Types of ShockCh6
advertisement

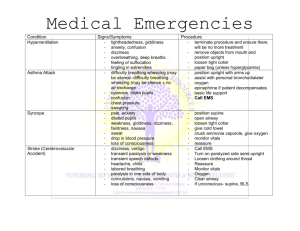
Types of Shock Chapter 6- DH 111 Hypovolemic Shock Most common. Decreases blood volume Causes: Bleeding, dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea Symptoms: Increased HR, Increased pulse, cool skin, decreased urine, confusion Treatment: 1. Stop cause of bleeding or dehydration 2. Lay patient supine 3. Call EMS 4. CPR 5. Monitor vitals 6. Oxygen 4-6 L/min 7. IV fluids Cardiogenic Shock Decreased circulation of blood caused by failure of the heart to function effectively Causes: damage to the heart due to heat attacks, arrhythmias, cardiac dysfunction Signs/Symptoms: Decreased BP, fast/weak pulse, cold/clammy skin, cyanosis, chest pain, shortness of breath, decreased urine, confusion Treatment: 1. Lay patient supine 2. Call EMS 3. CPR 4. Monitor vitals 5. Oxygen 4-6 L/min 6. IV fluids 7. Cardiac Meds 12-12 Distributive Shock: Vasogenic- 3 types: anaphylactic, septic, neurogenic Anaphylactic- Vasodilation and circulatory collapse due to exposure to an allergen Septic-Vasodilatory. Bacteria in blood stream causes an inflammatory response. Signs/Symptoms: Fever, increased cardiac output, swelling, pink/warm skin, increased HR, thirst, respiratory failure. Result of a severe infection, multiple organ failure, death Neurogenic- Loss of fight/flight response system in brain Caused by: emotional trauma, disease, drugs, tramatic injury to brain or spinal cord Loss of sympathetic nerve activity causes expansion of blood vessels= decrease in venous return= low cardiac output with low BP Sign/Symptoms: low BP, increased HR, brain and kidneys at risk of failure Treatment: 1. Lay patient supine 2. Call EMS 3. CPR 4. Monitor vitals 5. Oxygen 4-6 L/min 6. Drug therapy to restore cardiac output Obstructive Shock: Decreased cardiac function and reduced circulation Causes: narrowing of arteries, pulmonary embolism, cardiac tamponade Symptoms: Decreased BP, shortness of breath Treatment: 1. Lay patient supine 2. Call EMS 3. CPR 4. Monitor vitals 5. Oxygen 4-6 L/min 6. IV fluids 7. Surgical intervention 12-12 12-12