Ch 7 Review - Stephanie Dietterle Webpage
advertisement

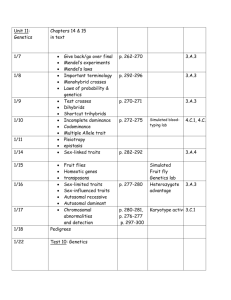
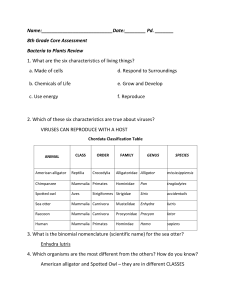
Ch 7 Review 1. Bacteriophages are viruses that attack and destroy a. Other viruses b. Bacteria c. Plants d. Humans 2. Which part of a virus determines which host cells it can infect? a. Nucleus b. Ribosomes c. Flagellum d. Surface proteins 3. Most bacteria are surrounded by a rigid protective structure called the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Protein coat d. Flagellum 4. Which of the following characteristics describes all protists? a. They are unicellular b. They can be seen with the unaided eye c. Their cells have nuclei d. They are unable to move on their own 5. A lichen is a symbiotic association between a. Fungi and plant roots b. Algae and fungi c. Algae and bacteria d. Protozoans and algae 6. Active viruses enter a cell and immediately begin to multiply a. True b. False 7. During conjugation, one bacterium transfers genetic material to another bacterial cell a. True b. False 8. Plantlike protists are called protozoans a. True b. False 9. Bacteria form endospores to survive unfavorable conditions in their surroundings a. True b. False 10. Most fungi are made up of threadlike structures called spores a. True b. False 11. Which of the following statements about a paramecium is correct? a. It has two contractile vacuoles that remove excess water from the cytoplasm b. It uses cilia to move c. It has two nuclei d. All of the above 12. Which of the following statements about fungus reproduction is true? a. Fungi reproduce sexually by budding b. Fungi reproduce by making spores c. Fungi reproduce asexually when two hyphae join together and exchange genetic material d. Fungi do not reproduce sexually 13. What will most likely happen after the virus in the diagram attaches to the bacterial cell? (use the picture to help answer this question) a. The virus will inject its proteins into the bacterial cell b. The virus will inject its genetic material into the bacterial cell c. The bacterial cell will inject its proteins into the virus d. The bacterial cell will inject its genetic material into the virus 14. Which of the following statements about viruses is not true? a. Viruses can multiply only inside a living cell b. Viruses have genetic material c. Virus particles are smaller than bacterial cells d. Diseases caused by viruses can be cured by antibiotics 15. Paola grew a new culture of bacteria and measured the population’s growth over time. The number of bacteria increased sharply over the first few hours but then tapered off. Which of the following statements about these observations is true? a. The initial conditions for bacterial growth were favorable b. The number of bacteria increased as the bacteria reproduced asexually c. After a period of time, the bacteria started to run out of food, space, and other resources d. All of the above 16. Compare and contrast viruses and bacteria with respect to their sizes, structures, and methods of reproduction. _________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 17. Give three real-life examples of ways bacteria can be helpful to humans a. b. c. 18. Where is the genetic material located in a bacterial cell? a. In the flagellum b. In the cytoplasm c. On the endospore d. All the above 19. What is the role of flagella in a bacterial cell? e. Make food f. Fight disease g. Help the bacterial cells move h. Convert carbon dioxide to oxygen 20. What are three ways in which bacteria obtain food? a. b. c. 21. What are the two types of ways that bacteria reproduce? a. b. 22. One cell divides to form two identical cells is called a. Sexual reproduction b. Conjugation c. Binary fission d. Asexual reproduction 23. One bacterium transfers some genetic material to another bacterium through threadlike bridge a. Sexual reproduction b. Conjugation c. Binary fission d. Asexual reproduction 24. Is a small, rounded, thick-walled, resting cell that forms inside a bacterial cell a. Conjugation b. Binary fission c. Cytoplasm d. Endospore 25. Food that is heated to a temperature that is high enough to kill most harmful bacteria without changing the taste of food is called a. Pasteurization b. Conjugation c. Binary fission d. Asexual reproduction 26. Organisms that break down large chemicals in dead organisms into small chemicals is called a. Pasteurization b. Cytoplasm c. Endospore d. Decomposers 27. A friend states that all bacteria are harmful to people. List three reasons why this statement is inaccurate. a. b. 28. Protists are eukaryotes that cannot be classified as animals, plants, or fungi? a. True b. False 29. Protozoan’s are multicellular a. True b. False 30. The word pseudopod means “false foot” a. True b. False 31. Amoebas and paramecium have a contractile vacuole that collects extra water and then stores it for later use a. True b. False 32. Cilia are hair-like projections from cells that move with a wavelike motion a. True b. False 33. Symbiosis is a close relationship in which at least two of the species benefit a. True b. False 34. Like plants, algae are Heterotrophs a. True b. False 35. A spore is a tiny cell that is able to grow into a new organism a. True b. False 36. Like fungi, fungus-like protists are Heterotrophs, have cell walls, and use spores to reproduce a. True b. False 37. Plant-like protists include: diatoms, dinoflagellates, eugleniods, red algae, green algae, brown algae a. True b. False