Services - School of Management

McGraw-Hill/Irwin
SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT
SEMESTER 1 2012/2013
AMW342 SERVICES MARKETING
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DR. AZIZAH OMAR
Lecture: Thursday
Venue: DK - R
Room: PhD/MA Office, Level 1
School of Management
Tel: 04 653 888 ext.2889
Email: aziemar@usm.my
http://www.management.usm.my/azizahomar
Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Part 1
FOUNDATIONS
FOR SERVICES
MARKETING
1-2
Introduction to Services
What are Services?
Why Service Marketing?
Service and Technology
Characteristics of Services
Service Marketing Mix
Staying Focused on the Customer
Chapter
1
1-3
Objectives for Chapter 1:
Introduction to Services
Explain what services are and identify important trends in services.
Explain the need for special service marketing concepts and practices and why the need has developed and is accelerating.
Explore the profound impact of technology on service.
Outline the basic differences between goods and services and the resulting challenges and opportunities for service businesses.
Introduce the expanded marketing mix for services and the philosophy of customer focus as powerful frameworks and themes that are fundamental to the rest of the text.
1-4
Examples of Service Industries
Health Care
hospital, medical practice, dentistry, eye care
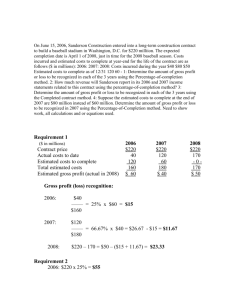
Professional Services
accounting, legal, architectural
Financial Services
banking, investment advising, insurance
Hospitality
restaurant, hotel/motel, bed & breakfast
ski resort, rafting
Travel
airline, travel agency, theme park
Others
hair styling, pest control, plumbing, lawn maintenance, counseling services, health club, interior design
1-5
Contributions of Service Industries to
U.S. Gross Domestic Product
1-6
Where the Money in Manufacturing Is: Services
The sale of a product accounts for only a small portion of overall revenues.
100%
80%
Providing services to customers is where the real money is.
60%
40%
20%
Personal Computers annual cost of
PC use: $6,259 network administration network technical support network equipment nonproductive operations by end user (downtime, file management, etc.) administration technical support desktop hardware
0% total expenditure:
5X product costs
Locomotives total annual cost of rail operations: $29 billion yard operations, railroad administration, other train operations
Infrastructure freight car services locomotive services locomotives total expenditure:
21X product costs
Automobiles average annual household expenditure: $6,064 other finance repair insurance gas used car purchase new car purchase total expenditure:
5X product costs
Source : GartnerGroup, Association of American Railroads, Federal Highway Administration Office of Highway
Information Management. (Railroad expenditures are for Class 1 railroads.)
Tangibility Spectrum
1-8
Why Service Marketing?
Services dominate U.S. and worldwide economies
Service as a business imperative in goodsfocused businesses
Deregulated industries and professional service needs
Service marketing is different
Service leads to profits
1-9
Percent of U.S. Labor Force by Industry
1-10
Percent of U.S. Gross Domestic
Product by Industry
1-11
Examples of Goods Companies that are
Expanding into Services
Boeing
1-12
Services in Malaysia
1.
Advertising
2.
Agency Services
3.
Assurance Services
4.
Auction
5.
Brokerage, Intermediary
Service
6.
Business Travel Services
7.
Certification, Inspection &
Credit Management
8.
Computer & Information
Technology Services
9.
Construction Services
10. Consulting
11. Corporate Register & Transfer
12. Design Services
13. Education & Training
14. Financial Services
15. Insurance
16. International Settlement
Services
17. Internet Service
18. Labour & Employment
19. Law Services
20. Leasing Services
21. Logistics Services
22. Other Business Services
Eight Central Paradoxes of Technological
Products
1-14
Characteristics of Services
Compared to Goods
Intangibility Heterogeneity
Simultaneous
Production and
Consumption
Perishability
1-15
Comparing Goods and Services
1-16
Implications of Intangibility
Services cannot be inventoried
Services cannot be easily patented
Services cannot be readily displayed or communicated
Pricing is difficult
1-17
Implications of Heterogeneity
Service delivery and customer satisfaction depend on employee and customer actions
Service quality depends on many uncontrollable factors
There is no sure knowledge that the service delivered matches what was planned and promoted
1-18
Implications of Simultaneous Production and Consumption
Customers participate in and affect the transaction
Customers affect each other
Employees affect the service outcome
Decentralization may be essential
Mass production is difficult
1-19
Implications of Perishability
It is difficult to synchronize supply and demand with services
Services cannot be returned or resold
1-20
Search, Experience, and Credence Qualities
1-21
Challenges and Questions for Service
Marketers
Defining and improving quality
Designing and testing new services
Communicating and maintaining a consistent image
Accommodating fluctuating demand
Motivating and sustaining employee commitment
Setting prices
Organizing to facilitate strategic and tactical decision-making
Finding a balance between standardization and personalization
Protecting new service concepts from competitors
Communicating quality and value to customers
Ensuring the delivery of consistent quality service
1-22
Traditional Marketing Mix
Elements an organization controls that can be used to satisfy or communicate with customers:
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
1-23
Expanded Mix for Services – The 7 Ps
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
People
All human actors who play a part in service delivery and thus influence the buyer’s perceptions: namely, the firm’s personnel, the customer, and other customers in the service environment.
Physical Evidence
The environment in which the service is delivered and where the firm and customer interact, and any tangible components that facilitate performance or communication of the service.
Process
The actual procedures, mechanisms, and flow of activities by which the service is delivered—the service delivery and operating systems.
1-24
Expanded Marketing Mix for Services
1-25
Ways to Use the 7 Ps
Overall Strategic
Assessment
How effective is a firm’s service marketing mix?
Is the mix well-aligned with overall vision and strategy?
What are the strengths and weaknesses in terms of the 7 Ps?
Specific Service
Implementation
Who is the customer?
What is the service?
How effectively does the service marketing mix for a service communicate its benefits and quality?
What changes/ improvements are needed?
1-26
Case Study 1
Read the articles given and prepare your case analysis.
1. Contributions of Service Industries to
Malaysia Gross Domestic Product.
2. Percent of Malaysian Labor Force by Industry.
3. Percent of Malaysia Gross Domestic
Product by Industry.