble solid is mixed with water, the water goes cloudy. Sometimes the solid will sink to the bottom of the water. If you keep adding solutes to a solvent, you will get to a point where no more will dissolve. A saturated solution cannot dissolve any more solute. More solid will dissolve if you add more solvent (e.g. water) or increase the temperature. There are many ways to separate mixtures: Method Filtering (Filtration) Used to separate Solid particles which do not dissolve from the liquid they are in Apparatus used Examples • Tea leaves from a cup of tea • Sand from a mixture of sand and water . Cup of coffee Evaporation Dissolved substances from a solution • Salt from salt solution Distillation (Evaporation followed by condensation) The liquid from the dissolved solid in a solution or one liquid from a mixture of liquids • Water from salt solution • Alcohol from a mixture of alcohol and water Chromatography The individual colours can be separated from a mixture of colours • The colours found in ink • The food colourings found in fruit juice Travelling heat The kinetic theory or particle model of matter helps to explain how some forms of heat energy travel. The theory suggests that everything is made of moving or vibrating particles. When these particles are heated they move faster. When the particles vibrate faster the material expands. When they vibrate slower the material contracts. This picture shows a bimetallic strip. It is a strip of two different metals joined together. It bends when it gets hot because one metal expands more than the other. It straightens out again when it gets cold. Diffusion The natural mixing of substances is called diffusion. Diffusion occurs because particles in a substance are always moving around. Diffusion is fastest in gases, and slower in liquids. Diffusion in solids is extremely slow. Subliming Physical changes In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting, evaporating, condensing and freezing are all examples of physical changes. For example: Carbon dioxide can sublime: it can change from a solid to a gas without becoming a liquid. So can Iodine. Changes of state Substances can change state when they are heated or cooled. The melting point and the freezing point of a substance are the same temperature. The temperature of a substance does not change while it is melting, even if it is still being heated. A flat line means it is a pure substance Pure substance have definite melting and boiling points: Mixtures do not. Chemical reactions In the periodic Table there are about 100 elements. About 80 ate metals and 20 non metals, An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. They cannot be split into anything simpler. TASK Draw a line separating Metals and non-metals A compound contains two or more types of atom chemically bonded together. Compounds are very difficult to separate. A mixture is when different elements or compounds are mixed. A mixture is easier to separate than the elements in a compound. Soil, river water and sea water are examples of mixtures that occur naturally. Elements and compounds melt and boil at a fixed temperature. Mixtures do not have definite melting points and boiling points. Elements can chemically join together to make compounds in a chemical reaction. In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a reaction has occurred if there is a colour change or when a gas is given off. Most chemical reactions also involve an energy change. This is usually in the form of heat, but can also involve light being given off (for example, when something burns). magnesium + oxygen reactants magnesium oxide products The properties of a compound are different from the elements that make it up. For example, hydrogen is an explosive gas and hydrogen will relight a glowing splint – but water is a liquid which will put fires out. A chemical formula tells you the name and number of atoms in a compound. Formula ending in – ide means there are two elements joined together, and endings in –ate means there are three ( of which one is oxygen). carbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide copper + sulphur +oxygen→ copper sulphate chlorine + copper →copper chloride Elements Compounds Mixtures atoms of helium (He) molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) a mixture of helium and oxygen molecules of oxygen (O2) molecules of water (H2O) a mixture of carbon dioxide and oxygen a lump of carbon (C) a lump of sodium chloride (NaCl) a lump of bronze (an alloy of copper and tin) CHROMATOGRAPHY 1 The scientists did not use water as a solvent when they carried out their tests. Why not? 2 Which manufacturer (or manufacturers) used one pure colour in their red paint? 3 Which manufacturer (or manufacturers) used a mixture of only two colours? 4 Which manufacturer (or manufacturers) used a mixture of three colours? 5 Which manufacturer uses the same paint as the paint from the gatepost? The chromatography test does not prove that the getaway vehicle was made by the manufacturer in your answer to question 5. Post Office vans are red, so the marks could have been made when a parcel was delivered. 1 = water is not a solvent for this paint 2 = B uses a pure colour. 3 = F uses only two colours 4 = A C D 5 = D