Newton`s Laws Notes
advertisement

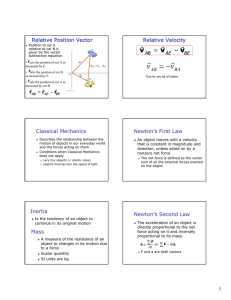
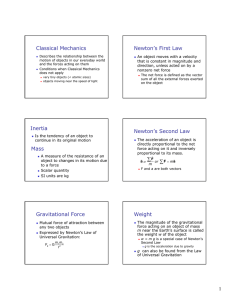
Newton’s Laws History of Development Aristotle (384-322 BC)- Ancient Greece Philosopher- All objects have a natural resting place and move to seek that place. Motion is classified as either Natural or Violent. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) All objects fall at the same rate (9.8 m/s2) and the rolling ball experiment. An object that is rolling would continue to roll to try and reach its original starting point. (An object in motion remains in motion) Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) - Developed Calculus at 19 years of age. Law of Universal Gravitation, Three Laws of Motion. 1st Law- Inertia- (resistance to change)- Objects at rest remain at rest, objects in motion remain in motion UNLESS an outside Force acts on them. If objects are at rest, then we say that they are in equilibrium. 2nd Law- (Fnet = ma) the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the Net Force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the mass. The Force and acceleration vectors point in the same direction. Weight is the force of gravity acting on a mass. W = mg 1 Newton = 1 kg m/s2 Newton is the unit of Force. 3rd Law- (Action/Reaction)- For every action force, there is an opposite and equal reaction force. Forces occur in pairs! Newton’s Laws Forces are equal and opposite but act on different masses, so they do not always produce the same acceleration. Free Body Diagrams- a pictorial representation of the forces acting on an object. Usually arrows drawn and labeled to show the direction of the forces. These are used to help solve problems, and determine the net force acting on an object. When drawing, start with gravitational force, (weight), and Normal Force. Normal Force- (FN or N) the support force that a surface provides in reaction to the weight of an object. The Normal force will ALWAYS be perpendicular to the surface. Friction Force (f) a resisting force that occurs between the surfaces of two objects. f = N. On a flat surface, the Normal force is equal to the weight of the object. Two types of friction- Static- non-moving Kinetic or Sliding- moving Coefficient of Friction () is the ratio of two forces, f/N. There are no units for .