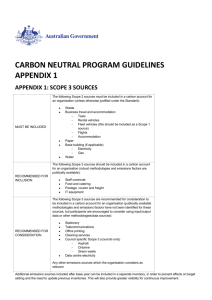
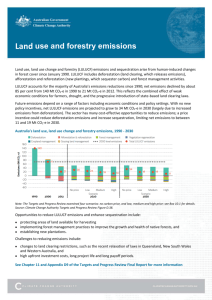
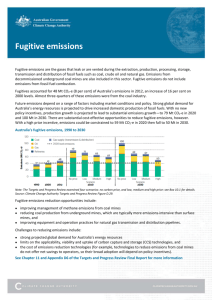
Waste emission - Climate Change Authority
advertisement
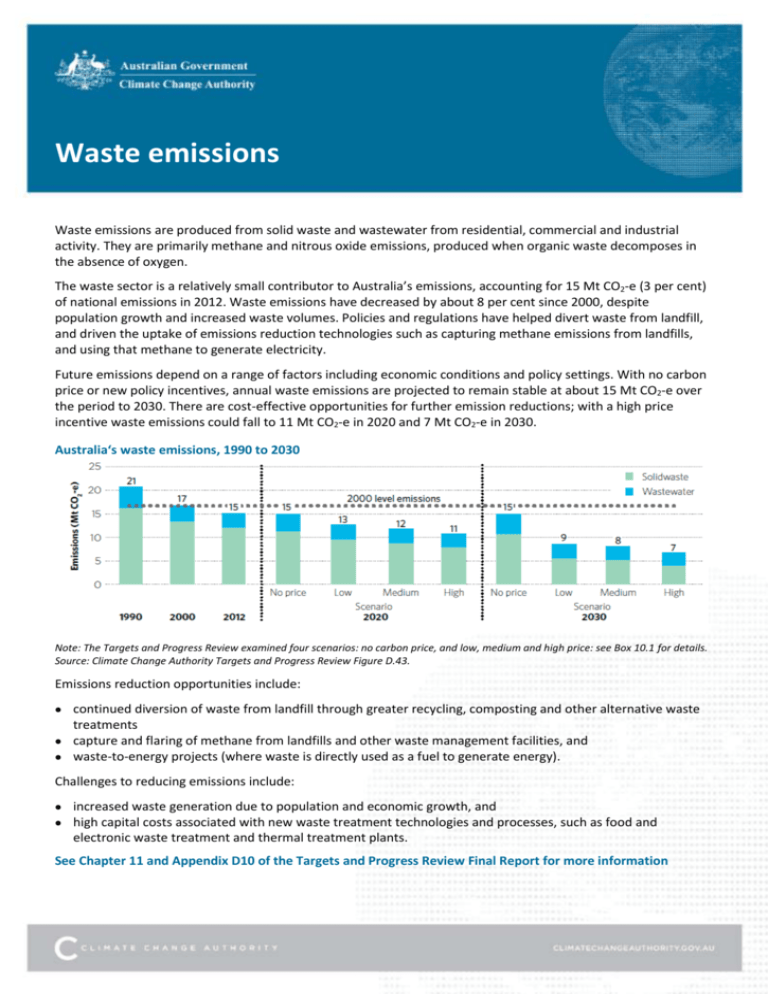
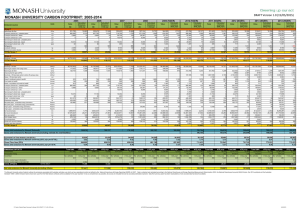
Waste emissions Waste emissions are produced from solid waste and wastewater from residential, commercial and industrial activity. They are primarily methane and nitrous oxide emissions, produced when organic waste decomposes in the absence of oxygen. The waste sector is a relatively small contributor to Australia’s emissions, accounting for 15 Mt CO2-e (3 per cent) of national emissions in 2012. Waste emissions have decreased by about 8 per cent since 2000, despite population growth and increased waste volumes. Policies and regulations have helped divert waste from landfill, and driven the uptake of emissions reduction technologies such as capturing methane emissions from landfills, and using that methane to generate electricity. Future emissions depend on a range of factors including economic conditions and policy settings. With no carbon price or new policy incentives, annual waste emissions are projected to remain stable at about 15 Mt CO2-e over the period to 2030. There are cost-effective opportunities for further emission reductions; with a high price incentive waste emissions could fall to 11 Mt CO2-e in 2020 and 7 Mt CO2-e in 2030. Australia‘s waste emissions, 1990 to 2030 Note: The Targets and Progress Review examined four scenarios: no carbon price, and low, medium and high price: see Box 10.1 for details. Source: Climate Change Authority Targets and Progress Review Figure D.43. Emissions reduction opportunities include: continued diversion of waste from landfill through greater recycling, composting and other alternative waste treatments capture and flaring of methane from landfills and other waste management facilities, and waste-to-energy projects (where waste is directly used as a fuel to generate energy). Challenges to reducing emissions include: increased waste generation due to population and economic growth, and high capital costs associated with new waste treatment technologies and processes, such as food and electronic waste treatment and thermal treatment plants. See Chapter 11 and Appendix D10 of the Targets and Progress Review Final Report for more information