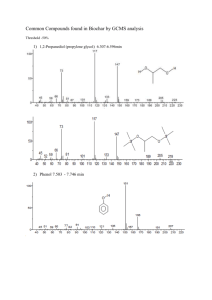
ESTER LAB-2014
advertisement

ESTER LAB “The smelliest lab of the year” Honors level 2014 Introduction: The purpose of this lab is to determine the ester created by reacting an organic acid and an alcohol, and to write the correct reaction showing the formation of the ester made. http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/alcohols/esterification.html This link helps to explain the entire “esterification” process. When an organic acid ( ) and an alcohol (R-OH) are mixed together and heated in the presence of an acid catalyst (such as H2SO4), the two will react to form an ester (plus H2O). This process is called esterification. Each ester has its own unique odor, and with a discriminating nose, one can use this fact to help identify them. http://www.chemguide.co.uk/physical/catalysis/esterify.html great link shows how the esters are made. Example of the reaction: Esterification reaction are both slow and reversable. The equation between an organic acid (-COOH) and an alcohol (-OH) where R and R’ can be the same or different is written below. The organic acid drops the OH at the end and the alcohol drops the H. The H and OH bond to make water and the remaining two structures bond to make the ester. Concepts: Work in these terms into your introduction. Esterification reaction, esters, organic acids, alcohols, acid catalyst, olfaction, olfactory epithelium, solubility, protein binding (lock and key model) you work on these terms last year when you worked on “The Smells Lab”. (Bibliography: 3 or more sources MLA format). Keep track of your research! Hypothesis: If (Independent variable) then (dependant variable)and (maybe) because _________________. Assume that your ester is n-pentyl hexanoate (this is just an example and is not one of the possibilities). The first part of the name, n-pentyl, refers to the alcohol needed to make the ester, in this case n-pentyl alcohol (1-pentanol). The second part of the name, hexanoate, refers to the carboxylic acid needed, in this case, hexanoic acid (drop -ate and add -ic acid). Next, use structural formulas to write out the balanced equation for the preparation of the ester. In this example, Procedure: GOGGLES MUST BE WORN AT ALL TIMES! In this lab you will be reacting various organic acids (acetic acid, salicylic acid, butryic acid*) with various alcohols (methyl, ethyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isopentyl, octyl alcohols) You will make five different esters with odors that should be familiar to you. * butryic acid (smells like vomit work in fume hood) Get 3 erlenmeyer flasks, labeled: “1”, “2”, & “3” Erlenmeyer flask #1: Add 10 drops of ethanoic acid (acetic acid), 10 drops of isopropanol (isoprpyl alcohol), and 2 drops of H2SO4. Erlenmeyer flask #2: Add 1 scoop of 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid (salicylic acid), 15 drops of methanol, and 2 drops of H2SO4. Erlenmeyer flask #3: Add 10 drops of acetic acid, 10 drops of ethanol, and 2 drops of H2SO4. Mix the content of each erlenmeyer flask by the knocking method. Clamp the erlenmeyer flask and lower into the warm water bath for approximately 1 minute. Remove (carefully!) the erlenmeyer flask from the hot water and note the smell of each ester by wafting the vapors towards your nose. Repeat the procedure for Erlenmeyer flask 2&3 A forth reaction can be done and the choice is your as to what ester you would like to make. To name of your ester you must first determine what alcohol and what carboxylic acid will be needed to prepare that ester. To do this you must know how esters are named. Read the references using an on-line source. Data/Data Analysis Table: Odor Reactants Organic Acid + water Example Pentanoic acid + + (n-butyl alcohol ) 1-butanol + Test Tube #1: Alcohol Products (name of ester) IUPAC name of ester butyl pentanoate + water + ______________ acid + __________alcohol Diagram the structural formulas for all the reactants and products + water Test Tube #2 Test Tube #3 _______________ acid + __________ alcohol + water Diagram the structural formulas for all the reactants and products _______________ acid + __________ alcohol + water Diagram the structural formulas for all the reactants and products Conclusion: Aside from the normal requirements given in your lab report writing standards relate 2 of the major themes of chemistry and real-world applications to the results of your experiment. Questions: Answer these questions after you have completed the requirements for the lab. 1. Why do you think you were instructed to use an electric hot plate to heat the water instead of a Bunsen burner? 2. Why do you think you were instructed to waft the odors instead of sniffing them directly? 3. What role did the H2SO4 play? How does it affect the esterification reaction? 4. Why did you use warm water instead of boiling hot water? 5. Explain a) How we are able to smell certain smells in the first place (what goes on in the nose and the brain). Name: Systematic/IUPAC name Ethanoic acid Structural Formula Common name or acetic acid or 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid Butanoic acid Systematic/IUPAC name or salicylic acid Butryic acid or Common name Methanol or Methyl alcohol Systematic/IUPAC name Common name Ethanol or Systematic/IUPAC name Isopropanol Systematic/IUPAC name n-butanol or Systematic/IUPAC name Ethyl alcohol Common name or Isopropyl alcohol Common name or n-butyl alcohol Common name Isopentyl alcohol (amyl alcohol) Isopentanol or Isopentyl alcohol Systematic/IUPAC name Common name n-octanol or Systematic/IUPAC name Ester odor n-octyl alcohol Common name Alcohol Acid Ester Name Water ? Banana Orange Wintergreen Raspberry Pineapple ** Isopentyl alcohol Octyl alcohol Methyl alcohol Isobutyl alcohol Ethyl alcohol Pear Rum Apple ** n-Propyl alcohol Isobutyl alcohol Methyl alcohol Pear-like Benzyl alcohol Perfume Isopropyl alcohol ** Work in the fume hood Acetic acid Acetic acid Salicylic acid Formic acid Butyric acid (smells like vomit) Acetic acid Propionic acid Butyric acid (smells like vomit) Acetic acid Acetic acid Water Water Water Water Water Water Water Water Water Water