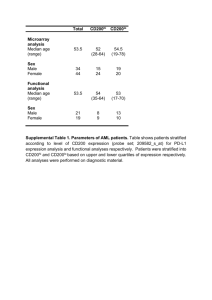
Cell surface immunophenotyping of AML patient blasts and
advertisement

Methods AML patient and healthy donor materials Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) or bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMNC) were collected from healthy donors or AML patients enrolled in the UK MRC/NCRI AML 14, 15, 16 and 17 clinical trials at point of diagnosis, before treatment and following informed consent from patients in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. Mononuclear cells were separated on Ficoll-Hypaque (Sigma-Aldrich, Poole Dorset U.K) as previously described.1 Cell surface immunophenotyping of AML patient blasts and T-cell subpopulations PBMC/BMMNC from AML patients or healthy donors were thawed and washed in prewarmed T-cell medium consisting of Iscove’s modified Dulbecco’s Medium supplemented with 10% heat inactivated human AB-serum (Invitrogen, Paisley, U.K.). Cells (106) were washed in chilled staining buffer (PBS, 2% FCS, 1mM EDTA, 0.02% NaN3) before incubation with the following anti-human antibodies purchased from BD Bioscience U.K. unless otherwise stated; CD45-FITC, CD200-PE, PD-L1-APC, CD34-PerCP-Cy5.5 for AML blast cell phenotyping and CD3-APC-H7, CD4 or CD8-pacific blue, (PD-1)-FITC, CD57-PE and CD28-PerCP-Cy5.5 (Biolegend, Cambridge, U.K.) for T-cell phenotyping. All incubations were carried out for 30 min and 4ºC after which cells were assessed by multi-parameter flow cytometry. For flow cytometric gating, AML blast cells were analyzed as previously described using CD34 and CD45 bivariate analysis.2 CD200 and PD-L1 expression was assessed on the AML blast cell population by means of an isotype match IgG control to set the negative population. For AML patient T cell subpopulation analysis, T cells were identified using CD45++ low SSC, CD3+, CD4+ or CD8+, followed by CD28/CD57 bivariate analysis. PD1 expression was assessed within CD28/CD57 regions by means of an isotype match IgG control to set the negative population (for full gating strategy see Supplemental Material Fig S1). AquaLive (Invitrogen) was used to exclude dead cells from the analysis. Cells were acquired using a FACSCantoII and analyzed post-acquisition in FCS Express V4 (De Novo Software, Canada). Generation of K562 cells expressing C200 and PD-L1 CD200 cDNA was kindly provided by IMAGE consortium; clone ID 5299899,1,3 and was sub-cloned into the PINCO retroviral expression vector, which co-expresses GFP from a CMV promoter as previously described.4 PD-L1 cDNA (Eurofins, Ebersberg, Germany) was sub-cloned into the PINCO retroviral expression vector, which co-expresses DSred from a CMV promoter using the same method. Phoenix packaging cells (gift from Garry Nolan, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA) were used to generate replication-defective retrovirus, before transducing K562 cells as previously described.1. PINCO co-expressing PD-L1 and DSred was use to co-transduce K562 cells stably expressing CD200 from a previous transduction. In this way, five cultures were generated: K562-mock, K562-CD200-PD-L1+ (PINCO-expressing GFP alone with PINCO-expressing DSred and PD-L1), K562-CD200+PDL1+ (PINCO-expressing GFP and CD200 with PINCO-expressing DSred and PD-L1), K562CD200+PD-L1- (PINCO-expressing GFP and CD200 with PINCO-expressing DSred alone) and K562-CD200-PD-L1- (PINCO-expressing GFP alone with PINCO-expressing DSred alone). Transduced K562 cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 (Sigma-Aldrich), 10% (v/v) FCS (Biosera, East Sussex, UK), 2 mM L-glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich) and cell sorted for DSred positivity using a FACSAria (BD). Cell purity, CD200 and PD-L1 protein expression were confirmed by flow cytometry. Functional assessment of CD200 and PD-L1 in co-culture assays In a 96-well flat bottomed plate, 5 x105 K562 cells were co-cultured with 105 7E7 CD8+ T cell clone5 at 37°C and 5% CO2 in the presence of Golgi-stop (1:1500) and 10 µg/ml brefeldinA. 7E7 cells are HPV16 E629-38 specific and produce IFNγ and TNFα following activation.6 In the co-culture assay, 7E7 T cells were activated through CD3 (OKT3, eBioscience) and CD28 (28.2, R&D) co-stimulation (5µ/106 cells) for 6 h, after which cells were surface stained for CD8, CD200R and PD1 (20ng/ml PMA and 1µ/ml ionomycin (Sigma-Aldrich) was used for stimulation as a positive control). Intracellular TNFα staining was performed on the CD8+ cells as previously described.2 For CD200 blocking experiments, incubations were carried out as above in the presence of 5µg/106 cells un-conjugated anti-human CD200 (clone MRC OX-104, BD) or IgG1, κ isotype matched control (BD). References 1 Tonks a, Pearn L, Musson M, Gilkes a, Mills KI, Burnett a K et al. Transcriptional dysregulation mediated by RUNX1-RUNX1T1 in normal human progenitor cells and in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2007; 21: 2495–505. 2 Coles SJ, Hills RK, Wang ECY, Burnett AK, Man S, Darley RL et al. Expression of CD200 on AML blasts directly suppresses memory T-cell function. Leukemia 2012; 26: 2148–51. 3 Lennon G, Auffray C, Polymeropoulos M, Soares MB. The I.M.A.G.E. Consortium: an integrated molecular analysis of genomes and their expression. Genomics 1996; 33: 151– 2. 4 Grignani F, Kinsella T, Mencarelli A, Valtieri M, Riganelli D, Lanfrancone L et al. Highefficiency gene transfer and selection of human hematopoietic progenitor cells with a hybrid EBV/retroviral vector expressing the green fluorescence protein. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 14–9. 5 Youde SJ, McCarthy CM, Thomas KJ, Smith KL, Man S. Cross-typic specificity and immunotherapeutic potential of a human HPV16 E7-specific CTL line. Int J Cancer 2005; 114: 606–12. 6 Thomas KJ, Smith KL, Youde SJ, Evans M, Fiander AN, Borysiewicz LK et al. HPV16 E6 29-38-specific T cells kill cervical carcinoma cells despite partial evasion of T-cell effector function. Int J Cancer 2008; 122: 2791–9.