Lesson Plan

Lesson: Nervous System
Objectives:
Define what a neurons are?
Identify the types of neurons and their functions?
Explain the purpose of the central nervous system?
Explain how does the peripheral nervous system serve the body?
Identify and explain common disorders of the nervous system?
Materials:
Brain and Neuron Illustrations for Labeling
Nervous System Videos iCEV
Chapter 35: Nervous System PPT
Note Taking Guide Sheet
Computer
Projector
COWS: Computers on Wheels
Nervous System Disorder List
Assessment:
Quiz: Nervous System
Disorder PPT/Presentation
Content:
We just covered the Musculo - Skeletal System. As you assembled the Equikken model you discovered just how everything is interconnected rather than layered. The skeleton provides structure and support, while the muscles, ligaments, and tendons help move the bones so that the body is mobile.
Ask what the skeleton does?
Ask what the functions of the muscles, tendons, ligaments are?
When you built your limbs we asked you to include the nerves. This is because these nerves are how your brain communicates with the rest of your body.
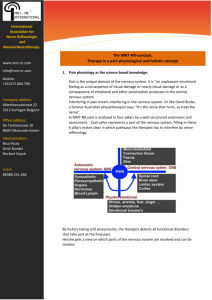
The nervous system can be broken into two parts:
Central Nervous System (CNS): o Spinal cord and brain
Receives signal from PNS
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)- provides protection to nerves
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
o Nerves
Detects stimuli
Informs the CNS
Causes a response
The parts of the Central Nervous System are the brain and spinal cord:
Brain – the major organ in the nervous system o Divided into 3 regions:
Cerebrum: controls voluntary movement and thought (largest part )
Cerebellum: provides coordination in movement
Brain Stem: controls functions to maintain life
Specific parts within the three regions include:
Medulla oblongata: in the brain stem; controls respiration and circulation (HR, RR, BP) o Damage to this region causes instant death
Midbrain: senses (sight, hearing, smell) o Damage to this region causes a coma (prolonged state of unconsciousness)
Thalamus- top of brain stem o Transfers senses
Hypothalamus- endocrine gland that produces hormones
Pituitary gland- produces hormones and controls body functions
The Peripheral Nervous System
Sympathetic System: o Fight or flight reactions o Increased vital signs o Certain drug stimuli
Parasympathetic System: o Opposite reactions o Systems slow down o Main nerve is VAGUS o Regulates system back to normal
Each segment of vertebra has 2 nerve branches: dorsal root and ventral root o Dorsal: contains sensory nerves o Ventral: contains motor nerves
Vagus Nerve o the main nerve in these systems
Coordinated Function of the CNS and PNS
CNS controls the brain and spinal cord by receiving signals from the PNS
PNS controls the nerves, detects a stimulus, sends signals to the CNS, and causes a response or action to occur
Volts – create a force within a cell in specific amounts
Voluntary reflexes – occur when an animal asks its body to perform a function
Involuntary reflexes – occur without thinking and serve as many of the body system functions such as the heart beating and breathing
Receptors o Are found within the nerves located throughout the body and allow for detecting changes within the body and the environment o Proprioception – movement o Chemoreceptors – chemical receptors that allow animals to smell, taste, and detect sounds
Testing
Cranial nerve test o Determines function of reflexes and nervous system
Spinal nerve test o Proprioceptive reflexes of muscles and tendons
Knee jerk reflex – probably easiest/safest to replicate on one’s self o Assessment of spinal nerves
Common Disease and Conditions
Diseases of the nervous system can originate from invasion of bacterial or viral organisms, other disease processes, or traumatic injury
Intervertebral Disc Disease o Causes pressure to be placed on an area of vertebral column, causing compression on the discs o Causes severe back pain and partial or complete paralysis
Epilepsy o Seizures o Loss of control of the body with degrees of consciousness o Can be caused by disease, heredity, or toxins o Signs of Seizure
Paddling motion of legs
Opening and closing of jaw
Muscle twitch
Excessive drooling or salivation
Uncontrolled urination
Vocalization
Loss of consciousness
Stiff appearance to body
Ocular dilation
Rabies o A deadly virus that can affect any mammal or human o Most common cases occur in wild animals— with bats, skunks, fox, and raccoons o Rabies Signs: excessive salivation, foaming at mouth, lack of coordination, or stumbling o Vaccinations should be given to dogs, cats, ferrets, and livestock in order to prevent it
West Nile Virus o Concern for birds and horses o Transmitted through a mosquito-borne disease o Signs of infection may take 5-15 days o Signs: stumbling, twitching, partial paralysis, loss of appetite, depression, death, coma, and fever
Assessment: Disease Report Instructions
Given a class period and a half – to work on in school
30% off after one block past in class work session – added some time because snow days prevented students without PPT at home from finishing during Pride Time.