EPS Vocabulary - Madison County Schools
advertisement

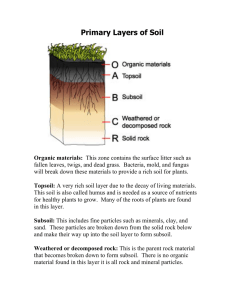
Environmental Problems and Solutions Vocabulary 1. Development –the construction of buildings, roads, bridges, dams and other structures 2. Litter-the layer of dead leaves and grass on top of the soil 3. Topsoil-the upper layer of soil consisting of rock fragments nutrients, water, air, and decaying plant and animal matter 4. Subsoil- the layer of soil below topsoil that has less plant and animal matter than topsoil 5. Bedrock-rock that makes up Earth’s crust 6. Erosion- the process by which water, wind or ice moves particle of rock or soil 7. Nutrient Depletion- the situation that arises when more soil nutrients are used than the decomposers can supply 8. Fertilizer- a substance that provides nutrients to help crops grow better 9. Desertification- the advance of desert- like conditions into areas that previously were fertile 10. Drought- a period of less rain that normal 11. Land Reclamation – the process of restoring land to a more natural state 12. Industrial Revolution- the transition from hand made to machine made products 13. Municipal Solid Waste-waste produced in homes, businesses and schools 14. Incineration- the burning of solid waste 15. Leachate- polluted liquid produced by water passing through buried wastes in a landfill. 16. Sanitary Landfill-a landfill that hold nonhazardous waste such as municipal solid and construction debris 17. Recycling- the process of reclaiming and reusing raw materials 18. Biodegradable-capable of being broken down my bacterial & other decomposers 19. Composting- the process of helping biodegradable wastes to decompose naturally 20. Hazardous Waste- a material that can be harmful if it is no properly disposed of 21. Groundwater- water stored in underground layers of soil and rock 22. Pollutant- a substance that causes pollution 23. Sewage- water and human waste that is washed down sinks, showers, toilets 24. Pesticide- a chemical that kills crop-destroying organisms 25. Sediment- particles of rock and sand 26. Emissions- pollutants that are released into the air 27. Photochemical Smog- a thick, brownish haze formed when certain gases react with sunlight 28. Ozone- a toxic form of oxygen 29. Temperature Inversion- a condition in which a layer of warm air traps polluted air close to earth’s surface 30. Acid Rain- precipitation that is more acidic than normal because of air pollution 31. Radon-a colorless, odorless, radioactive gas 32. Ozone Layer- the layer of the atmosphere that contains a higher concentration of ozone that the rest of the atmosphere 33. Chlorofluorocarbon- human-made gases containing chlorine and flouring (CFCs) 34. Greenhouse effect- the trapping of heat near Earth’s surface by certain gases in the atmosphere 35. Global Warming – the theory that increasing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will raise Earth’s average temperature