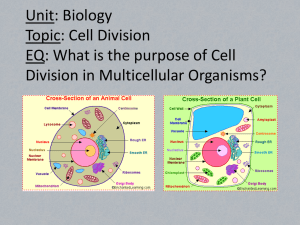
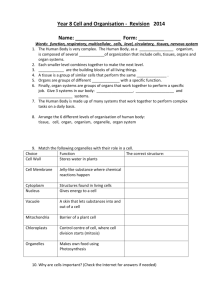
tissue - TeacherWeb
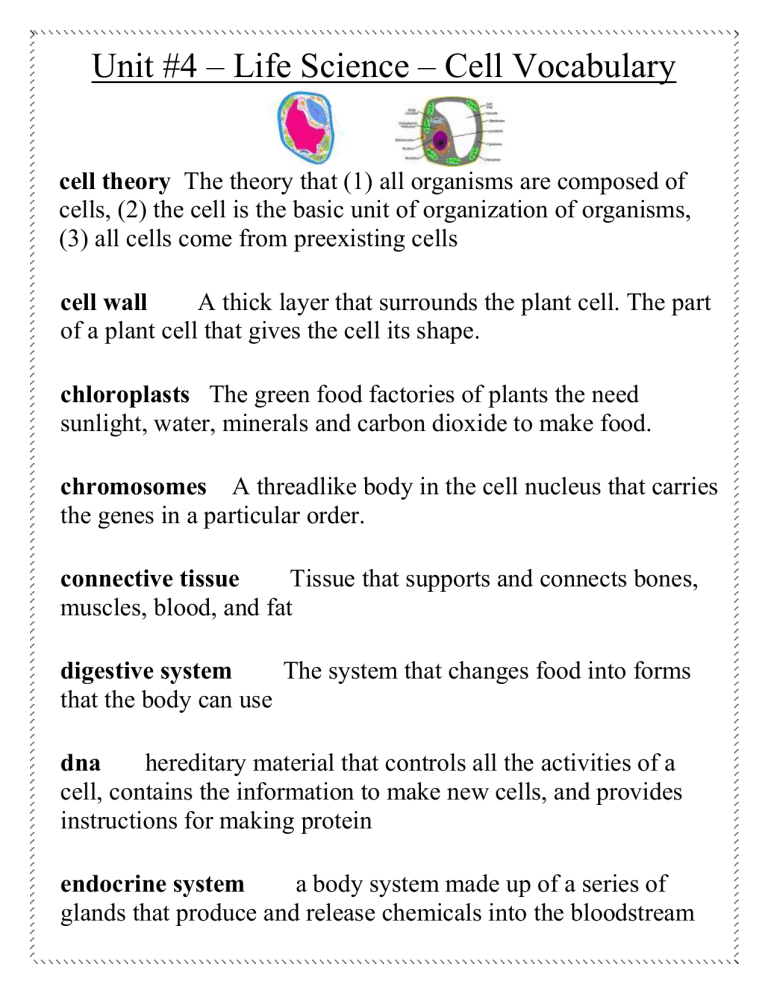
Unit #4 – Life Science – Cell Vocabulary
cell theory The theory that (1) all organisms are composed of cells, (2) the cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms,
(3) all cells come from preexisting cells cell wall A thick layer that surrounds the plant cell. The part of a plant cell that gives the cell its shape. chloroplasts The green food factories of plants the need sunlight, water, minerals and carbon dioxide to make food. chromosomes A threadlike body in the cell nucleus that carries the genes in a particular order. connective tissue Tissue that supports and connects bones, muscles, blood, and fat digestive system The system that changes food into forms that the body can use dna hereditary material that controls all the activities of a cell, contains the information to make new cells, and provides instructions for making protein endocrine system a body system made up of a series of glands that produce and release chemicals into the bloodstream
epithelial tissue one of four main types of tissue in the body; the tissue that covers and protects underlying tissue excretory system body system involved in removing waste products from body genes A segment of DNA found on a chromosome that codes for a particular protein; a unit of heredity. integumentary system a collection of organs that helps the body maintain a stable and healthy internal environment; the organs in this system include skin, hair, and nails. meiosis
1.
a form of cell division that halves the number of chromosomes when forming reproductive cells
2.
the division of a nucleus to produce gametes (sex cells) mitosis Cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes. multicellular an organism with more than one cell muscle tissue tissue made up of muscle cells, which contract to move parts of the body. muscular system collection of organs whose primary function is movement
nerve tissue tissue that carries messages back and forth between the brain and every other part of your body nucleus
1.
control center of a cell
2.
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction. organ part of body that does a job (for example, the heart and lungs) organ system organs working together to do a job organism
1.
A living thing that has (or can develop) the ability to act or function independently.
2.
a living thing made up of one or more cells reproductive system the organs that make possible the production of offspring respiratory system
1.
The system that includes your nose, trachea, lungs, and diaphragm.
2.
the system that takes in oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide sexual reproduction process by which most multicellular animals and plants reproduce, it involves the joining of male and
female sex cells tissue Cells that work together to perform a particular function are called tissues.