Forces in 1 Dimension
advertisement

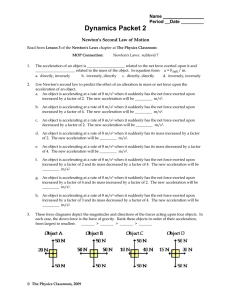
Forces in 1 Dimension Chapter 4 4.1 Force and Motion • Force is push or pull exerted on object • Forces change motion – Makes it important to know the forces on an object • Force diagrams (free body diagrams) show all forces acting on object – Both direction and magnitude – vector – Define system Contact and Field Forces • Contact – touching • Field – non-contact (not touching) • Every touch generates force • Table 4-2, pg 94 Force and Acceleration • Forces change motion • Newton’s 2nd Law – a = Fnet/m – Net forces and mass will affect the acceleration of an object • Applying a force changes the object’s motion – generates an acceleration • Changing mass, changes forces Newton’s 1st Law • “An object that is at rest will remain at rest, and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the net force acting on that object is zero” • Inertia – tendency of an object to resist change – Not a force • Equilibrium – net force on object is zero 4.2 Using Newton’s Laws • Weight – gravitational force acting on object – Changes depending on where you are in Universe • Scales – How it Works, pg 110 • Apparent weight – weight changes with motion – Example: elevator – Weightlessness – apparent weight is zero • No contact forces pushing up on object Drag Force • Particles of air exert forces on an object – Often is a huge force • Drag force – force exerted by a fluid on an object moving through the fluid – Direct relationship – increase speed, increase drag force – Affected by size and shape of object, and temperature and viscosity of fluid Terminal Velocity • Constant velocity is reached when drag force equals gravitational force 4.3 Interaction Forces • Interaction pairs • Newton’s 3rd Law states that all forces come in pairs – One doesn’t cause the other – Because there is one, there is the other – Equal in magnitude and opposite in direction – 2 force diagrams – each one contains one of the forces in the interaction pair The Normal Force • Support force • Perpendicular contact force exerted by a surface on another object Lab • Force table lab • Newton’s second lab