Weather Unit Study Guide
advertisement

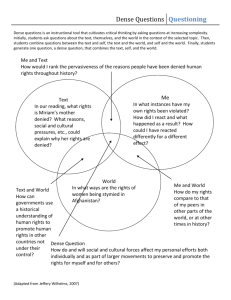
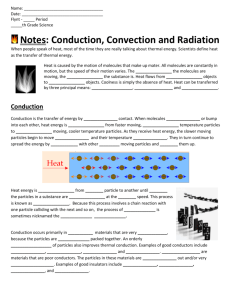
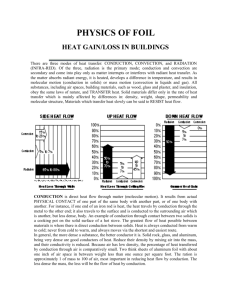
Weather Unit Study Guide *Fill in the blanks for these Key Elements Unit I Can Statements 1. _Light__ energy from the sun is mostly transmitted through I Can develop a model of the water cycle. I Can describe how water enters and leaves the atmosphere. I Can describe the difference between temperature and heat. I Can describe the three ways that heat moves(transfers). I Can model radiation, conduction, and convection. I Can conduct an investigation focusing on recording and analyzing data to determine if thermal energy can be transferred from one object to another. I Can conduct an investigation to explain what happens if hot air and cold air are next to each other. I Can create a model using evidence from data to describe what happens to air when it is heated and cooled. I Can make observations to determine how storm clouds are different from other clouds. I Can analyze and interpret data to identify patterns from an actual storm and can construct an explanation to tell why the storm happened. I Can construct and use a model to describe how the Earth’s air is heated by conduction. **You should be able to explain what each of these I Can statements is referring to by giving examples. **Things to study: Vocabulary definitions All bellringers the air before reaching the __ground__, and the ground ___absorbs__ some of the light energy that reaches it. 2. Molecules transfer __thermal__ energy from one end of an of an object to another and to other objects by _collisions__ between molecules that transfer the kinetic energy of one molecule to another (__conduction_). 3. The _air__ at the Earth’s surface is primarily heated by the transfer of __thermal_ energy from the ground below it. 4. _Less__ dense air rises when surrounded by more dense things. The __more__ dense air moves in to take its place. The movement of air masses is called _convection__. 5. Air _pressure_ at a location is related to the total weight of the air above that location. Low-density air columns have _less_ pressure and high-density columns have _more_ pressure. 6. A __front_ is the boundary between large air masses. 7. Air masses move when _high_ -pressure air pushes into the space of __lower_-pressure air. At the surface, higher differences in pressure over smaller distances result in stronger _winds__. Demonstration analyses Reading questions Read over any notes & Key Elements from water cycle, heat transfer and weather information! 8. Air masses move when _more_ dense air slides underneath less dense air, causing the __less_ dense air to be lifted upward. This _less_ dense air is unstable as it is forced upward. It transfers __energy_ to the surrounding air and cools as it rises. 9. Movement of air masses causes _changes_ in weather in predictable ways. 10. Complete the table. 15. Create and label models related to how air heats and cools on Cold Air Mass Warm Air Mass Low High Density More Less Air Pressure High Low Temperature 11. What is the difference between a weather event and weather condition? -conditions are things that act together to create an event such as temperature, air pressure, wind, humidity, precipitation, etc -events are the culmination of conditions –storms, tornadoes, etc 12. Heat always moves in what direction? -heat moves from warmer areas/objects to cooler areas/objects 13. Why is air considered to be matter? -it is made of molecules, has mass and volume 14. What are the processes that water goes through the water cycle to change its state of matter? -evaporation -liquid to gas -transpiration – liquid to gas -condensation –gas to liquid -precipitation -liquid to liquid/solid Earth and its atmosphere. *Be sure to be able to show/label -radiation, conduction, convection, temperatures, air pressure, heat sources, air molecule arrangements, arrows for movement -class models