Refracation Review Questions ANSWERS
advertisement
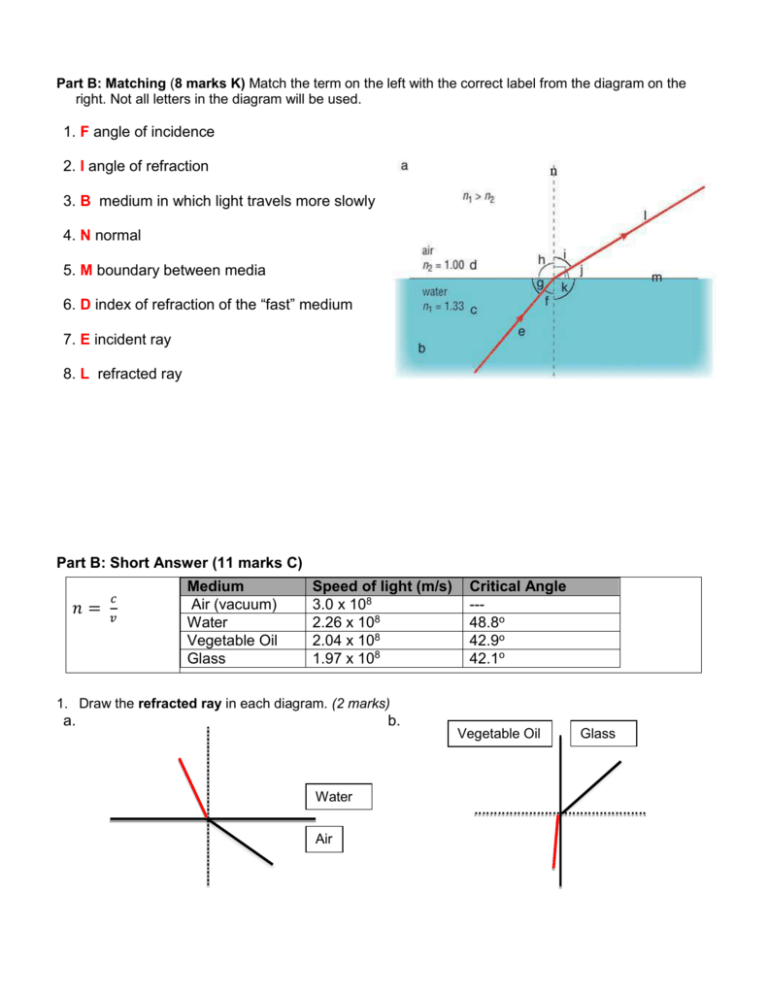
Part B: Matching (8 marks K) Match the term on the left with the correct label from the diagram on the right. Not all letters in the diagram will be used. 1. F angle of incidence 2. I angle of refraction n 3. B medium in which light travels more slowly 4. N normal 5. M boundary between media 6. D index of refraction of the “fast” medium 7. E incident ray 8. L refracted ray Part B: Short Answer (11 marks C) 𝑛= 𝑐 𝑣 Medium Air (vacuum) Water Vegetable Oil Glass Speed of light (m/s) 3.0 x 108 2.26 x 108 2.04 x 108 1.97 x 108 Critical Angle --48.8o 42.9o 42.1o 1. Draw the refracted ray in each diagram. (2 marks) a. b. Water Air Vegetable Oil Glass 2. a) In which scenario above could total internal reflection occur? Explain how you know. (2 marks) b) Using your answer from 2a, sketch the diagram showing the location of the refracted ray at the critical angle. Include any other ray(s) that occur. (2 marks) Vegetable Oil GLASS TO VEG OIL because light is speeding up from medium 1 to medium 2 (light will bend toward boundary of media). Glass Refracted ray reflected ray 3. Give an example where light undergoes partial reflection and refraction at the same time. Briefly explain the “partial reflection” and the “refraction” that is occurring in this example. (2 marks) Two – way mirror, mirrored sunglasses Partial reflection = one side looks like a mirror Refraction = you can see through the other side 4. The index of refraction in arsenic trisulfide glass is 2.04. What is the speed of light in this medium? Use GRASS! (3 marks) G: c = 3.0 x 108 m/s N = 2.04 S: v = 3.0x 108 / 2.04 V = 1.47 x 108 R: v of arsenic trisulfide S: The speed of light in arsenic trifluoride A: n = c/v ------> v = c/n is 1.47 x 108 m/s