Case Studies Exam #3 - Multiple Sclerosis
advertisement

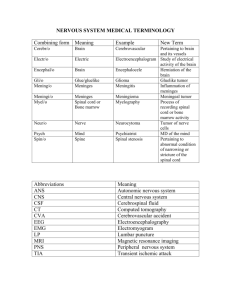
Case Studies Exam #3 - Multiple Sclerosis 1. The central nervous system includes: a. Brain and spinal cord b. Ganglia and sensory nerves c. Peripheral nervous tissue d. Brain and spinal nerves e. Spinal cord and sensory receptors 2. Which division of the nervous system is affected by the Multiple Sclerosis? a. Central nervous system b. Peripheral nervous system c. Spinal nerves d. Ganglia e. Sensory receptors 3. The function of a neuron is: a. Conduct action potentials b. Maintain the proper chemical environment for nervous tissue c. Phagocytize foreign invaders d. Produce CSF e. Produce myelin sheaths 4. Which statement best describes the function of the myelin sheath? a. Acts as a receptor for nerve impulses b. Allows passage of electrolytes to generate an action potential c. Increases the speed of an action potential d. Suppresses an action potential 5. Which two types of neuroglia produce myelin sheaths? a. Astrocytes and ependymal cells b. Astrocytes and Schwann cells c. Ependymal cells and oligodenrocytes d. Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells e. Schwann cells and microgia 6. Schwann cells are found in the: a. Autonomic nervous system b. Central nervous system c. Peripheral nervous system d. Ganglia e. Sensory nervous system 7. Which statement best describes a relapsing-remitting MS? a. Frequent attacks accompany a steady decline in abilities b. Gradual decline in abilities with only short periods of relief c. Series of attacks followed by complete or partial disappearance of symptoms until another attack occurs d. None of the above 8. Common symptoms of MS do NOT include: a. Sudden weight gain b. Dizziness c. Lack of coordination d. Muscle spasm e. Visual disturbances 9. MRI is preferred over CT scans in diagnosing MS because: a. CT is more painful to the patient b. CT cannot produce images of the CNS c. MRI is less expensive d. MRI produces images with greater detail and resolution e. All of the above 10. What abnormality found in the cerebral spinal fluid would aid in the diagnosis of MS? a. Bacteria present b. Elevated protein levels c. Elevated white blood cells d. Presence of red blood cells e. Characteristic plaques 11. A visual field exam tests for: a. Visual acuity b. Glaucoma c. Nystagmus d. Peripheral vision e. All of the above 12. MS can be cured by: a. Immunosuppressive drugs b. Preventing acute attacks c. Reducing inflammation d. Regular use of beta interferons e. There is no known cure 13. Which of the following patients would typically be referred to a neurologist? a. 4th grade student with blurred vision and trouble seeing the board in school b. 34 year old woman with severe, uncontrollable headaches c. 45 year old man complaining of fatigue, increased thirst, and frequent urination d. 33 year old pregnant female with low hematocrit e. 65 year old alcoholic male complaining of frequent, rattling cough 14. As a neurologist, you wish to confirm your suspicion of MS in a female patient with characteristic symptoms. Which group of tests would be most useful in confirming the diagnosis? a. CT scan, CBC, MRI b. CT scan, serum protein levels, visual acuity c. Evoked potentials, lumbar puncture, MRI d. Serum beta interferon levels, MRI e. Visual acuity, visual fields, CBC 15. An MRI scan would be interpreted by a/an: a. Clinical laboratory specialist b. Home health nurse c. Ophthalmologist d. Radiologist and/or Neurologist e. Specialized radiological technician 16. Which of the following would be included in the responsibilities of a home health nurse? a. Administer medications b. Identify clinical problems c. Provide client care in home d. Teach family and caregivers e. All of the above 17. Demyelination of nerves in MS is caused by: a. Attack of the body’s immune system with subsequent inflammation b. Bacterial toxins c. Elevated serum protein levels d. Slowing of nerve impulses e. All of the above On the picture of a neuron, identify the following: 18. Axon _____ 19. Myelin ______ 20. Dendrite _____