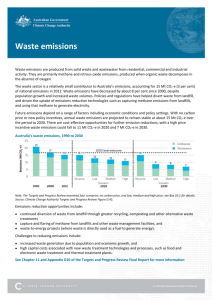
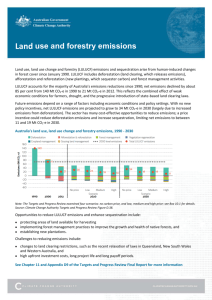
Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial
advertisement

EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 I, Greg Hunt, Minister for the Environment, make the following determination. Dated 2014 Greg Hunt [DRAFT ONLY—NOT FOR SIGNATURE] Minister for the Environment EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Contents Part 1—Preliminary 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 Name ........................................................................................................................... 1 Commencement .......................................................................................................... 1 Authority ..................................................................................................................... 1 Duration ...................................................................................................................... 1 Definitions .................................................................................................................. 1 Meaning of implementation ........................................................................................ 3 Meaning of relevant energy ........................................................................................ 4 Part 2—Industrial fuel and energy efficiency project 8 5 Industrial fuel and energy efficiency project ............................................................... 5 Part 3—Project requirements 9 10 11 12 6 Operation of this Part .................................................................................................. 6 Declaration requirements ............................................................................................ 6 Implementations must be as described in application ................................................. 6 No limiting output or services provided by equipment ............................................... 6 Part 4—Net abatement amount 7 Division 1—Preliminary 13 14 15 7 Operation of this Part .................................................................................................. 7 Overview of gases accounted for in abatement calculations ....................................... 7 References to factors and parameters from external sources ....................................... 7 Division 2—Method for calculating net abatement amount 16 17 8 Carbon dioxide equivalent net abatement amount ...................................................... 8 Using a sub-method .................................................................................................... 8 Division 3—Requirements for emissions models 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 10 General requirements .................................................................................................10 Minimum statistical requirements ..............................................................................10 Requirements for baseline emissions models .............................................................11 Requirements for operating emissions models ...........................................................12 Baseline measurement period and operating measurement period .............................13 Independent variables ................................................................................................13 Site constants .............................................................................................................14 Interactive effects .......................................................................................................14 Accuracy factor ..........................................................................................................15 Decay factor ...............................................................................................................18 Division 4—Implementation using measured emissions—sub-method 1 28 29 30 31 32 20 Emissions abated........................................................................................................20 Interactive effects .......................................................................................................21 Modelled baseline emissions .....................................................................................21 Baseline emissions model ..........................................................................................22 Measured emissions ...................................................................................................22 Division 5—Implementation using operating emissions model—sub-method 2 33 34 35 36 23 Emissions abated........................................................................................................23 Interactive effects .......................................................................................................24 Modelled baseline emissions .....................................................................................24 Baseline emissions model ..........................................................................................25 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT i EXPOSURE DRAFT 37 38 Modelled operating emissions....................................................................................25 Operating emissions model ........................................................................................25 Division 6—Sample using measured emissions—sub-method 3 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 27 Emissions abated by population .................................................................................27 Emissions abated by sample ......................................................................................27 Emissions abated by implementation .........................................................................27 Interactive effects .......................................................................................................29 Modelled baseline emissions .....................................................................................29 Baseline emissions model ..........................................................................................30 Measured emissions ...................................................................................................30 Division 7—Sample using operating emissions model—sub-method 4 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 31 Emissions abated by population .................................................................................31 Emissions abated by sample ......................................................................................31 Emissions abated by implementation .........................................................................31 Interactive effects .......................................................................................................33 Modelled baseline emissions .....................................................................................33 Baseline emissions model ..........................................................................................34 Modelled operating emissions....................................................................................34 Operating emissions model ........................................................................................34 Division 8—Measured emissions 54 36 Measured emissions ...................................................................................................36 Part 5—Reporting, record-keeping and monitoring requirements 38 Division 1—Offsets report requirements 55 56 38 Operation of this Division ..........................................................................................38 Offsets report requirements ........................................................................................38 Division 2—Record-keeping requirements 57 58 39 Operation of this Division ..........................................................................................39 Record-keeping requirements ....................................................................................39 Division 3—Monitoring requirements 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 40 Operation of this Division ..........................................................................................40 Monitoring requirements—general ............................................................................40 Monitoring requirements—sub-method 1 ..................................................................40 Monitoring requirements—sub-method 2 ..................................................................40 Monitoring requirements—sub-method 3 ..................................................................41 Monitoring requirements—sub-method 4 ..................................................................41 Monitoring requirements—independent variables and site constants ........................42 Schedule 1—Monitored parameters 1 ii 43 Monitored parameters ................................................................................................43 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Preliminary Part 1 Section 1 Part 1—Preliminary 1 Name This determination is the Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014. 2 Commencement This determination commences on the day after it is registered. 3 Authority This determination is made under subsection 106(1) of the Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Act 2011. 4 Duration This determination remains in force for the period that: (a) begins when this determination commences; and (b) ends on the day before this determination would otherwise be repealed under subsection 50(1) of the Legislative Instruments Act 2003. 5 Definitions In this determination: accuracy factor has the meaning given by section 26. Act means the Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Act 2011. baseline emissions model means a baseline emissions model used for the purposes of Part 4. baseline measurement period has the meaning given by subsection 22(1). completed: an implementation is completed when the equipment relating to the implementation has begun operating under normal conditions. decay coefficient has the meaning given by subsection 27(2). decay coefficient year has the meaning given by subsection 27(2). decay factor has the meaning given by subsection 27(1). dependent variable, for an implementation, means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for the implementation. Note: Total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for an implementation is worked out using equation 35. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 1 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 1 Preliminary Section 5 direct emission of greenhouse gas, in relation to a site, means the release of greenhouse gas into the atmosphere as a direct result of fuel combustion at the site. effective range, for an emissions model, has the meaning given by subsection 17(7). emissions model means a baseline emissions model or an operating emissions model. IFEE implementation descriptions document means the document entitled “IFEE implementation descriptions”, published by the Regulator and as in force from time to time. implementation has the meaning given by section 6. independent variable has the meaning given by section 23. indirect emission of greenhouse gas, in relation to a site, means the release of greenhouse gas into the atmosphere as a direct result of fuel combustion at another site to generate electricity for consumption at the site. industrial fuel and energy efficiency project has the meaning given by section 8. interactive effects has the meaning given by section 25. measurement time interval has the meaning given by subsection 17(6). monitoring requirements means the requirements set out in Division 3 of Part 5. National Energy Retail Rules means the National Energy Retail Rules, as in force from time to time, made under the National Energy Retail Law set out in the Schedule to the National Energy Retail Law (South Australia) Act 2011 (SA). NGA Factors document means the document entitled “National Greenhouse Accounts Factors”, published by the Department and as in force from time to time. NGER (Measurement) Determination means the National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (Measurement) Determination 2008. NMI document M6 means the document entitled “NMI M 6-1 Electricity Meters”, published by the National Measurement Institute and as in force from time to time. NMI document R137 means the document entitled “NMI R 137 Gas Meters”, published by the National Measurement Institute and as in force from time to time. normal value, for a site constant, has the meaning given by subsection 24(2). operating emissions model means an operating emissions model used for the purposes of Part 4. operating measurement period has the meaning given by subsection 22(2). 2 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Preliminary Part 1 Section 6 population in a project means a group of implementations in the project consisting of the same type of activity or group of related activities. random selection method means a selection method under which each implementation in a population has the same chance as any other implementation in the population of being selected for the sample of the population, and includes a restricted random selection method. Note: An example of a restricted random selection method is a method where the population is first stratified according to a variable that influences energy consumption. relative precision: (a) of the emissions level predicted by an emissions model—has the meaning given by subsection 19(2); or (b) of the emissions abated by an implementation—has the meaning given by subsection 26(2). relevant energy has the meaning given by section 7. site means: (a) a physical location; or (b) a series of physical locations in close proximity to one another that are under common control. site constants has the meaning given by section 24. sub-method means one of the sub-methods set out in Part 4. 6 Meaning of implementation (1) An activity or group of activities undertaken at a site is an implementation for an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project if the activities consist of the following: (a) modifying existing equipment; (b) changing the way existing equipment is used; (c) replacing existing equipment; (d) installing equipment as part of replacing, modifying or augmenting existing equipment; (e) removing existing equipment; (f) changing the energy sources used by existing equipment; (g) changing the mix of energy sources used by existing equipment. (2) However, the following activities are not an implementation or part of an implementation: (a) the installation of equipment other than in circumstances referred to in paragraph (1)(d); (b) the installation of a type of equipment in relation to which a renewable energy certificate can be created under the Renewable Energy (Electricity) Act 2000. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 3 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 1 Preliminary Section 7 7 Meaning of relevant energy (1) Relevant energy for an implementation in a time period means fuel or electricity consumed by the following equipment in the time period: (a) existing equipment to which the implementation relates; (b) equipment installed as part of the implementation; (c) if the consumption of fuel or electricity by other equipment at the site changes as a result of the implementation in the time period—the other equipment; (d) if the consumption of fuel or electricity by equipment referred to in paragraphs (a) to (c) is not measured separately to the consumption of fuel or electricity by other equipment (the co-metered equipment) in the time period—the co-metered equipment. (2) However, fuel or electricity consumed in the time period is only relevant energy for an implementation to the extent that: (a) the change is likely to be material; and (b) the equipment is at the same site as the equipment to which the implementation relates; and (c) the project proponent has not treated the change in consumption in the time period as an interactive effect for the implementation in the time period. (3) A change in the consumption of energy is material in relation to an implementation in a reporting period if the change in emissions related to that consumption is 5% or greater of the emissions abated by the implementation. Note: 4 The emissions abated by an implementation is calculated using the sub-methods in Part 4. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Industrial fuel and energy efficiency project Part 2 Section 8 Part 2—Industrial fuel and energy efficiency project 8 Industrial fuel and energy efficiency project (1) For paragraph 106(1)(a) of the Act, this determination applies to an offsets project that aims to reduce the following in relation to one or more sites: (a) direct emissions of greenhouse gas from equipment used to generate: (i) electricity; or (ii) useful physical work; or (iii) cooling, heat or steam for use at the site or another site; (b) indirect emissions of greenhouse gas from equipment that consumes electricity. Note: Examples of useful physical work are the following: (a) running a diesel engine to create shaft power; (b) storing energy chemically; (c) pumping water to a higher location; (d) compressing gasses. (2) A project covered by subsection (1) is an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 5 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 3 Project requirements Section 9 Part 3—Project requirements 9 Operation of this Part For paragraph 106(1)(b) of the Act, this Part sets out requirements that must be met for an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project to be an eligible offsets project. 10 Declaration requirements (1) For an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project to be an eligible offsets project at the time the project is declared to be an eligible offsets project: (a) the project must involve undertaking one or more implementations at one or more sites that are in the project; and (b) each implementation must aim to reduce direct or indirect emissions (or both) in relation to the site of the implementation; and (c) the reduction in emissions as a result of an implementation must be capable of being calculated under Part 4; and (d) the application made under section 22 of the Act in relation to the project must include a description of: (i) the implementations, or type of implementations, in the project; and (ii) the sites, or type of sites, for those implementations; and (iii) the sub-methods to be used for those implementations. (2) If an implementation or type of implementation is covered by a description in the IFEE implementation descriptions document, then the project proponent must use the description in that document to satisfy subparagraph (1)(d)(i) for the implementation or type of implementation. 11 Implementations must be as described in application The implementations undertaken in the project must be as described in the application, or as otherwise approved by the Regulator. 12 No limiting output or services provided by equipment The project must not involve undertaking an activity that limits the output of, or reduces the service levels provided by, equipment at a site for the purposes of reducing electricity or fuel consumption at the site unless: (a) the activity reduces the emissions intensity of equipment at the site; or (b) the activity reduces the emissions intensity of the site overall. Note: 6 An example of an activity that must not be included in the project is removing lighting equipment from a site to the extent that lighting levels at the site are reduced to below Australian standards. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Preliminary Division 1 Section 13 Part 4—Net abatement amount Division 1—Preliminary 13 Operation of this Part For paragraph 106(1)(c) of the Act, this Part specifies the method for working out the carbon dioxide equivalent net abatement amount for a reporting period for an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project that is an eligible offsets project. 14 Overview of gases accounted for in abatement calculations The following table provides an overview of the greenhouse gases and emissions sources that are relevant to working out the carbon dioxide equivalent net abatement amount for an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project. Greenhouse gases and emissions sources Item Relevant emissions calculation Emissions source Greenhouse gas 1 Baseline emissions for an implementation or sample of a population Direct emissions Carbon dioxide (CO2) Baseline emissions for an implementation or sample of a population Indirect emissions Operating emissions or measured emissions for an implementation or sample of a population Direct emissions Operating emissions or measured emissions for an implementation or sample of a population Indirect emissions 2 3 4 Methane (CH4) Nitrous oxide (N2O) Carbon dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Nitrous oxide (N2O) Carbon dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Nitrous oxide (N2O) Carbon dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Nitrous oxide (N2O) 15 References to factors and parameters from external sources (1) If a calculation in this Part includes a factor or parameter that is defined by reference to another instrument or writing, the factor or parameter to be used for a reporting period is the factor or parameter referred to in the instrument or writing as in force on the earlier of the following days: (a) the day the offsets report for the reporting period is given to the Regulator; (b) the day that report is required to be given to the Regulator. (2) Subsection (1) does not apply to a parameter that is required to be worked out in accordance with the monitoring requirements. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 7 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 2 Method for calculating net abatement amount Section 16 Division 2—Method for calculating net abatement amount 16 Carbon dioxide equivalent net abatement amount The carbon dioxide equivalent net abatement amount for a reporting period (Anet), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 1): A net = A + h h A p p where: Anet means the carbon dioxide equivalent net abatement amount for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Ah means the emissions abated by implementation (h) in the project for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using sub-methods 1 and 2. Ap means the emissions abated by population (p) in the project for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using sub-methods 3 and 4. Note: The project proponent may choose to work out the carbon dioxide equivalent net abatement amount through working out emissions abated for an individual implementation or for a population by calculating emissions abated from a sample of the population. If the project proponent chooses to work out emissions abated by individual implementations only or by samples of populations only, then respectively, Ap or Ah will have a value of zero. 17 Using a sub-method (1) For each implementation that is in the project the project proponent must choose one sub-method to work out the emissions abated by the implementation. (2) Subject to subsection (3), the sub-method chosen to work out the emissions abated by the implementation in the first reporting period for the project must be used for all subsequent reporting periods. (3) If sub-method 2 has been used to work out the emissions abated by the implementation in a reporting period, the project proponent may use sub-method 1 for all subsequent reporting periods. Sample and population (4) If the project proponent chooses sub-method 3 or 4 to work out the emissions abated by a population in the project, the project proponent must choose a sample of implementations within that population. (5) The sample must be representative of the population and chosen by a random selection method. Measurement time intervals (6) A measurement time interval for an implementation, or sample of a population, means a time period during: 8 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Method for calculating net abatement amount Division 2 Section 17 (a) a baseline measurement period or operating measurement period for the implementation or sample of the population; or (b) a reporting period for the project; in which: (c) site constants are at their normal values; and (d) measured values for all independent variables: (i) fall within the effective range of the independent variable; or (ii) fall outside the effective range of the independent variable by an amount which is equal to or less than 5% of the minimum value of the effective range; or (iii) fall outside the effective range of the independent variable by an amount which is equal to or less than 5% of the maximum value of the effective range. (7) The effective range of an independent variable for an emissions model is the range of measured values for the independent variable on which the emissions model was based. (8) In using a sub-method to work out the emissions abated by an implementation, or sample of a population, the same measurement time interval must be used for every parameter throughout the baseline measurement period, operating measurement period and reporting period for the sub-method. (9) For the purposes of using the same measurement time interval to work out the emissions abated by the implementation, or the sample of the population: (a) the longest measurement time interval that a parameter is measured or observed in must be the same as the measurement time interval for the sub-method; and (b) if a parameter is measured or observed in a measurement time interval that is shorter than the measurement time interval for the sub-method—those shorter measurement time intervals must be aggregated to form a measurement time interval for the parameter that is the same as the measurement time interval for the sub-method. Note: This means that a measurement time interval for a parameter cannot be divided into 2 or more smaller measurement time intervals. However, smaller measurement time intervals may be aggregated so that they are the same as the measurement time interval for the sub-method. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 9 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 3 Requirements for emissions models Section 18 Division 3—Requirements for emissions models 18 General requirements (1) This section sets out the requirements for using a baseline emissions model or an operating emissions model for the purposes of this Part. (2) An emissions model for an implementation must be developed using regression analysis to relate independent variables to the dependent variable for the implementation. (3) An emissions model for a sample of a population must be developed using regression analysis to relate independent variables to the dependent variables for the implementations in the sample. (4) An emissions model for an implementation, or a sample of a population, must include the following as independent variables or site constants: (a) the output of equipment at the site of the implementation or sites of the implementations in the sample; (b) the service levels provided by equipment at the site of the implementation or sites of the implementations in the sample. (5) An emissions model for an implementation, or a sample of a population, must include the effects of variable input or output quality as independent variables or site constants unless the emissions associated with changes in input or output quality are interactive effects for the implementation or an implementation in the sample. 19 Minimum statistical requirements Minimum statistical requirements (1) An emissions model for an implementation or a sample of a population must, at a minimum, meet the following statistical requirements: (a) each independent variable coefficient must have a t-statistic that is greater than the value for the t-distribution at the 97.5% single-sided confidence level for the number of degrees of freedom in the regression (equivalent to 95% confidence in a two-sided distribution); (b) the lesser of the coefficient of determination (R2) and the adjusted coefficient of determination (adjusted R2) is greater than 0.75; (c) the relative precision of the emissions level predicted by the emissions model for the baseline measurement period or the operating measurement period (as the case may be) for the model calculated at the 95% confidence level is within 100%; (d) the percentage of time intervals in the measurement period, that would otherwise be measurement time intervals if the value of site constants in the time intervals were at their normal value, is less than 20%. 10 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Requirements for emissions models Division 3 Section 20 Relative precision (2) The relative precision of the emissions level predicted by the emissions model for the baseline measurement period or the operating measurement period (as the case may be) for the model (RPE,h,mod) is worked out using the formula (equation 2): RPE,h,mod = t SE E,h Eh where: RPE,h,mod means the relative precision of the emissions level predicted by the emissions model for the baseline measurement period or the operating measurement period (as the case may be) for the model. t means the critical tabulated Student’s T value for the appropriate number of degrees of freedom at the 95% confidence level. SEE,h means the standard error of the emissions model for the baseline measurement period or the operating measurement period (as the case may be) for the model. Eh means: (a) for sub-method 1—the emissions level for implementation (h) predicted by the emissions model for the baseline measurement period; and (b) for sub-method 2—the emissions level for implementation (h) predicted by the emissions model: (i) for a baseline emissions model—for the baseline measurement period; and (ii) for an operating emissions model—for the operating measurement period; and (c) for sub-method 3—the average emissions level for the implementations in the sample of the population predicted by the emissions model for the baseline measurement period; and (d) for sub-method 4—the average emissions level for the implementations in the sample of the population predicted by the emissions model: (i) for a baseline emissions model—for the baseline measurement period; and (ii) for an operating emissions model—for the operating measurement period. 20 Requirements for baseline emissions models (1) A baseline emissions model for an implementation or a sample of a population must be based on measurements of the consumption of relevant energy and independent variables: (a) taken over the baseline measurement period for the model; and (b) made in accordance with the monitoring requirements. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 11 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 3 Requirements for emissions models Section 21 (2) If a site constant is an independent variable for a baseline emissions model used for the purposes of sub-method 3 or 4, the baseline emissions model must be also be based on measurements of the site constant: (a) taken over the baseline measurement period for the model; and (b) made in accordance with the monitoring requirements. (3) The value of the dependent variable for an implementation for a measurement time interval that a baseline emissions model is based on must equal the value of the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for the implementation for the measurement time interval. Note: Total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for an implementation is worked out using equation 35. (4) Estimates of baseline emissions for an implementation worked out using a baseline emissions model must reasonably reflect emissions that would have occurred if the implementation had not been undertaken. (5) A baseline emissions model must be worked out for: (a) each implementation covered by sub-method 1 or 2; and (b) the sample of each population covered by sub-method 3 or 4. 21 Requirements for operating emissions models (1) An operating emissions model for an implementation or a sample of a population must be based on measurements of the consumption of relevant energy and independent variables: (a) taken over the operating measurement period for the model; and (b) made in accordance with the monitoring requirements. (2) The value of the dependent variable for an implementation for a measurement time interval that an operating emissions model is based on must equal the value of the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for the implementation for the measurement time interval. Note: Total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for an implementation is worked out using equation 35. (3) Estimates of operating emissions for an implementation worked out using an operating emissions model must reasonably reflect actual emissions from undertaking the implementation. (4) An operating emissions model must be worked out for: (a) each implementation covered by sub-method 2; and (b) the sample of each population covered by sub-method 4. (5) The operating emissions model for an implementation or a sample of a population used for the purposes of a reporting period may be updated for the purposes of any subsequent reporting period. Note: 12 The updated model will be based on a new operating measurement period. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Requirements for emissions models Division 3 Section 22 22 Baseline measurement period and operating measurement period (1) A baseline emissions model for an implementation or a sample of a population must be based on a measurement period (the baseline measurement period) that: (a) covers at least one full operating cycle for the equipment that relates to the implementation or implementations in the sample; and (b) covers the full range of operating conditions for the equipment likely to exist during the crediting period; and (c) reasonably weights different operating conditions; and (d) accounts for cycles in energy consumption; and (e) is in accordance with the monitoring requirements. (2) An operating emissions model for an implementation or a sample of a population must be based on a measurement period (the operating measurement period) that: (a) covers at least one full operating cycle for the equipment that relates to the implementation or implementations in the sample; and (b) covers the full range of operating conditions for the equipment likely to exist during the crediting period; and (c) reasonably weights different operating conditions; and (d) accounts for cycles in energy consumption; and (e) is in accordance with the monitoring requirements. (3) The project proponent must choose a start date and time and an end date and time for the baseline measurement period and the operating measurement period. (4) The start date for the baseline measurement period must be no earlier than 24 months before: (a) for a baseline emissions model used for the purposes of sub-method 1 or 2—the date the implementation commences; and (b) for a baseline emissions model used for the purposes of sub-method 3 or 4—the first date on which an implementation in the sample commences. (5) The end date for the baseline measurement period must be before: (a) for a baseline emissions model used for the purposes of sub-method 1 or 2—the date the implementation commences; and (b) for a baseline emissions model used for the purposes of sub-method 3 or 4—the first date on which an implementation in the sample commences. (6) The start date for the operating measurement period must be: (a) for an operating emissions model used for the purposes of sub-method 2— a day after the implementation has been completed; and (b) for an operating emissions model used for the purposes of sub-method 4— a day after all the implementations in the sample of the population have been completed. 23 Independent variables (1) A parameter is an independent variable for an implementation if it: Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 13 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 3 Requirements for emissions models Section 24 (a) varies over time or, if the implementation is included in a sample of a population, varies between implementations in the sample; and (b) can be measured or derived from one or more measurements using a mathematical formula without material loss of precision; and (c) causes or explains changes in emissions from the consumption of relevant energy. (2) An independent variable must be independent from any other independent variable used in the emissions model. (3) However, an independent variable may be a linear or non-linear function of itself or another independent variable. (4) A site constant may be an independent variable for the purposes of sub-methods 3 and 4. 24 Site constants (1) A parameter is a site constant for an implementation or sample of a population if: (a) varying the parameter would materially change the consumption of relevant energy for the implementation or an implementation in the sample; and (b) under normal operating conditions at the site of the implementation, or sites of the implementations in the sample, the parameter does not vary. (2) A site constant is at its normal value in a measurement time interval if: (a) for a baseline emissions model—the site constant is within the range observed during the baseline measurement period; and (b) for an operating emissions model—the site constant is within the range observed during the operating measurement period. 25 Interactive effects (1) A material change in the consumption of fuel or electricity at a site is an interactive effect for an implementation in a reporting period if: (a) the consumption of fuel or electricity is not relevant energy for the implementation in the reporting period; and (b) the change in consumption of fuel or electricity in the reporting period occurs as a result of the implementation. Note: The change in consumption may occur at the site of the implementation or a different site. (2) Interactive effects for the implementation must be calculated using an approach for estimating the change in the consumption of fuel or electricity at the site of the implementation that: (a) uses data from the records of the site; and (b) is consistent with an estimation approach that applies to the change in consumption under another methodology determination or, if there is no 14 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Requirements for emissions models Division 3 Section 26 methodology determination that deals with that change, is consistent with one of the following approaches: (i) an estimation approach that applies to changes of that kind under another emissions reduction scheme; (ii) a generally accepted energy efficiency measurement and verification practice that applies to changes of that kind; (iii) a generally accepted engineering methodology, model or formula that applies to changes of that kind; and (c) is consistent with relevant measuring and estimation requirements that apply to changes in consumption of fuel or electricity under the NGER (Measurement) Determination; and (d) results in an estimate that is measurable, capable of being verified and conservative; and (e) is credible and robust. Note 1: An approach applying to a change in consumption for the purposes of paragraph (2)(b) may involve the calculation of baseline and operating energy consumption, the direct calculation of a change in consumption, or a combination of both. Note 2: Energy consumed at a site may come within the definitions of relevant energy and interactive effects for an implementation. For the purposes of calculating emissions abated by the implementation under Part 4, the project proponent may choose to treat energy consumed at the site as relevant energy because the sub-methods in the Part limit the amount of energy that can be included as interactive effects. 26 Accuracy factor Accuracy factor (1) The accuracy factor for implementation (h) for a reporting period (AF) is worked out using the following table. Accuracy factors Item Relative precision of the emissions abated by implementation (h) in the reporting period at 95% confidence level Accuracy factor 1 less than 25% 2 25% to 50% 0.9 3 50% to 75% 0.8 4 75% to 100% 0.6 5 100% to 150% 0.4 6 150% to 200% 0.2 7 greater than 200% 1 0 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 15 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 3 Requirements for emissions models Section 26 Relative precision (2) The relative precision of the emissions abated by implementation (h) in the reporting period (RPA,h) is worked out using the formula (equation 3): RPA,h = t SE A,h Ah where: RPA,h means the emissions abated by implementation (h) in the reporting period. t means the critical tabulated Student’s T value for the appropriate number of degrees of freedom (the number of measurement intervals in the reporting period) at the 95% confidence level. SEA,h means the standard error of the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period, worked out: (a) for sub-methods 1 and 3—using equation 4; and (b) for sub-methods 2 and 4—using equation 5. Ah means the emissions abated by the implementation (h) for the reporting period worked out: (a) for sub-methods 1 and 3—using equation 6; and (b) for sub-methods 2 and 4—using equation 7. Standard error for sub-methods 1 and 3 (3) The standard error of the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period (SEA,h) is worked out using the formula (equation 4): SE A,h = SE b,h 2 + u 2h,i n i h,i where: SEA,h means the standard error of the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period. SEb,h means the standard error of the baseline emissions model for implementation (h). uh,i means the instrument tolerance or uncertainty for measurements of energy type (i) for implementation (h). nh,i means the number of measurements of energy type (i) in the reporting period. Note: Energy type (i) may be electricity or a fuel. Standard error for sub-methods 2 and 4 (4) The standard error of the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period (SEA,h) is worked out using the formula (equation 5): 16 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Requirements for emissions models Division 3 Section 26 SE A,h = SE b,h 2 + SE p,h 2 where: SEA,h means the standard error of the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period. SEb,h means the standard error of the baseline emissions model for implementation (h). SEp,h means the standard error of the operating emissions model for the implementation (h) for the reporting period. Emissions abated—sub-methods 1 and 3 (5) The emissions abated by the implementation (h) for the reporting period (Ah) is worked out using the formula (equation 6): Ah = E b_mod,h - E meas,h + E IN,h where: Ah means the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Eb_mod,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out: (a) for sub-method 1—using equation 11; and (b) for sub-method 3—using equation 24. Note: Eb_mod,h is Eb_mod,p,s,h in sub-method 3. Emeas,h means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out: (a) for sub-method 1—using equation 13; and (b) for sub-method 3—using equation 26. Note: Emeas,h is Emeas,p,s,h in sub-method 3. EIN,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out: (a) for sub-method 1—using equation 10; and (b) for sub-method 3—using equation 23. Note: EIN,h is EIN,p,s,h in sub-method 3. Emissions abated—sub-methods 2 and 4 (6) The emissions abated by the implementation (h) for the reporting period (Ah) is worked out using the formula (equation 7): Ah = E b_mod,h - E p_mod,h + E IN,h Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 17 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 3 Requirements for emissions models Section 27 where: Ah means the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Eb_mod,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out: (a) for sub-method 2—using equation 16; and (b) for sub-method 4—using equation 31. Note: Eb_mod,h is Eb_mod,p,s,h in sub-method 4. Ep_mod,h means the total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out: (a) for sub-method 2—using equation 18; and (b) for sub-method 4—using equation 33. Note: Ep_mod,h is Ep_mod,p,s,h in sub-method 4. EIN,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out: (a) for sub-method 2—using equation 15; and (b) for sub-method 4—using equation 30. Note: EIN,h is EIN,p,s,h in sub-method 4. 27 Decay factor (1) The decay factor for a reporting period (DF) is worked out using the formula (equation 8): DC y n MI,h,y y DF = n MI,h where: DF means the decay factor for a reporting period. DCy means the decay coefficient for decay coefficient year (y). nMI,h,y means the number of measurement time intervals for implementation (h) that occur in year (y). nMI,h means the total number of measurement time intervals in the reporting period. (2) The decay coefficient for a year of operation of an operating emissions model (decay coefficient year) is worked out using the following table (where year 1 begins on the start date of the operating measurement period for the operating emissions model). 18 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Requirements for emissions models Division 3 Section 27 Decay coefficients Item Year Decay coefficient 1 1 1.00 2 2 0.80 3 3 0.64 4 4 0.51 5 5 0.41 6 6 0.33 7 7 0.26 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 19 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 4 Implementation using measured emissions—sub-method 1 Section 28 Division 4—Implementation using measured emissions—sub-method 1 28 Emissions abated (1) The emissions abated by implementation (h) in the project for the reporting period (Ah), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using subsections (2) and (3). (2) If: E IA,h 0.1 × E b_mod,h - E meas,h then: Ah = E b_mod,h - E meas,h + E IN,h × AF where: EIA,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 9. Eb_mod,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 11. Emeas,h means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 13. Ah means the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. EIN,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 10. AF means the accuracy factor for implementation (h) for the reporting period worked out in accordance with section 26. (3) If: E IA,h 0.1 × E b_mod,h - E meas,h then: Ah = 0 EIA,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 9. Eb_mod,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 11. 20 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Implementation using measured emissions—sub-method 1 Division 4 Section 29 Emeas,h means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 13. Ah means the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. 29 Interactive effects (1) The sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in the reporting period (EIA,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 9): E IA,h E I,h,u u where: EIA,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. |EI,h,u| means the absolute value of interactive effect (u) for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out in accordance with section 25. (2) The net interactive effects for implementation (h) for the reporting period (EIN,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 10): E IN,h E I,h,u u where: EIN,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. EI,h,u means interactive effect (u) for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out in accordance with section 25. 30 Modelled baseline emissions The total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period (Eb_mod,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 11): E b_mod,h E b_mod,h,m m where: Eb_mod,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Eb_mod,h,m means the total baseline emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, modelled under section 31. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 21 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 4 Implementation using measured emissions—sub-method 1 Section 31 31 Baseline emissions model The total baseline emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period (Eb_mod,h,m), in tonnes CO2-e, is modelled by entering the values of the independent variables (x1,b, x2,b,…,xk,b) measured in the measurement time interval into the baseline emissions model for the implementation (equation 12): E b_mod,h,m = f x1,b ,x 2,b ,...,x k,b h,m = b + β1,b x1,b + β 2,b x 2,b + + β k,b x k,b h,m where: Eb_mod,h,m means the total baseline emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. x1,b means the measured value of the independent variable x1 for measurement time interval (m). k means the number of independent variables in the baseline emissions model. ∝b means the regression constant from the baseline emissions model. β1,b means the regression coefficient for independent variable x1 from the baseline emissions model. 32 Measured emissions The total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) for the reporting period (Emeas,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 13): E meas,h E meas,h,m m where: Emeas,h means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Emeas,h,m means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 35. 22 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Implementation using operating emissions model—sub-method 2 Division 5 Section 33 Division 5—Implementation using operating emissions model— sub-method 2 33 Emissions abated (1) The emissions abated by implementation (h) in the project for the reporting period (Ah), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using subsections (2) and (3). (2) If: E IA,h 0.1 × E b_mod,h - E p_mod,h then: Ah = E b_mod,h - E p_mod,h + E IN,h × AF × DF where: EIA,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 14. Eb_mod,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 16. Ep_mod,h means the total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 18. Ah means the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. EIN,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 15. AF means the accuracy factor for implementation (h) for the reporting period worked out in accordance with section 26. DF means the decay factor for the reporting period worked out using equation 8. (3) If: E IA,h 0.1 × E b_mod,h - E p_mod,h then: Ah = 0 where: EIA,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 14. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 23 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 5 Implementation using operating emissions model—sub-method 2 Section 34 Eb_mod,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 16. Ep_mod,h means the total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 18. Ah means the emissions abated by implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. 34 Interactive effects (1) The sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in the reporting period (EIA,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 14): E IA,h E I,h,u u where: EIA,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. |EI,h,u| means the absolute value of interactive effect (u) for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out in accordance with section 25. (2) The net interactive effects for implementation (h) for the reporting period (EIN,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 15): E IN,h E I,h,u u where: EIN,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. EI,h,u means interactive effect (u) for implementation (h) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out in accordance with section 25. 35 Modelled baseline emissions The total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period (Eb_mod,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 16): E b_mod,h E b_mod,h,m m where: Eb_mod,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. 24 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Implementation using operating emissions model—sub-method 2 Division 5 Section 36 Eb_mod,h,m means the total baseline emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, modelled under section 36. 36 Baseline emissions model The total baseline emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period (Eb_mod,h,m), in tonnes CO2-e, is modelled by entering the values of the independent variables (x1,b, x2,b,…,xk,b) measured in the measurement time interval into the baseline emissions model for the implementation (equation 17): E b_mod,h,m = f x1,b ,x 2,b ,...,x k,b h,m = b + β1,b x1,b + β 2,b x 2,b + + β k,b x k,b h,m where: Eb_mod,h,m means the total baseline emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. x1,b means the measured value of the independent variable x1 for measurement time interval (m). k means the number of independent variables in the baseline emissions model. ∝b means the regression constant from the baseline emissions model. β1,b means the regression coefficient for independent variable x1 from the baseline emissions model. 37 Modelled operating emissions The total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period (Ep_mod,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 18): E p_mod,h E p_mod,h,m m where: Ep_mod,h means the total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Ep_mod,h,m means the total operating emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, modelled under section 38. 38 Operating emissions model The total operating emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period (Ep_mod,h,m), in tonnes CO2-e, is modelled by entering the values of the independent variables (x1,p, x2,p,…,xk,p ) measured in the measurement time interval into the operating emissions model for the implementation for the measurement time interval (equation 19): Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 25 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 5 Implementation using operating emissions model—sub-method 2 Section 38 E p_mod,h,m = f x1,p ,x 2,p ,...,x k,p h,m = p + β1,p x1,p + β 2,p x 2,p + + β k,p x k,p h,m where: Ep_mod,h,m means the total operating emissions for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) for the measurement time interval, in tonnes CO2-e. x1,p means the measured value of the independent variable x1 in measurement time interval (m). k means the number of independent variables in the operating emissions model. ∝p means the constant or fixed coefficient from the operating emissions model. β1,p means the regression coefficient for independent variable x1 from the operating emissions model. 26 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Sample using measured emissions—sub-method 3 Division 6 Section 39 Division 6—Sample using measured emissions—sub-method 3 39 Emissions abated by population The emissions abated by population (p) in the project for the reporting period (Ap), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 20): A p = A p,s × Np n p,s where: Ap means the emissions abated by population (p) in the project for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Ap,s means the emissions abated by sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 21. Np means the number of implementations in population (p) that were completed before the start of the reporting period. np,s means the number of implementations in sample (s) of population (p) that were completed before the start of the reporting period. 40 Emissions abated by sample The emissions abated by sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (Ap,s), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 21): A p,s A p,s,h h where: Ap,s means the emissions abated by sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Ap,s,h means the emissions abated by implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out under section 41. 41 Emissions abated by implementation (1) The emissions abated by implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (Ap,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using subsections (2) and (3). (2) If: E IA,p,s,h 0.1 × E b_mod,p,s,h - E meas,p,s,h then: Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 27 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 6 Sample using measured emissions—sub-method 3 Section 41 Ap,s,h = E b_mod,p,s,h - E meas,p,s,h + E IN,p,s,h × AF where: EIA,p,s,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 21. Eb_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 24. Emeas,p,s,h means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 26. Ap,s,h means the emissions abated by implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. EIN,p,s,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 23. AF means the accuracy factor for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, worked out in accordance with section 26. (3) If: E IA,p,s,h 0.1 × E b_mod,p,s,h - E meas,p,s,h then: A p,s,h = 0 where: EIA,p,s,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 21. Eb_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 24. Emeas,p,s,h means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 26. Ap,s,h means the emissions abated by implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. 28 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Sample using measured emissions—sub-method 3 Division 6 Section 42 42 Interactive effects (1) The sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period (EIA,p,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 22): E IA,p,s,h E IA,p,s,h,u u where: EIA,p,s,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. |EIA,p,s,h,u| means the absolute value of interactive effect (u) for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out in accordance with section 25. (2) The net interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (EIN,p,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 23): E IN,p,s,h E I,p,s,h,u u where: EIN,p,s,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. EI,p,s,h,u means interactive effect (u) for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out in accordance with section 25. 43 Modelled baseline emissions The total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (Eb_mod,p,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 24): E b_mod,p,s,h E b_mod,p,s,h,m m where: Eb_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Eb_mod,p,s,h,m means the total baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, modelled under section 44. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 29 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 6 Sample using measured emissions—sub-method 3 Section 44 44 Baseline emissions model The total baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period (Eb_mod,p,s,h,m), in tonnes CO2-e, is modelled by entering the values of the independent variables (x1,b, x2,b,…,xk,b) measured in the measurement time interval into the baseline emissions model for the sample (equation 25): E b_mod,p,s,h,m = f x1,b ,x 2,b ,...,x k,b p,s,h,m = b + β1,b x1,b + β 2,b x 2,b + + β k,b x k,b p,s,h,m where: Eb_mod,p,s,h,m means the total baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e. x1,b means the measured value of the independent variable x1 for measurement time interval (m). k means the number of independent variables in the baseline emissions model. ∝b means the regression constant from the baseline emissions model. β1,b means the regression coefficient for independent variable x1 from the baseline emissions model. 45 Measured emissions The total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (Emeas,p,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 26): E meas,p,s,h E meas,p,s,h,m m where: Emeas,p,s,h means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Emeas,p,s,h,m means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 35. 30 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Sample using operating emissions model—sub-method 4 Division 7 Section 46 Division 7—Sample using operating emissions model—sub-method 4 46 Emissions abated by population The emissions abated by population (p) in the project for the reporting period (Ap), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 27): A p = A p,s × Np n p,s where: Ap means the emissions abated by population (p) in the project for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Ap,s means the emissions abated by sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 28. Np means the number of implementations in population (p) that were completed before the start of the reporting period. np,s means the number of implementations in sample (s) of population (p) that were completed before the start of the reporting period. 47 Emissions abated by sample The emissions abated by sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (Ap,s), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 28): A p,s A p,s,h h where: Ap,s means the emissions abated by sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Ap,s,h means the emissions abated by implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out under section 48. 48 Emissions abated by implementation (1) The emissions abated by implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (Ap,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using subsections (2) and (3). (2) If: E IA,p,s,h 0.1 × E b_mod,p,s,h - E p_mod,p,s,h then: Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 31 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 7 Sample using operating emissions model—sub-method 4 Section 48 Ap,s,h = Eb_mod,p,s,h - Ep_mod,p,s,h + EIN,p,s,h × AF × DF where: EIA,p,s,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 29. Eb_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 31. Ep_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 33. Ap,s,h means the emissions abated by implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. EIN,p,s,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 30. AF means the accuracy factor implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period worked out in accordance with section 26. DF means the decay factor for the reporting period worked out using equation 8. (3) If: E IA,p,s,h 0.1 × E b_mod,p,s,h - E p_mod,p,s,h then: A p,s,h = 0 where: EIA,p,s,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 29. Eb_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 31. Ep_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 33. Ap,s,h means the emissions abated by implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. 32 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Sample using operating emissions model—sub-method 4 Division 7 Section 49 49 Interactive effects (1) The sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period (EIA,p,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 29): E IA,p,s,h E IA,p,s,h,u u where: EIA,p,s,h means the sum of the absolute values of the interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. |EIA,p,s,h,u| means the absolute value of interactive effect (u) for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out in accordance with section 25. (2) The net interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (EIN,p,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 30): E IN,p,s,h E I,p,s,h,u u where: EIN,p,s,h means the net interactive effects for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. EI,p,s,h,u means interactive effect (u) for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, worked out in accordance with section 25. 50 Modelled baseline emissions The total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period (Eb_mod,p,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 31): E b_mod,p,s,h E b_mod,p,s,h,m m where: Eb_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Eb_mod,p,s,h,m means the total baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, modelled under section 51. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 33 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 7 Sample using operating emissions model—sub-method 4 Section 51 51 Baseline emissions model The total baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period (Eb_mod,p,s,h,m), in tonnes CO2-e, is modelled by entering the values of the independent variables (x1,b, x2,b,…,xk,b ) measured in the measurement time interval into the baseline emissions model for the sample (equation 32): E b_mod,p,s,h,m = f x1,b ,x 2,b ,...,x k,b p,s,h,m = b + β1,b x1,b + β 2,b x 2,b + + β k,b x k,b p,s,h,m where: Eb_mod,p,s,h,m means the total baseline emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. x1,b means the measured value of the independent variable x1 for measurement time interval (m). k means the number of independent variables in the baseline emissions model. ∝b means the regression constant from the baseline emissions model. β1,b means the regression coefficient for independent variable x1 from the baseline emissions model. 52 Modelled operating emissions The total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period (Ep_mod,p,s,h), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 33): E p_mod,p,s,h E p_mod,p,s,h,m m where: Ep_mod,p,s,h means the total modelled operating emissions for implementation (h) for the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. Ep_mod,p,s,h,m means the total operating emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e, modelled under section 53. 53 Operating emissions model The total operating emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period (Ep_mod,p,s,h,m), in tonnes CO2-e, is modelled by entering the values of the independent variables (x1,p, x2,p,…,xk,p ) measured in the measurement time interval into the operating emissions model for the sample for the measurement time interval (equation 34): 34 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Sample using operating emissions model—sub-method 4 Division 7 Section 53 E p_mod,p,s,h,m = f x1,p ,x 2,p ,...,x k,p = p + β1,p x1,p + β 2,p x 2,p + + β k,p x k,p p,s,h,m where: Ep_mod,p,s,h,m means the total operating emissions for implementation (h) in sample (s) of population (p) for measurement time interval (m) in the reporting period, in tonnes CO2-e. x1,p means the measured value of the independent variable x1 for measurement time interval (m). k means the number of independent variables in the operating emissions model. ∝p means the constant or fixed coefficient from the operating emissions model. β1,p means the regression coefficient for independent variable x1 from the operating emissions model. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 35 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 4 Net abatement amount Division 8 Measured emissions Section 54 Division 8—Measured emissions 54 Measured emissions (1) The total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for an implementation for a measurement time interval (m) (Emeas,h,m), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 35): E meas,h,m = E DIR,h,m + E IND,h,m where: Emeas,h,m means the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e. EDIR,h,m means the total direct emissions from the combustion of fuel that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 36. EIND,h,m means the total indirect emissions from the consumption of electricity that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 38. (2) The total direct emissions from the combustion of fuel that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) (EDIR,h,m), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 36): E DIR,h,m = E i h.m.i,j j where: EDIR,h,m means the total direct emissions from the combustion of fuel that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e. Eh,m,i,j means the total emissions from the combustion of fuel type (i) of greenhouse gas (j) that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e, worked out using equation 37. (3) The total emissions from the combustion of fuel type (i) of greenhouse gas (j) that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) (Eh,m,i,j), in tonnes CO2-e, is worked out using the formula (equation 37): E h,m,i,j = Qh,m,i × ECi × EFi,j 1000 where: Eh,m,i,j means the total emissions from the combustion of fuel type (i) of greenhouse gas (j) that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e. 36 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Net abatement amount Part 4 Measured emissions Division 8 Section 54 Qh,m,i means the total quantity of fuel type (i) combusted that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), worked out in accordance with the monitoring requirements, in gigajoules (or other appropriate units). ECi means the energy content factor of fuel type (i) estimated in accordance with Schedule 1 to the NGER (Measurement) Determination. EFi,j means the emission factor for each greenhouse gas type (j) released due to the combustion of fuel type (i) that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), estimated in accordance with Schedule 1 to the NGER (Measurement) Determination. (4) However, if Qh,m,i is measured in gigajoules, then the value of ECi is taken to be 1. (5) The total indirect emissions from the consumption of electricity that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e (EIND,h,m), is worked out using the formula (equation 38): E IND,h,m = Qelec,h,m × EFelec 1000 where: EIND,h,m means the total indirect emissions from the consumption of electricity that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in tonnes CO2-e. Qelec,h,m means the quantity of purchased electricity that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m), in kilowatt hours, worked out in accordance with the monitoring requirements. EFelec means: (a) for electricity obtained from an electricity grid that is a grid in relation to which the NGA Factors document, in force on the day the project is declared to be an eligible offsets project, includes an emissions factor—that factor, in kilograms CO2-e per kilowatt hour (or its equivalent of tonnes CO2-e per megawatt hours); or (b) for electricity obtained from an electricity grid not covered by paragraph (a) or obtained from a source other than an electricity grid: (i) if the supplier of the electricity is able to provide an emissions factor that reflects the emissions intensity of the electricity and is applicable on the day the project is declared to be an eligible offsets project— that factor, in kilograms CO2-e per kilowatt hour (or its equivalent of tonnes CO2-e per megawatt hours); or (ii) otherwise—the emissions factor, in kilograms CO2-e per kilowatt hour (or its equivalent of tonnes CO2-e per megawatt hours), for off-grid electricity included in the NGA Factors document in force on the day the project is declared to be an eligible offsets project. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 37 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 5 Reporting, record-keeping and monitoring requirements Division 1 Offsets report requirements Section 55 Part 5—Reporting, record-keeping and monitoring requirements Division 1—Offsets report requirements 55 Operation of this Division For paragraph 106(3)(a) of the Act, this Division sets out information that must be included in an offsets project report about an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project that is an eligible offsets project. 56 Offsets report requirements (1) The information referred to in subsection (2) is to be included in an offsets report for the project if the information is: (a) different from what has previously been provided to the Regulator (whether in an application for declaration of the project as an eligible offsets project or a previous offsets report or otherwise); or (b) the information has not been previously provided to the Regulator, (whether in an application for declaration of the project as an eligible offsets project or a previous offsets report or otherwise). (2) The information for the purposes of subsection (1) is the following: (a) details of an implementation undertaken during the reporting period; (b) the address of the site in relation to which an implementation was undertaken during the reporting period; (c) the sub-method used for an implementation or a population in the reporting period; (d) the total modelled baseline emissions and baseline emissions model for an implementation, or a sample of a population, for the reporting period; (e) the total measured emissions from the consumption of relevant energy for an implementation covered by sub-method 1, or an implementation in a sample of a population covered by sub-method 3; (f) the total modelled operating emissions and the operating emissions model for an implementation covered by sub-method 2, or a sample of a population covered by sub-method 4, for the reporting period; (g) the relative precision of the emissions level predicted by the baseline emissions model for an implementation, or a sample of a population for the baseline measurement period, for the model; (h) the relative precision of the emissions level predicted by the operating emissions model for an implementation covered by sub-method 2, or a sample of a population covered by sub-method 4, for the operating measurement period for the model; (i) the interactive effects for an implementation covered by sub-method 1 or 2, or an implementation in a sample of a population covered by sub-method 3 or 4. 38 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Reporting, record-keeping and monitoring requirements Part 5 Record-keeping requirements Division 2 Section 57 Division 2—Record-keeping requirements 57 Operation of this Division For paragraph 106(3)(c) of the Act, this Division sets out record-keeping requirements for an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project that is an eligible offsets project. 58 Record-keeping requirements The project proponent must keep records about: (a) the consumption of fuel and electricity that is relevant energy for an implementation; and (b) the choice of implementations in a population for the sample of the population using a random selection method (including evidence of the day the sample was chosen). Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 39 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 5 Reporting, record-keeping and monitoring requirements Division 3 Monitoring requirements Section 59 Division 3—Monitoring requirements 59 Operation of this Division For paragraph 106(3)(d) of the Act, this Division sets out requirements to monitor an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project that is an eligible offsets project. 60 Monitoring requirements—general (1) The project proponent for an industrial fuel and energy efficiency project must monitor a parameter mentioned in the table in Schedule 1 in accordance with the requirements in that table. (2) Relevant energy for an implementation at a site must be monitored separately to other energy use at the site during: (a) for sub-methods 1 and 3—the baseline measurement period and the reporting period; and (b) for sub-methods 2 and 4—the baseline measurement period and the operating measurement period. (3) Project proponents may exclude any data for a parameter if the data: (a) is not within the typical distribution of measured values; or (b) does not represent the normal operating conditions of the equipment to which the parameter relates. 61 Monitoring requirements—sub-method 1 If the emissions abated by an implementation is worked out under sub-method 1 for a reporting period, the following must be measured or monitored during the baseline measurement period and the reporting period: (a) the consumption of relevant energy for the implementation; (b) independent variables for the implementation for the baseline emissions model; (c) site constants for the implementation for the baseline emissions model; (d) interactive effects for the implementation. 62 Monitoring requirements—sub-method 2 (1) This section applies if the emissions abated by an implementation is worked out under sub-method 2 for a reporting period. (2) The following must be measured or monitored during the baseline measurement period: (a) the consumption of relevant energy for the implementation; (b) independent variables for the implementation for the baseline emissions model; (c) site constants for the implementation for the baseline emissions model; 40 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Reporting, record-keeping and monitoring requirements Part 5 Monitoring requirements Division 3 Section 63 (d) interactive effects for the implementation. (3) The following must be measured or monitored during the operating measurement period for the operating emissions model for the reporting period: (a) the consumption of relevant energy for the implementation; (b) independent variables for the implementation for the operating emissions model for the reporting period; (c) site constants for the implementation for the operating emissions model for the reporting period; (d) interactive effects for the implementation. (4) The following must be measured or monitored during the reporting period: (a) independent variables for the implementation for the baseline emissions model; (b) site constants for the implementation for the baseline emissions model; (c) independent variables for the implementation for the operating emissions model for the reporting period; (d) site constants for the implementation for the operating emissions model for the reporting period; (e) interactive effects for the implementation. 63 Monitoring requirements—sub-method 3 (1) This section applies if the emissions abated by a population in a project is worked out under sub-method 3 for a reporting period. (2) The following must be measured or monitored during the baseline measurement period and the reporting period: (a) the consumption of relevant energy for implementations in the sample of the population; (b) independent variables for the sample of the population for the baseline emissions model; (c) site constants for the sample of the population for the baseline emissions model; (d) interactive effects for implementations in the sample of the population. 64 Monitoring requirements—sub-method 4 (1) This section applies if the emissions abated by a population in a project is worked out under sub-method 4 for a reporting period. (2) The following must be measured or monitored during the baseline measurement period: (a) the consumption of relevant energy for implementations in the sample of the population; (b) independent variables for the sample of the population for the baseline emissions model; Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT 41 EXPOSURE DRAFT Part 5 Reporting, record-keeping and monitoring requirements Division 3 Monitoring requirements Section 65 (c) site constants for the sample of the population for the baseline emissions model; (d) interactive effects for implementations in the sample of the population. (3) The following must be measured or monitored during the operating measurement period for the operating emissions model for the population for the reporting period: (a) the consumption of relevant energy for implementations in the sample of the population; (b) independent variables for the sample of the population for the operating emissions model for the reporting period; (c) site constants for the sample of the population for the operating emissions model for the reporting period; (d) interactive effects for implementations in the sample of the population. (4) The following must be measured or monitored during the reporting period: (a) independent variables for the sample of the population for the baseline emissions model; (b) site constants for the sample of the population for the baseline emissions model; (c) independent variables for the sample of the population for the operating emissions model for the reporting period; (d) site constants for the sample of the population for the operating emissions model for the reporting period; (e) interactive effects for implementations in the sample of the population. 65 Monitoring requirements—independent variables and site constants The project proponent may measure the independent variables and site constants for an emissions model used for the purposes of Part 4: (a) directly; or (b) by using a proxy method that enables the value of the parameter to be reliably calculated. Note: 42 An example of a proxy method is measuring the temperature and pressure of steam flow to calculate energy flow. Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Monitored parameters Schedule 1 Clause 1 Schedule 1—Monitored parameters Note: See subsection 60(1). 1 Monitored parameters The following table sets out monitoring requirements for parameters. Monitored Parameters Item Parameter Description Unit of monitoring Manner of monitoring Accuracy requirements Measurement frequency Determination of parameter from measurements 1 Qelec,h,m The quantity of purchased electricity that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) KWh Measured using a commercial grade electricity meter The meter must: (a) comply with NMI document M6; and (b) be calibrated in accordance with the NGER (Measurement) Determination Throughout each measurement time interval, at a frequency such that variance within the measurement interval is less than variance between intervals Where multiple measurements of a variable are taken in a measurement time interval, the variable is worked out by multiplying the average value of those measurements during the time interval by the period of the time interval If measured in gigajoules, the quantity of megawatt hours is calculated by dividing the amount in gigajoules by the conversion factor of 3.6 If measured using data from the supplier of the electricity, the data must be calculated in accordance with: (a) the National Energy Retail Rules; or (b) the law relating to Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 43 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Schedule 1 Monitored parameters Clause 1 Monitored Parameters Item Parameter Description Unit of monitoring Manner of monitoring Accuracy requirements Measurement frequency Determination of parameter from measurements Throughout each measurement time interval, at: (a) a frequency such that variance within the measurement interval is less than variance between intervals; and (b) a frequency that meets or exceeds the requirements in Schedule 2 to the NGER (Measurement) Determination Where multiple measurements of a variable are taken in a measurement time interval, the variable is worked out by multiplying the average value of those measurements during the time interval by the period of the time interval electricity supply of the State or Territory in which the site is located 2 Qh,m,i, where (i) is gaseous fuel The total quantity of gaseous fuel combusted that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) GJ (or other appropriate units) Measured using gas measuring equipment (including flow devices) in accordance with Part 2.3 of the NGER (Measurement) Determination The measuring equipment must: (a) comply with NMI document R137; and (b) be calibrated in accordance with the NGER (Measurement) Determination If measured using data from the supplier of the fuel, the data must be calculated in accordance with: (a) the National Energy Retail Rules; or (b) the law relating to natural gas supply of the State or Territory in which the site is located 44 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT If Qi is measured for a population, the frequency must be the same for each site in the sample of the population EXPOSURE DRAFT Monitored parameters Schedule 1 Clause 1 Monitored Parameters Item Parameter Description Unit of monitoring Manner of monitoring Accuracy requirements Measurement frequency Determination of parameter from measurements 3 Qh,m,i, where (i) is liquid fuel The total quantity of liquid fuel combusted that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) GJ (or other appropriate units) Measured using measuring equipment (including fuel flow meters) in accordance with Part 2.3 of the NGER (Measurement) Determination The measuring equipment must be calibrated in accordance with the NGER (Measurement) Determination Throughout each measurement time interval, at a frequency such that variance within the measurement interval is less than variance between intervals Where multiple measurements of a variable are taken in a measurement time interval, the variable is worked out by multiplying the average value of those measurements during the time interval by the period of the time interval 4 Qh,m,i, where (i) is solid fuel The total quantity of solid fuel combusted that is relevant energy for implementation (h) for measurement time interval (m) GJ (or other appropriate units) Measured using measuring equipment: (a) estimated based on mass, volume, moisture etc.; and (b) in accordance with Part 2.2 of the NGER (Measurement) Determination The measuring equipment must be calibrated in accordance with the NGER (Measurement) Determination Throughout each measurement time interval, at a frequency such that variance within the measurement interval is less than variance between intervals Where multiple measurements of a variable are taken in a measurement time interval, the variable is worked out by multiplying the average value of those measurements during the time interval by the period of the time interval 5 Independent variables See section 23 Appropriate units Measured using measuring equipment in accordance with: (a) the NGER (Measurement) Determination; or The measuring equipment must be calibrated in accordance with the NGER (Measurement) Determination Throughout each measurement time interval, at a frequency such that variance within the measurement interval is less than variance Where multiple measurements of a variable are taken in a measurement time interval, the variable is the average value of those measurements during Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 45 EXPOSURE DRAFT EXPOSURE DRAFT Schedule 1 Monitored parameters Clause 1 Monitored Parameters Item Parameter Description Unit of monitoring Manner of monitoring Accuracy requirements between intervals (b) industry practice 6 46 Site constants See section 24 Appropriate units Measured using measuring equipment in accordance with: (a) the NGER (Measurement) Determination; or (b) industry practice Measurement frequency The measuring equipment must be calibrated in accordance with the NGER (Measurement) Determination Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 EXPOSURE DRAFT Throughout each measurement time interval, at a frequency such that variance within the measurement interval is less than variance between intervals Determination of parameter from measurements the time interval EXPOSURE DRAFT Monitored parameters Schedule 1 Section 1 Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Methodology (Industrial Fuel and Energy Efficiency) Determination 2014 47 EXPOSURE DRAFT