SYLLABUS AP CHEMISTRY 11_12
advertisement

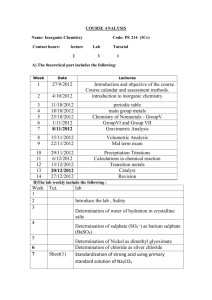
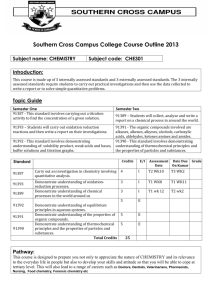
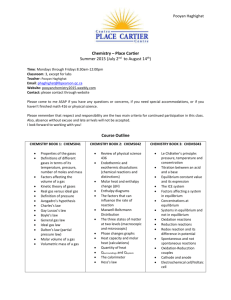
SYLLABUS for AP CHEMISTRY 2011-2012 Class Prerequisites The prerequisites for Advanced Placement Chemistry are: Conceptual Physics, 1 st year Chemistry, and at least 2nd year Algebra. Additionally, students must be highly motivated and have the recommendation of their previous science teachers and the Office of College Counseling. All students are counseled on the course requirements prior to the start of the course to ensure they have a full understanding of the time and effort that will be required throughout the year. A work packet is provided to each student for their use during the summer prior to the course. Course Overview The Advanced Placement Chemistry course is a second year chemistry program open to Junior and Senior students who meet the prerequisites. Many of the topics required of an Advanced Placement Chemistry course have been covered in the first year course. Those topics will be reviewed and discussed in greater depth. The time allotted weekly for this course is four periods of 45 minutes and one evening lab period of 120 minutes for a total of 300 minutes per week. With 300 minutes available per week, the course is heavily lab based (120 minutes/week). The College Board’s twenty two recommended chemistry labs are used during this year-long course. Additional hands-on activities are added. The lab facility in the Clay Center has state of the art equipment and complies with all appropriate safety standards. Students are required to keep a Chemistry notebook and a separate Chemistry Lab book. Instructional materials All AP Chemistry students are provided with the following: Chemistry: The Central Science, 12th edition Authors: Bursten, Brown, and LeMay © 2012 AP Test Prep Series: AP Chemistry Author: Waterman © 2012 Various computer simulations; tutorials; video programs; relevant news articles; and Chemical Journals Course Outline Students will be prepared: to be independent and critical thinkers, to make relevant observations, collect data, form conclusions, and to communicate with others in written form. Instructional strategies will include: problem sets; AP practice tests; project assignments; class discussions of current issues (emphasizing critical thinking skills); lecture/demonstrations; research papers; and laboratory. activities. Unit 1: Calculations and Uncertainty 0.5 weeks Dimensional analysis, uncertainty, significant figures Experiments Safety in the lab. Refresh lab techniques and proper use of equipment such as the balance, etc. Unit 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1.0 week Review of formula writing, oxidation states, inorganic and organic nomenclature, etc. Experiments Spectral analysis (AP Lab #17) Chromatography (AP Lab #18) Synthesis, purification, and analysis of an organic compound (AP Lab #22) Unit 3: Stoichiometry 2.0 weeks Mole, atomic mass, molecular formula, balancing equations, limiters, empirical formulas, percent composition, percent yield, and solution stoichiometry. Experiments Determination of the formula of a compound (AP Lab #1) Determination of the percent of water in a hydrate (AP Lab #2) Determination of molar mass by vapor density (AP Lab #3) Unit 4: Gases 2.0 weeks Ideal gas law, van der Waal’s equation, Avogadro’s Law, STP, Dalton’s Law, Graham’s Laws, Kinetic theory of gases, etc. Experiments Determination of the molar volume of a gas (AP Lab #5) Determination of mass and mole relationship in a chemical reaction ( AP Lab #9) Unit 5: Thermochemistry 2.0 weeks Enthalpy, thermochemical equations, heats of formation, bond energies, heats of reactions, etc. Experiments Determination of enthalpy change associated with a reaction (AP Lab #13) Calorimetry Unit 6: Atomic Structure and Periodicity 2.0 weeks Atomic spectra, Bohr atom, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals, electron configurations, periodic table, trends in the periodic table in terms of physical and chemical properties. Experiments Flame tests Borax bead tests Page two Unit 7: Chemical Bonding 3.0 weeks Lewis structures, ionic bonding, character of bonds, covalent model, octet rule and exceptions, resonance, VSEPR model, and hybridization. Experiment VSEPR model building Unit 8: Liquids and solids 1.5 weeks Dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, London forces, liquid state, types of solids, metallic bonding, network solids, vapor pressure, change of state, phase diagrams, and specific heat. Experiment Crystal growing Unit 9: Properties of Solutions 2.0 weeks Electrolytes and nonelectrolytes, molarity, mole fraction, colligative properties, Raoult’s Law, Henry’s Law, freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure. Experiments Determination of molar mass by freezing point depression (AP Lab #4) Standardization of a solution using a primary standard (AP Lab #6) Unit 10: Chemical Thermodynamics 2.5 weeks Gibbs free energy equation, laws of thermodynamics, enthalpy, entropy, free energy, energy and work, exothermic and endothermic reactions, and state functions. Experiment Analytical gravimetric determination (AP Lab #16) Unit 11: Chemical Kinetics 2.5 weeks Reaction kinetics, rate law expressions, order of reactions, rate constant, half life, activation energy, catalysis, and reaction mechanism. Experiment Determination of the rate of a reaction and its order (AP Lab #12) Unit 12: Chemical Equilibrium 2.0 weeks Laws of mass action, equilibrium expressions, calculations of K and equilibrium concentrations, Le Chatelier’s principle, and how equilibrium is shifted by temperature, concentration, and pressure etc. Experiment Determination of the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction (AP Lab #10) Synthesis of a coordination compound and its chemical analysis (AP Lab 15) Unit 13: Acids and Bases 2.5 weeks pH, Ka and Kb expressions, titration, degree of ionization, Kw expressions, indicators, equivalence points, Arrhenius, Bronsted Lowry and Lewis acid theories, and salt hydrolysis. Experiments Determination of concentration by acid base titration, including a weak acid or a weak base (AP Lab #7) Determination of concentration by oxidation reduction titration (AP Lab #8) Determination of appropriate indicators for various acid base titrations; pH determination (AP Lab #11) Preparation and properties of buffer solutions (AP Lab #19) Unit 14: Electrochemistry 1.5 weeks Oxidation and reduction half cells and equations; electrochemical cells, standard voltages, standard voltages from a table, Nernst equation, Faraday’s laws, writing redox equations, and balancing equations in acid base solutions. Experiments Determination of electrochemical series (AP Lab # 20) Measurements using electrochemical cells and electroplating (AP Lab #21) Separation and qualitative analysis of cations and anions (AP Lab #14) Unit 15: Nuclear Chemistry and Organic Chemistry 1.0 week Nuclear equations, half lives, nuclear particle emissions, fission and fusion, and nuclear reactors. Experiment Measurement of half life AP Exam Review 3.0-4.0 weeks Practice AP exams and problem solving skills; discuss/recap exam taking strategies