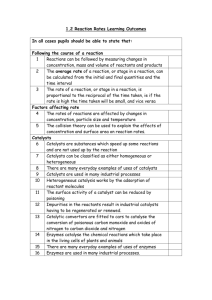
Summary ppt

Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Chemical reactions can be fast :
Like this explosion
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Chemical reactions can be slow:
Like the decomposition of this apple .
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Chemical reactions can be very slow :
Like the rusting of iron .
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
We can speed up chemical reactions :
By increasing the temperature .
When heated the particles of substances:have more energy move faster collide more often are more likely to react successfully .
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
We can speed up chemical reactions :
By increasing the concentration.
•
A more concentrated solution has more reacting particles
•
Particles have a bigger chance of coming into contact and reacting.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
We can speed up chemical reactions :
By decreasing the particle size.
When a lump of a reacting substance is broken into smaller pieces:
• the substance can more easily come into contact with the other reactant
• material from the inside of the lump can now react not just the outside surface.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
There are many examples of reactions which are affected by temperature.
•
Glucose reacts more quickly with Benedict’s solution as the temperature is increased.
•
Rusting of ships sunk in deep cold waters takes place very slowly .
•
Decay of food speeds up when it is removed from the fridge into a higher temperature.
•
Stains are more easily removed from washing at higher temperatures.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
There are many examples of reactions which are affected by changing concentration.
•
Clothes can be bleached more quickly using a more concentrated bleach.
•
Magnesium dissolves quicker and gives off hydrogen faster in 2% acid than it does in 1% acid.
•
When the amount of washing powder is less , clothes are not cleaned so effectively because the reaction is slower .
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
There are many examples of reactions which are affected by changing particle size.
•
Chalk lumps react with acid much more slowly than chalk powder.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Smaller particle size speeds up reaction.
• Potatoes cut into smaller pieces cook more quickly than whole potatoes.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Large surface area - quick reaction
•
Iron powder blown into a flame burns rapidly while an iron bar just glows.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Catalysts
• Speed up chemical reactions
•
Are not used up in the reaction
•
Can be recovered at the end of the reaction.
•
Save energy because they allow many reactions to be carried out at a lower temperature.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Catalysts have many uses:
• Iron is used as a catalyst in the production of ammonia, an important chemical used in fertiliser production.
•
Nickel is used in hydrogenation of vegetable oils. This process hardens oils to make margarine.
Note: the catalysts above are transition metals.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Platinum is used in catalytic converters in car exhausts to speed up the breakdown of harmful gases into harmless gases.
Topic 2 - Speed of Reactions
Enzymes
• are biological catalysts
• speed up reactions in living things.
•
In the human body reactions have to take place at 37 0 C and many are helped by enzymes.
•
Amylase is an enzyme in our saliva which speeds up the breakdown of starch.
•
Enzymes are used in the production of beer, wine, cheese and yoghurt.