Refraction ppt - Kelso High School
advertisement

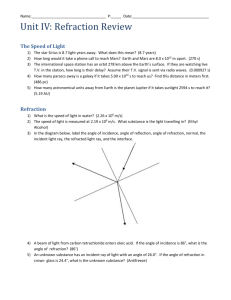
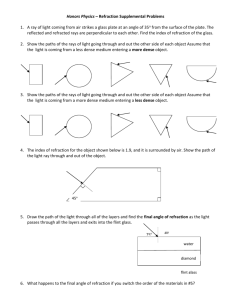
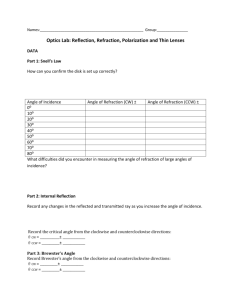
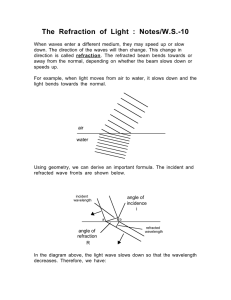
Light •Refraction of light including identification of the normal, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. •Description of refraction in terms of change of wave speed. Refraction : Waves change speed when they travel from on medium to another. This means they sometimes change direction. An analogy to explain refraction. Soldiers marching on concrete and sand, concrete When they reach the sand the soldiers slow up. The soldiers at the left of each row reach the sand first so slow before the ones at the right. The column changes direction. sand air Normal – at right angles t the boundary i i – incident angle r – refracted angle water r Shine a single ray of light through a rectangular block. Draw where it goes on a diagram in your jotter. You should draw an arrow each time the line changes direction. Now use 3 rays of light to shine on the two lenses. The middle ray should go straight through. Convex lens Concave lens When the angle in the air gets to 90o it can no longer be refracted and is then reflected. This is called total internal reflection. Total internal reflection refraction Smaller than critical angle demo Critical angle – when refracted angle is 90o Larger than critical angle Use of total internal reflection - Optical fibre demo Endoscopes – to look inside people Uses of refraction - Glasses No correction needed Demo of eyesight correction Normal eye Myopia (nearsightedness) Hyperopia (farsightedness) Corrected with concave lens Corrected with convex lens No one’s perfect