Energy Transfers revision sheet
advertisement

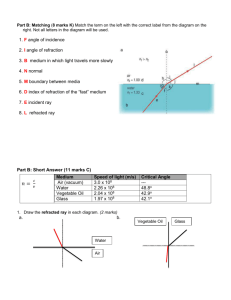
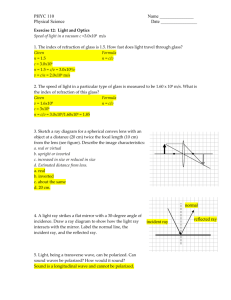
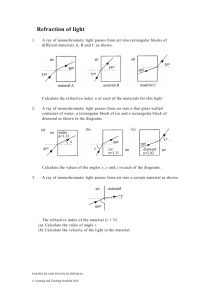
Sources of light (pg 132-133) Mirrors (pg 134-137) Write definitions for: Draw three different diagrams to show how light rays reflect off the stated type of mirror. Also list some features of the image e.g. upside down, smaller than the object (diminished) LUMINOUS Refraction (pg 140-141) NON-LUMINOUS The diagram to the left shows refraction. Select Use the table below to give examples of objects that are luminous or non-luminous LUMINOUS Diagram PLANE MIRROR Features of the image the correct words in these sentences to explain how it works. NON-LUMINOUS A ray of light enters a glass block. The glass block is more / less dense than the air around it. This causes the ray of light to slow down / speed up so that it bends towards / away from the normal line. CONVEX MIRROR As the ray of light leaves the glass block, it slows down / speeds up and bends towards / away from the normal line. Total internal reflection (pg 138-139) Use these words to fill in the gaps below: SHAPE REFRACTED CRITICAL INCIDENCE ANGLE REFLECTED INTERNALLY Colour (pg 142-145) List the seven colours of the spectrum in order: CONCAVE MIRROR When light enters glass, the way that it behaves depends on the __________ of the glass and the __________ at which the light enters the glass. The light may be The splitting of white light into the spectrum of colours is called d____________. ______________ at both glass surfaces and emerge, or it may be ______________ in whole or in part from the second surface. If the angle of ________________ is increase so that it is greater than the __________ angle (42o for glass), then the light ray is not refracted at all at the second surface. Instead it is total _______________ reflected and emerges on the Why do red objects appear red? Why do some objects appear white? Why do some objects appear black? What is the purpose of a coloured filter? Colour mixing (pg 146-147) Name the three primary colours of light. same side that it entered. Which colours should we mix to make: Add lines to the diagram below to show how a light ray can MAGENTA be total internally reflected through an optical fibre. YELLOW CYAN WHITE Seeing the Light (pg 148-149) Label this eye diagram with the following words: RETINA OPTIC NERVE PUPIL CORNEA IRIS LENS CONJUNTIVA Using electricity (pg 156-157) Resistance (pg 152-153) What are the energy changes in the following What is resistance? objects? List three things that can affect resistance. LOUDSPEAKER ELECTRIC FAN Why is high resistance wire used for the heating element List three ways we can use electricity in a medical in a kettle? sense. 1 Why is low resistance copper wire used in most electrical 2 cables? 3 Modelling circuits (pg 154-155) Use this space to draw out your own model of electricity. You must state what represents the battery, bulb, wires, electrons, energy Electricity in the home (pg 158-159) Define the word power What two units can power be measured in? What does it mean to make electrical appliance more sustainable? Give three ways that someone could reduce their ‘carbon footprint’. 1 2 3