Eighth Grade Science Pacing
advertisement

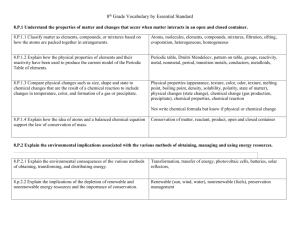
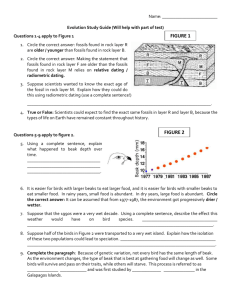
Eighth Grade Science First Quarter 8.P.1 Understand the properties of matter and changes that occur when matter interacts in an open and closed container. P.1.1 Classify matter as elements, compounds, or mixtures based on how the atoms are packed together in arrangements. P.1.2 Explain how the physical properties of elements and their reactivity have been used to produce the current model of the Periodic Table of the elements. P.1.3 Compare physical changes such as size, shape, and state to chemical changes that are the result of a chemical reaction to include changes in temperature, color, formation of a gas or precipitate. P.1.4 Explain how the idea of atoms and a balanced chemical equation support the law of conservation of mass. Vocabulary: Atom, proton, electron, neutron, molecule, element, compound, mixture, heterogeneous, homogeneous, solution, filtration, distillation, evaporation, conductivity, reactivity, metals, nonmetals, metalloids, periods, groups (families), transition metals, alkali metals, noble gases, physical properties/changes, chemical properties/changes, solubility, density, polarity, melting point, boiling point, states of matter, precipitate, law of conservation of matter, law of conservation of mass, closed/open systems, reactant, product. Writing Tasks: Explain how the periodic table is organized. Include patterns that Mendeleev recognized as he created the table. After burning for 3 hours, a candle has lost half of its mass. Explain why this indicates a physical and chemical change. Investigations/Lab Activities: Eighth Grade Science Second Quarter 8.E.1 Understand the hydrosphere and the impact of humans on local systems and the effects of the hydrosphere on humans. E.1.1 Explain the structure of the hydrosphere including: Water distribution on Earth Local river basins and water availability E.1.2 Summarize evidence that Earth’s oceans are a reservoir of nutrients, minerals, dissolved gases, and life forms: Estuaries Marine Ecosystems Upwelling Behavior of gases in the marine environment Value and sustainability of marine resources Deep ocean technology and understandings gained E.1.3 Predict the safety and potability of water supplies in North Carolina based on physical and biological factors, including: Temperature Dissolved oxygen pH Nitrates and phosphates Turbidity Bio-indicators E.1.4 Conclude that the good health of humans requires: Monitoring of the hydrosphere Water quality standards Methods of water treatment Maintaining safe water quality Stewardship 8.E.2 Understand the history of Earth and its life forms based on evidence of change recorded in fossil records and landforms. E.2.1 Infer the age of Earth and relative age of rocks and fossils from index fossils and ordering of rock layers (relative dating and radioactive dating). E.2.2 Explain the use of fossils, ice cores, composition of sedimentary rocks, faults, and igneous rock formations found in rock layers as evidence of the history of the Earth and its changing life forms. Vocabulary: Hydrosphere, water cycle, polarity, solvent, solubility, universal solvent, watershed, river basin, tributaries, ground water, aquifer, impermeable, estuary, water cycle, salinity, desalination, evaporation, oceanic zones (benthos, plankton, nekton, intertidal zone, neritic zone, upwelling, photosynthesis, respiration, food webs (terrestrial and aquatic), producer, consumer, decomposer, buffer zone, coral reef, marine ecosystems, shore, open ocean, deep ocean, oceanography, sonar, chemosynthetic organisms, hydrothermal vents, microbes, healthy water system, temperature, turbidity, water movement, dissolved oxygen, pH, nitrates, salinity, population diversity, tolerance, nutrients, algal bloom, bio-indicators, geologic column, fossil, rock layer, erosion, deposition, lithospheric plate movement, plate tectonics, continental drift, catastrophes, index fossils, folding, breaking, faults, uplifting, intrusions, absolute dating, radioactive dating, Carbon-14, relative dating, law of superposition, undisturbed rock layers, unconformity, dissolved minerals, rock cycle, ice cores, evolution, geologic time scale, eon, era, period, epoch, igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic rock, faults, extinct. Writing Tasks: Two main sources of pollution are point- and nonpoint-source pollution. Explain the difference between these two sources and include examples to support your answer. Investigations/Lab Activities: Eighth Grade Science Eighth Grade Science Third Quarter 8.L.1 Understand the hazards caused by agents of diseases that affect living organisms. L.1.1 Summarize the basic characteristics of viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites relating to the spread, treatment, and prevention of disease. L.1.2 Explain the difference between epidemic and pandemic as it relates to the spred, treatment and prevention of disease. 8.L.2 Understand how biotechnology is used to affect living organisms. L.2.1 Summarize aspects of biotechnology including: Specific genetic information available Careers Economic benefits to North Carolina Ethical issues Implication for agriculture 8.L.3 Understand how organisms interact with and respond to the biotic and abiotic components of their environment. L.3.1 Explain how factors such as food, water, shelter, and space affect populations in an ecosystem. L.3.2 Summarize the relationships among producers, consumer, and decomposers including the positive and negative consequences of such interactions including: Coexistence and cooperation Competition (predator/prey) Parasitism Mutualism L.3.3 Explain how the flow of energy within food webs is interconnected with the cycling of matter (including water, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and oxygen.) Vocabulary: Microbiology, virus, bacteria, protozoa, parasites, fungi, algae, tissue differentiation, unicellular, host cell, chlorophyll, antibiotics, vectors, disease, infectious, microbial pathogens, biomedical research, microbes, computer modeling, cell culture, clinical trials, hygiene, antimicrobial chemicals, industrial microbiology, contamination, food spoilage, pharmaceuticals, epidemic, pandemic, biotechnology, careers, microbial hazards, genetic modification, cloning, organism, biotic, abiotic, populations, ecosystem, factors, oxidizing, thermal energy, habitat, niche, species, ecology, biotic abiotic, producer, consumer, decomposer, scavenger, coexistence, predator, prey, ecosystems, terrestrial, aquatic, marine, microscopic, fertile, molecule, matter, food web, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, symbiosis, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, nutrients, ecology, food chain, food web, replenish, autotroph, heterotroph, herbivore, water cycle, evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, oxygen, chemical compounds, atoms. Writing Tasks: List three common parasites that cause disease in humans and describe the effects on humans of each disease. What are the benefits and risks of adding a non-native species to a given environment? Provide real examples to support your claims. Investigations/Lab Activities: Eighth Grade Science Eighth Grade Science Fourth Quarter 8.L.4 Understand the evolution of organisms and landforms based on evidence, theories and processes that impact the Earth over time. L.4.1 Summarize the use of evidence drawn from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy to form the basis for biological classification systems and the theory of evolution. L.4.2 Explain the relationship between genetic variation and an organism’s ability to adapt to its environment. 8.L.5 Understand the composition of various substances as it relates to their ability to serve as a source of energy and building materials for growth and repair of organisms. L.5.1 Summarize how food provides the energy and the molecules required for building materials, growth and survival of all organisms to include plants. L.5.2 Explain the relationship among a healthy diet, exercise and the general health of the body, (emphasis on the relationship between respiration and digestion). 8.P.2 Explain the environmental implications associated with the various methods of obtaining, managing, and using energy resources. P.2.1 Explain the environmental consequences of the various methods of obtaining, transformation and distributing energy. P.2.2 Explain the implications of the depletion of renewable and nonrenewable energy resources and the importance of conservation. Vocabulary: Evolution, geologic time scale, rocks, fossils, ice cores, Theory of Evolution, adaptation, extinct, biological diversity, natural selection, Plate Tectonics Theory, variation, adaptation, selection pressures, gene pool, vestigial structure, heritability, over production, continental drift, mountains, ocean trenches, convergent boundary, divergent boundary, transform boundary, Law of Superposition, cell, molecule, mitosis, meiosis, selectively permeable, prokaryotic, eukaryotic, unicellular, multicellular, organelles, active transport, passive transport, abnormalities, life-style personal health, Law of Conservation of Energy, transfer of energy, photovoltaic, renewable, non-renewable, conservation, fuel, solar energy, wind energy, hydroelectric. Writing Tasks: Explain how natural selection works by giving and developing specific examples (at least three). Use the following science vocabulary in context for full credit: variation, adaption, selection pressures (give example), selected against, selected, gene pool, fitness, population, species, fossil, vestigial structure, descent w/ modification, heritability and overproduction. Investigations/Lab Activities: