Reaction Rates Practice
advertisement
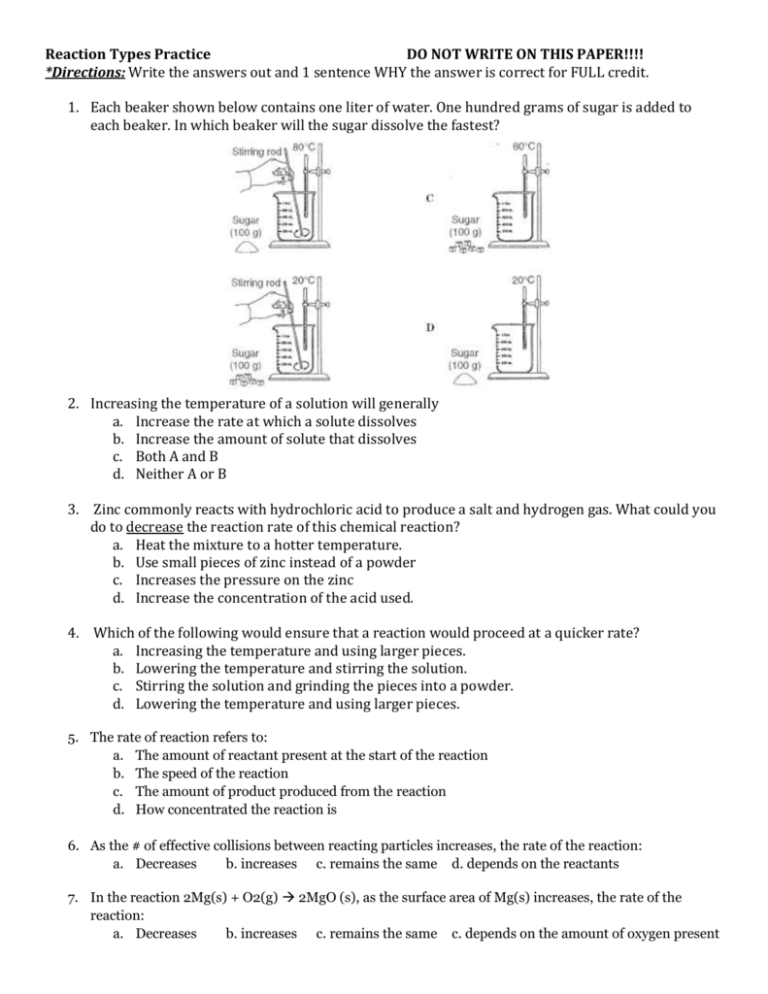
Reaction Types Practice DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER!!!! *Directions: Write the answers out and 1 sentence WHY the answer is correct for FULL credit. 1. Each beaker shown below contains one liter of water. One hundred grams of sugar is added to each beaker. In which beaker will the sugar dissolve the fastest? 2. Increasing the temperature of a solution will generally a. Increase the rate at which a solute dissolves b. Increase the amount of solute that dissolves c. Both A and B d. Neither A or B 3. Zinc commonly reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce a salt and hydrogen gas. What could you do to decrease the reaction rate of this chemical reaction? a. Heat the mixture to a hotter temperature. b. Use small pieces of zinc instead of a powder c. Increases the pressure on the zinc d. Increase the concentration of the acid used. 4. Which of the following would ensure that a reaction would proceed at a quicker rate? a. Increasing the temperature and using larger pieces. b. Lowering the temperature and stirring the solution. c. Stirring the solution and grinding the pieces into a powder. d. Lowering the temperature and using larger pieces. 5. The rate of reaction refers to: a. The amount of reactant present at the start of the reaction b. The speed of the reaction c. The amount of product produced from the reaction d. How concentrated the reaction is 6. As the # of effective collisions between reacting particles increases, the rate of the reaction: a. Decreases b. increases c. remains the same d. depends on the reactants 7. In the reaction 2Mg(s) + O2(g) 2MgO (s), as the surface area of Mg(s) increases, the rate of the reaction: a. Decreases b. increases c. remains the same c. depends on the amount of oxygen present 8. Consider the following equation: Mg(s) + 2H2O (l) Mg(OH)2 + H2 (g) For the reaction to occur at the fastest rate, 1 g of Mg(s) should be added in the form of: a. Large chunks b. Small chunks c. A ribbon d. A powder 9. When a catalyst is added to a system at equilibrium, a decrease occurs in the a. activation energy b. heat of reaction c. energy of the reactants d. energy of the products 10. Increasing the temperature increases the rate of a reaction by 11. Which set of reaction conditions produces H2(g) at the fastest rate? 12. Given the equation: Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g) This reaction occurs more quickly when powdered iron is used instead of an iron bar of the same mass because the powdered iron: a. b. c. d. a. b. c. d. lowering the activation energy increasing the activation energy lowering the frequency of effective collisions between reacting molecules increasing the frequency of effective collisions between reacting molecules a 1.0 g lump of Zn(s) in 50 mL of 0.5M HCl(aq) at 20°C a 1.0 g lump of Zn(s) in 50 mL of 0.5M HCl(aq) at 30°C a 1.0 g powdered Zn(s) in 50 mL of 0.5M HCl(aq) at 20°C a 1.0 g powdered Zn(s) in 50 mL of 0.5M HCl(aq) at 30°C a. b. c. d. acts as a better catalyst than the single piece of iron absorbs less energy than the single piece of iron has a smaller surface area than the single piece of iron is more metallic than the single piece of iron











