Glass Analysis: Properties of Matter Presentation
advertisement

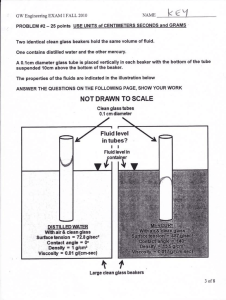
Background for Glass Analysis Quiz Monday 10/03 • Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. –Mass: the number of particles in something, how much there is of an object –Space: scientific word for “space” is volume, which describes the size of a substance. –Both of these variables can be observed and measured We can measure mass using a triple beam balance or digital scale. Mass is measured in grams (SI Unit) We can measure volume using a ruler or a graduated cylinder Volume can be measure in two ways: • Volume of a regular solid (cube): L xW x H • unit: cm3 • Volume of a irregular solid (rock): Density is defined as mass per unit of volume The formula for density is… density = mass volume If the density of the object is greater than that of the fluid, the object will sink. If the density of the object is equal to that of the fluid, the object will neither sink or float (suspended) If the density of the object is less than that of the fluid, the object will float. SOL ID LIQUID GAS Plasma least common form on Earth - but most common in the universe • radiation from the sun, light from a fluorescent light, stars Amorphous solid • Greek amorphos, from a- (without) + morphē (form) • Non-crystalline solid • Can change shape with heating • Heating at a range of temperatures- not a set temperature like a crystalline solid • Behaves more like liquids with high viscosities • EX: honey, syrup, & gels Matter is Classified into 2 groups 1 . Physical Property: any property of an object that can be observed without changing it’s composition (without changing what the object or substance is made up of) EX: weight, volume, color, boiling or melting point, viscosity, brittleness, buoyancy, phase changes For the forensic scientist, the need to find and measure those properties that will associate one glass fragment with another--also minimizing or eliminating other sources. To compare glass fragments, a forensic scientist evaluates two important physical properties: density and refractive index. Chemical Property: a characteristic of a substance that indicates whether it can undergo a certain chemical change • Flammable • Reaction to light • Reaction to sound Chemical Change: a change of one substance to another, an “unexpected” change Burning, fizzing, or popping (fireworks exploding) are helpful indicators that a new substance is produced. Routine drug tests for cocaine or heroine- fast test before sending to lab for detailed analysis Uses a chemical reagent called Marquis reagent. Chemical reaction occurs turning the unknown sample various colors detecting the type of drug Can test for ecstasy, meth, aspirin, codeine, LSD, morphine Ancient Greek philosophers suggested that earth, air, water, and fire as matters fundamental building blocks Atom = basic unit of matter Elements: Substance in which all atoms in a sample are alike Compounds: substance made of two or more atoms (two or more elements) Water: Salt: Hydrogen and Oxygen Sodium and Chlorine Molecules Silica(SiO2) is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Element or compound? Transfer of a substance into glass FUN FACT: In nature, vitrification of quartz occurs when lightning strikes sand, forming hollow, branching root like structures called fulgurites.