Optics Test Review Questions
advertisement

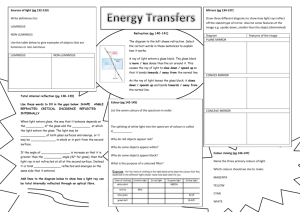
SNC 2P Name___________________________ Optics Test Review 1. Your friend has never heard of the ‘electromagnetic spectrum’. Explain in your own words what is meant by this term. 2. How is the frequency of a wave affected by the wavelength? 3. What is the difference between incandescence and luminescence? 4. For each of the following identify the method of light production: a. Glow sticks ________________________________________ b. Glow in the dark toys ________________________________ c. Highlighter glowing under black light ___________________ d. Light produced in neon sign __________________________ 5. List the following in order from longest to shortest wavelength: X rays, microwaves, yellow light, green light, infrared, radio waves, ultraviolet 6. Roughly, how big is a microwave? A radiowave? 7. Name the 3 primary colours of light. 8. Name the 3 secondary colours of light. 9. State which colour would be produced if the following colours were combined: a. RED + BLUE __________________ b. GREEN + BLUE _________________ c. RED + Cyan___________________ d. GREEN and Magenta____________ 10. What are complementary colours? Why does mixing 2 complementary colours always produce white? 11. A banana appears yellow because of the colours it reflects. a. Which 2 primary colours are reflected by a yellow banana? b. How would the banana look under a red light? Explain your choice. c. How would the banana look under a blue light? Explain your choice. 12. If you were to stare at a blue coloured object for a few minutes and then look at a white background, what colour would you see? Explain why this happens. 13. State the law of reflection and draw diagram to illustrate the meaning 14. Draw two diagrams to show how light behaves differently when it hits a smooth surface vs a rough surface: 15. Draw two diagrams to show how light behaves differently when it hits a translucent object vs a transparent object: 16. Explain why you can’t see your reflection in materials like cotton or wool. 17. Name and draw the three types of mirrors discussed in this unit. Describe some uses of each. 18. Refraction a. What is meant by the term “refraction”? b. Give an example of where you have observed refraction. c. What causes refraction to occur? 19. Lenses a. Name the two types of lenses discussed in this unit b. Draw a ray diagram to show what happens when light shines through each. c. Name 2 uses of convex lenses 20. Explain the cause of each of the following vision problems: a. Colour blindness b. Nearsightedness (myopia) c. Farsightedness (hyperopia) 21. What types of lens could be used to correct hyperopia? Draw a diagram to support your answer. SNC 2P Optics Test Practice: Ray Diagrams For each type of mirror below, list the rules you need to follow to draw a proper diagram. Use a ray diagram to draw the image, and summarize the characteristics of the image. Use a ruler and protractor where necessary. Mirror Plane Mirror Rules: Image Characteristics: Size: Distance: Orientation: Type: Convex Mirror Rules: F Image Characteristics: Size: Distance: Orientation: Type: Concave Mirror Rules: Image Characteristics: Size: Distance: Orientation: Type: What other type of image can be produced by a concave mirror? Where does the object have to be?