Type of variables
advertisement

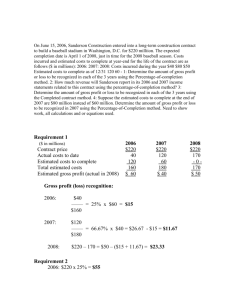
Visit www.universityassignmenthelp.com.au E-Mail – info@ universityassignmenthelp.com.au Call/WhatsApp - +61 478 793 640 Contents Introduction ............................................................................................................................................. 1 Type of variables..................................................................................................................................... 1 Descriptive statistics on gross sales ........................................................................................................ 1 Descriptive statistics type of customer and gross sales ........................................................................... 3 Charts ...................................................................................................................................................... 5 Interpretation of results ........................................................................................................................... 5 Recommendation .................................................................................................................................... 6 Conclusion .............................................................................................................................................. 7 Bibliography ........................................................................................................................................... 7 Introduction The purpose of this report is to perform and discuss the findings of statistical analysis with the sample data collected for hundred credit card transactions. Initially the variables are defined and descriptive statistics has been calculated for gross sales. Use of graphs and charts has been done for the analysis. Further analysis of the data is done for the card payment type and type of customers. There after interpretation part is done and at the end of report conclusion is provided. Type of variables Variable Type of variable Customer Quantitative Discrete variable Type of Customer Qualitative Items Quantitative Discrete variable Gross Sales Quantitative Discrete Continuous Method of Payment Qualitative Descriptive statistics on gross sales The descriptive statistics for the gross sales variable is as under: Gross Sales Mean 107.4174 Standard Error 6.357078359 Median 84.73 Mode 75.36 Standard Deviation 63.57078359 Sample Variance 4041.244527 Kurtosis 0.277800944 Skewness 0.932902491 Range 294.77 Minimum 23.95 Maximum 318.72 Sum 10741.74 Count 100 1 The mean of the gross sales is 107.41. Mean is a measure of central tendency, it is statistical term for average. It is important to know the gross sales per customer, which is the value of mean. A median is a value which divides the sample in to half. As the mean and median are not equal, the data set is skewed. As in the present case, the mean is greater than the median, the dataset is positively skewed. The histogram of the dataset shows that it is having a long tail. As the dataset is skewed, median is a better representative of central tendency as compared to mean. Mode is the most frequency occurring value in the dataset. It is relevant when the data is qualitative. However in the present case, the gross sale is a quantitative data, hence mode does not have much role to play in this case. After analysis of measures of central tendency, there is need to interpret the important measures of disperse, which are standard deviation and variance. The range of gross sales is 294.77; however it is better to focus on the variance and standard deviation as range suffers from the drawback that it is based upon two values only. The variance and standard deviation states that there is not unreasonable spread of data from the central tendency. It may be noted that the variance and standard deviations are calculated for sample and not for population. Class Start Finish f Rf crf Class Mark 1st Class $24 $64 29 29% 29% $44 2nd Class $64 $104 30 30% 59% $84 3rd Class $104 $144 15 15% 74% $124 4th Class $144 $184 11 11% 85% $164 5th Class $184 $224 9 9% 94% $204 6th Class $224 $264 5 5% 99% $244 7th Class $264 $304 0 0% 99% $284 8th Class $304 $344 1 1% 100% $324 For initiation of the class range, Sturges rule has been used. For calculating the class width the difference between the largest value and smallest value is divided by the number of observations. The class range is approximately 40. Besides the calculation of frequency, percentage frequency and cumulative percentage frequency is calculated. The frequency and relative frequency percentage appears to be same as the number of observations is 100. Relative frequency is used so that dataset having different observations can be compared. 2 Histogram- Gross Sales 35 30 25 f 20 15 10 5 0 $44 $84 $124 $164 $204 $244 $284 $324 It is better to have a pictorial view of the frequency table. Histogram serves this purpose. The above histogram shows the frequency distribution of gross sales. Descriptive statistics type of customer and gross sales The total gross sales and average sales for each of the three categories of customer has been calculated in the excel sheet. Table of calculation and bar charts are presented as under. Type of No. Customer of Gross customer Avg. Sales Sales per customer Promotional 36 3690.16 102.50 Regular 37 3731.99 100.86 Walk In 27 3319.59 122.95 Total 100 10741.74 3 Gross Sales 3800 3700 3600 3500 Gross Sales 3400 3300 3200 3100 Promotional Regular Walk In Avg. Sales per customer 140.00 120.00 100.00 80.00 Avg. Sales per customer 60.00 40.00 20.00 0.00 Promotional Regular Walk In A study of above charts and table indicates that the number of walk in customers is lowest and so the gross sales for walk in customers (Field, 2009). However the interesting fact is that average sales per customer are highest for walk in customer. Thus if the company is able to increase the number of walk in customers then it is most beneficial for the company. The number and sales for promotional customer and regular customers are almost same. 4 Charts Relative Frequency Polygon 100% crf 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% $64 $104 $144 $184 $224 $264 $304 $344 Distribution of Gross Sales 35 30 25 f 20 15 10 5 0 $44 $84 $124 $164 $204 $244 $284 $324 Interpretation of results Further analysis of the dataset has been done (Leblanc, 2004). There are three types of customers and four types of payment methods. It makes sense to do an analysis on this data. As the types of customer 5 and types of payment methods are qualitative data times, these have been converted to quantitative data type by assigning numerical values to it. 1 Type of Customer Promotional 2 - Regular 3- Walk In 2 - Globuy Charge 3Method of Payment 1 - Visa Engine Type Total Diesel 36 Gasoline 37 Grand Total 73 Card Master Card 4- AMEX Method of Payment Grand Type of Customer Visa Globuy Charge Card MasterCard AMEX Total Promotional 21 0 12 3 36 Regular 0 37 0 0 37 Walk In 11 0 9 7 27 Grand Total 32 37 21 10 100 The above table has been created in MS Excel, after applying the formulas. The analysis states that the least used payment method is AMEX, while Globuy Charge Card is most widely used payment method. Another interesting finding is that only regular customers are using the Globuy Charge Card. The promotional customers are mostly using the VISA card as payment method. Recommendation The statistical analysis of the data revealed several facts. The dataset is positively skewed; hence management should expect most of the sales with in the $ 150 mark. The walk in customers are providing highest sales per customer, hence management should focus on increasing the number of walk in customers (Siegel, 2010). Incidentally, at present the walk in customers are lowest in number. Company can also focus on the Visa card and Globuy Charge card holders, in order to generate more revenue. This statement is supported by the analysis that the most of the existing customers of Markole Stores are using these cards. Company has advertising on the target audience having these cards. 6 Conclusion The statistical analyses are based upon the historical data and there is no guarantee that the results will repeat in future (Zappe & Winston, 2011). However the statistical analysis provides an idea of what may happen in future. The management should focus on the walk in customers and Visa and Globuy Charge Card holders on first priority. If this is done than it is expected that the sale and profit of the company will increase. Bibliography Field, A. (2009). Discovering Statistics Using SPSS. London: SAGE. Leblanc, D. (2004). Statistics: Concepts and Applications for Science. NY: Jones & Bartlett Learning. Siegel, A. (2010). Practical Business Statistics. NY: Academic Press. Zappe, C., & Winston, W. (2011). Data Analysis and Decision Making with Microsoft Excel, Revised. London: Cengage. 7