Newton's Laws of Motion Notes - Middle School Physics
advertisement

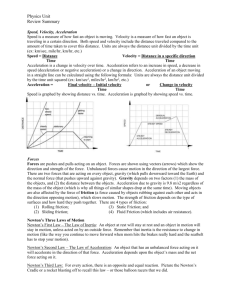
Section 1 – Newton’s First Law Section 1 – Vocabulary 0 Force: a push or a pull (p. 310) 0 Net Force: combination of all forces acting on an object (p. 311) 0 Balanced Forces: two or more forces whose effects cancel each other out and do not change the motion of an object (p. 311) 0 Unbalanced Forces: two or more forces acting on an object that do not cancel, and cause the object to accelerate (p. 311) 0 Newton’s First Law of Motion: states the if the net force acting on an object is zero, the object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with a constant speed (p. 312) 0 Friction: force that acts to oppose sliding between two surfaces that are touching (p. 312) Section 1 - Notes A. _____Force______________________ - Push or Pull on an Object 1. The combination of all the forces acting on an object is the ______net______ force. 2. When forces are ___balanced____ forces, they cancel each other out and do not change an object’s motion; when forces are _____unbalanced______forces, the motion of an object changes. B. Newton’s ____first law_____ of motion - an object will remain at rest or move with constant speed unless a net force is applied C. ____Friction___________is a force that resists sliding between two touching surfaces or through air or water. 1. Friction ____slows down______ an object’s motion. 2. ___Static_______friction – the type of friction that prevents an object from moving when a force is applied 3. ____Sliding______ friction is due to the microscopic roughness of two surfaces; it slows down a sliding object. 4. ____Rolling____ friction between the ground and a wheel allows a wheel to roll. Section 2 – Newton’s Second Law Section 2 – Vocabulary 0 Newton’s Second Law of Motion: states that an object acted upon by a net force will accelerate in the direction of the force, and that the acceleration equals the net force divided by the object’s mass (p. 316) 0 Weight: a measurement of force that depends on gravity; measured in newtons (pp. 53, 317) 0 Center of Mass: point in an object that moves as if all of the object’s mass were concentrated at that point (p. 322) Section 2 - Notes A. Newton’s ____second law____ of motion connects force, acceleration, and B. C. D. E. F. mass; it explains that an object acted upon by a force will accelerate in the direction of the force; acceleration equals net force divided by mass. ___Gravity_______- attractive force between two objects; depends on the mass of the objects and distance between them; gravitational force is also called ____ weight_____. The second law explains how to ___calculate_____ the acceleration of an object if its mass and the forces acting on it are both known. In circular motion, the _____centripetal______ force is always perpendicular to the motion. The ___terminal velocity_____is reached when the force of gravity is balanced by air resistance; the size of the air resistance force depends on the shape of an object and its speed. An object can speed up, slow down, or turn in the direction of the net force when ___unblanced______ forces act on it. Section 3 – Newton’s Third Law Section 3 – Vocabulary 0 Newton’s Third Law of Motion: states that forces always act in equal but opposite pairs (p. 323) Section 3 - Notes A. Newton’s ______third law________ of motion states that forces always act in equal but opposite pairs; for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. B. Action – reaction forces are always the same size but are in ____opposite_______ directions and act on different objects. 1. When the mass of one object is considerably ____larger________ than the mass of another object, the action-reaction force is not noticeable. 2. ____Air______ and ______Water_____ exert action-reaction forces with objects such as hands or canoe paddles 3. A ______rocket______ launches due to the equal but opposite forces of the burning fuel.