Earth Science Chapter 9 Study Guide
advertisement

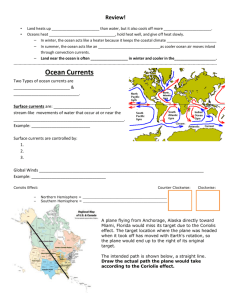
Earth Science Chapter 9 Study Guide Name: _____________________ Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The average, year-after-year conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds, and cloud in an area are known as its a. climate. b. weather. c. global warming. d. seasons. 2. The farther you live from an ocean, the more likely your climate will be a a. marine climate. b. tropical climate. c. continental climate. d. subtropical climate. 3. The climate zones lying between 23.5° and 66.5° north and south latitude are called the a. temperate zones. b. polar zones. c. tropical zones. d. subtropical zones. 4. The climate on the leeward side of a mountain differs from that on the windward side mostly in a. the strength of the winds. b. the direction of the winds. c. the angle of sunlight. d. the amount of rainfall. 5. Sea and land breezes over a large region that change direction with the season are called a. savannas. b. prevailing westerlies. c. monsoons. d. doldrum winds. 6. Summers are caused by a. a combination of longer days and more direct rays from the sun. b. less direct rays from the sun. c. longer days and longer nights. d. Earth in its orbit moving closer to the sun. 7. The seasons are caused by a. Earth’s varying distance from the sun. b. Earth’s changing rate of rotation. c. the tilt of Earth’s axis as Earth revolves around the sun. d. shifting climates on Earth’s surface. 8. The sun’s rays are least direct a. near the poles. b. near the equator. c. at high altitudes. d. far from the ocean. 9. Near the end of both March and September, a. spring begins in both hemispheres. b. the sun’s rays strike Earth with the same intensity everywhere. c. Earth’s axis is no longer pointing at the North Star. d. neither end of Earth’s axis is tilted toward the sun. 10. A large stream of moving water that flows through the oceans is called a(n) a. current. b. tsunami. c. tide. d. undertow. 11. In the Northern Hemisphere, currents curve to the right because of the a. longshore drift. b. density. c. Coriolis effect. d. moon’s gravity. 12. Which of the following is true of El Niño? a. Scientists fully understand the conditions that create El Niño. b. El Niño affects only the ocean, not the land. c. El Niño can cause severe weather conditions around the world. d. El Niño usually occurs twice per year. 13. What causes cold, deep currents to form in the oceans near the poles? a. sinking of dense, cold water with high salinity b. the Coriolis force c. movement of a large mass of warm water across the Pacific d. sinking of cold, freshwater from melting icebergs 14. Deep currents are caused mostly by a. surface winds. b. differences in density. c. the Coriolis effect. d. upwelling. 15. Which of the following types of current typically carries cold, dense water from the poles toward the equator? a. surface currents b. longshore currents c. deep currents d. rip currents 16. The movement of cold, deep ocean water to replace warm water at the surface is called a. upwelling. b. a surface current. c. the Coriolis effect. d. El Niño. 17. Climates are classified according to two major factors: a. elevation and precipitation. b. latitude and temperature. c. elevation and latitude. d. precipitation and temperature. 18. In addition to temperature and precipitation, Köppen’s climate system classified climates by a region’s a. microclimates. b. vegetation. c. seasonal winds. d. air masses. 19. The Great Plains east of the Rocky Mountains have a(n) a. temperate marine climate. b. arid climate. c. semiarid climate. d. humid continental climate. 20. The three kinds of temperate marine climates all have a. severe winters. b. mild winters. c. rainy summers. d. little rainfall and high temperatures. 21. A tropical wet climate exists in the United States only in a. Oregon and Washington. b. Florida. c. Hawaii. d. California. 22. Regions that receive less than 25 centimeters of rain annually are called a. tundras. b. savannas. c. deserts. d. steppes. 23. A temperate continental climate with short cool summers and long, bitterly cold winters is the a. polar climate. b. subarctic climate. c. humid continental climate. d. tundra climate. 24. Permafrost and mosses, lichens, and wildflowers are common in the a. tundra climate. b. subtropical climate. c. temperate climate. d. ice cap climate. 25. Over the past 200 years, the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has a. decreased slightly. b. increased until recently, and then decreased. c. increased steadily. d. stayed about the same. 26. Increased carbon dioxide may cause global warming by a. allowing more sunlight into the atmosphere. b. reflecting more sunlight from clouds. c. reducing the amount of oxygen in the air. d. trapping more heat in the atmosphere. 27. Earth’s ozone layer a. has been thickening over the past several years. b. filters harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. c. exists only over Antarctica. d. traps carbon dioxide in the stratosphere. 28. Chlorine atoms in the stratosphere a. break down ozone into oxygen atoms. b. increase the amount of ozone. c. combine with oxygen to form poisonous gases. d. prevent light from passing through the ozone layer. 29. Scientists predict that banning the use of chlorofluorocarbons will a. have no effect on the ozone layer. b. gradually restore the ozone layer. c. increase ultraviolet light reaching Earth. d. increase the rate of ozone depletion. 30. Distinct vegetation can help scientists a. classify a climate. b. determine a temperature zone. c. assign a season. d. predict an El Niño. Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 31. Factors that affect an area’s temperature are prevailing winds and mountains. _________________________ 32. Oceans make the temperatures of nearby land more extreme. _________________________ 33. In winter in the Southern Hemisphere, the south end of Earth’s axis is tilted away from the sun. _________________________ 34. Winds are the main cause of deep currents in the ocean. _________________________ 35. In general, surface currents that flow from the tropics toward the poles carry warm water. _________________________ 36. Temperate continental climates have cold winters. _________________________ 37. An arid or semiarid climate occurs where precipitation is greater than potential evaporation. _________________________ 38. Over the last 120 years, the average temperature of the troposphere has decreased. _________________________ 39. Global warming is the trapping of energy from the sun by Earth’s atmosphere. _________________________ 40. As the amount of ozone in the atmosphere decreased, the amount of ultraviolet radiation that reached Earth increased. _________________________ Completion Complete each statement. 41. ____________________ temperature zones occur between tropical and polar zones. 42. The land on the ____________________ side of a mountain range is in a rain shadow. 43. Because of its high ____________________, Mount Kilimanjaro has a cool climate all year. 44. Streams of water called ocean ____________________ move warm or cold water, warming or cooling the nearby land. 45. The ____________________ Hemisphere receives fewer direct rays from the sun in January than in July. 46. Because Earth’s axis is ____________________, the hemispheres receive different amounts of solar energy at different times. 47. A cool surface current in the Pacific Ocean that affects the climate of California is the ____________________. 48. The abnormal climate event called ____________________ occurs in the Pacific Ocean every 2 to 7 years. 49. Deep currents are caused by differences in the ____________________ of ocean water. 50. El Niño prevents ____________________ along the Pacific coast of South America. 51. Without the motion caused by upwelling, the surface waters of the open ocean would be very scarce in ____________________. 52. Tropical grasslands called _________________________ are found in the tropical wet-and-dry climate region. 53. Trees do not grow in the ____________________ climate region, which has short, cool summers, bitterly cold winters, and permafrost. 54. A cool type of climate called ____________________ is found at the tops of mountains and is surrounded by other climate regions. 55. ____________________ are forests in which plenty of rain falls all year. 56. _________________________ climates are found along the coasts of continents in the temperate zone. 57. Tundra and ice cap climates are examples of ____________________ climates. 58. People add the greenhouse gas _________________________ to the atmosphere by burning wood, oil, natural gas, and coal. 59. The gradual increase in the temperature of the atmosphere is known as _________________________. 60. Humans have damaged the ozone layer by using _________________________ in refrigerators and spray cans.