Study Guide for Core Answer Sheets

Name:___________________________Date:________ Pd. _______
8th Grade Core Assessment
Bacteria to Plants Review
1. What are the six characteristics of living things? a. Made of cells d. Respond to Surroundings b. Chemicals of Life c. Use energy e. Grow and Develop f. Reproduce
2. Which of these six characteristics are true about viruses?
VIRUSES CAN REPRODUCE WITH A HOST
Chordata Classification Table
CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS
ANIMAL
American alligator Reptilia Crocodylia Alligatoridae Alligator
SPECIES mississippiensis
Chimpanzee
Spotted owl
Sea otter
Mammalia Primates Hominidae Pan
Aves Strigiformes Strigidae Strix
Mammalia Carnivora Mustelidae Enhydra troglodytes occidentalis lutris
Raccoon Mammalia Carnivora Procyonidae Procyon lotor
Human Mammalia Primates Homindae Homo sapiens
3. What is the binomial nomenclature (scientific name) for the sea otter?
Enhydra lutris
4. Which organisms are the most different from the others? How do you know?
American alligator and Spotted Owl – they are in different CLASSES
In this experiment, broth was placed in two identical flasks and boiled. One was left open and the other was closed. After a period of time, the flask left open produced bacterial growth and the broth became cloudy. There was no bacterial growth in the sealed flask.
5. What is the manipulated variable? SEALING THE FLASK
6. What is the responding variable? GROWTH OF BACTERIA
7. Describe each step below for active virus multiplication. (AIRAB)
VIRUS ATTACHES TO HOST
VIRUS INJECTS GENETIC MATERIAL
GENETIC MATERIAL IS REPRODUCED/COPIED
VIRUSES ARE ASSESMBLED
VIRUSES BURST OUT OF HOST
8. How do the cells of bacteria differ from those of eukaryotes?
NO NUCLEUS (PRO MEANS NO)
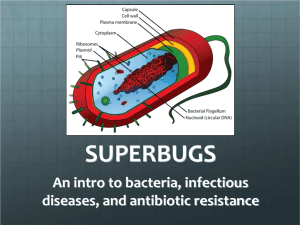
9. Identify the structure and describe the function of the parts in a bacterial cell.
Structure
A. FLAGELLA
B. CELL WALL
C. GENETIC MATERIAL
D. Cell Membrane
E. Ribosome
Function
A. MOVEMENT
B. PROTECTION CELL
C. CONTROL CENTER
D. ALLOWS THINGS IN/OUT
E. PRODUCES PROTEINS
Bacterial Growth
Time (hours)
10. Under what conditions do bacteria thrive and reproduce?
PLENTY OF FOOD AND RIGHT TEMPERATURE (WARM) , MOISTURE (WATER)
11. How would a mild temperature increase effect the growth of bacteria?
BACTERIA GROWTH INCREASES IF TEMPERATURE INCREASES
12. How would a temperature decrease effect the growth of bacteria?
BACTERIA GROWTH DECREASES IF TEMPERATURE DECREASES
13. Compare and Contrast BINARY FISSION and CONJUGATION in the number of parents, what happens to the genetic material, conditions of growth, and resultant offspring of bacteria.
BINARY FISSION – ONE PARENT DIVIDES INTO two IDENTICAL DAUGtHER CELL
(THE GENETIC MATERIAL IS COPIED)
CONJUGATION – 2 PARENT CELLS EXCHANGE GENETIC MATERIAL AND RESULTS IN two DAUGHTER CELL THAT are DIFFERENT FROM BOTH PARENTS
14. Using the taxonomic key (dichotomous), what is the name of this organism?
PSEUDOSCORPION _
15.
HAS 8 LEGS, HAS TWO BODY REGIONS, HAS CLAWLIKE PINCERS, HAS NO TAIL OR STINGER
16. What treatments are effective for bacterial infections?
ANTIBIOTICS WHEN HAVE INFECTION
VACCINE TO PREVENT INFECTION
17. What treatments are effective for viral diseases?
NO TREATMENT – BED REST AND FLUIDS WHEN HAVE INFECTION
VACCINE TO PREVENT INFECTION
18. How does a vaccine work to prevent disease in the human body?
STIMULATES BODY TO PRODUCE CHEMICALS THAT CAN DESTROY
VIRUSES OR BACTERIA
19 . Identify the names of the protists pictured below.
PARAMECIUM (CILIATE) EUGLENA (FLAGELLATE) AMOEBA(PSEUDOPOD)
Protist 3
E
D
20. Identify the key structures and functions
Structure
A. CONTRACTILE
VACUOLE
B. CILIA
C. FLAGELLA
D. CHLOROPLAST
E. PSEUDOPOD
Function
COLLECTS AND EXPELS EXCESS
WATER
MOVEMENT AND EATING
MOVEMENT
SITE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS/FOOD PRODUCTION
MOVEMENT AND FEEDING
21. Into which kingdom is the mushroom classified? FUNGI
22. Why is the mushroom not classified in the plant kingdom?
PLANTS CAN MAKE THEIR OWN FOOD (AUTOTROPHIC); FUNGI CANNOT MAKE
THEIR OWN FOOD – THEY ARE HETEROTROPHIC
23. Which structure in the mushroom diagram is responsible for transporting water, food and minerals throughout the organism and also gives the organism shape? HYPHAE
24. List roles fungus can play in nature.
Helpful Roles
a. MAKE FOOD b. MAKE ANTIBIOTICS /
Disease fighting c. DECOMPOSE /RECYCLE
Harmful Roles
a. CAUSE DISEASE b. DESTROY ORGANIC
MATERIAL c.PARASITES TO A HOST
D. TOXIC TO ANIMALS,
PLANTS (EDIBLE)
E. ALLERGIC REACTIONS
F. REPRODUCE EASILY/
QUICKLY
25. What is the difference between vascular and nonvascular plants?
VASCULAR HAVE A TRANPORT SYSTEM TO MOVE WATER AND FOOD THROUGH
THE PLANT (THEY CAN GROW TALL)
NONVASCULAR DO NOT HAVE A TRANSPORT SYSTEM TO MOVE WATER AND
FOOD. THEY OBTAIN WATER THROUGH OSMOSIS. THEY ARE USUALLY LOW TO
THE GROUND.
6H
2
O +
energy
6CO
2
Chlorophyll
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
26. What is the name of the process shown above used by all plants to make food? PHOTOSYNTHESIS
27. Where in the plant cell does this process occur?
CHLOROPLASTS
28. a. Are organisms that use this process classified as autotrophs or heterotroph?
AUTOTROPHS
b. How do you know?
CAN MAKE THEIR OWN FOOD THROUGH PHOTOSYNTHESIS
29. What are the functions of roots?
ABSORB WATER FROM THE GROUND, ANCHOR THE PLANT, STORE FOOD
30. What are the functions of stems?
TRANSPORT FOOD, WATER AND MINERALS, AND PROVIDES MAIN SUPPORT
31. What is the main functionS of leaves?
PREVENT WATER LOSS, ALLOWS FOR GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPIRATION _
CREATE FOOD FOR THE PLANT WHERE PHOTOSYNTHESIS OCCURS