Study guide answers
advertisement

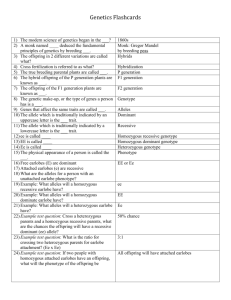
Name __________________________________________________ Date ________________ Period ________ Chapter 3 and 4 Study Points Discuss the following study points on a separate sheet of paper. You will receive 10 classwork points for this completed study guide. Use examples or drawings as appropriate. What do you know about Mendel, his observations, and his research? Mendel was a monk who studied pea plants. He crossed plants with specific characteristics, and his results formed the foundation of modern genetics. He found that when he crossed two purebred plants (tall x short) the dominant characteristic appeared in all offspring. He then crossed the F1 generation (children) and found that the lost trait reappeared ¼ of the time. Know the difference between hybrid/purebred and homozygous/heterozygous. How are offspring different based on the different types of parents? Hybrid and heterozygous are synonyms. These organisms have one dominant allele and one recessive allele (Bb) Purebred and homozygous are synonyms. These organisms have two dominant or two recessive alleles (BB or bb). Offspring can be different if their parents are heterozygous and they get the recessive from each parent (Bb and Bb parents and child is bb) What are traits and how are they determined? Traits are specific characteristics, like hair color or seed shape. Traits are determined by the genes we have. We get these genes from our parents. Describe and be able to give an example of genotypes and phenotypes. Genotype is the allele combination. An example is Bb Phenotype is the physical description of the alleles. An example would be brown hair or blue eyes. Complete a Punnett square and determine the genotypes of the parents based on a description (dominant, recessive, heterozygous, etc.). You choose the trait and the parents. Be able to explain the possible offspring with evidence from your Punnett square. Parents are both heterozygous. Offspring are homozygous dominant, heterozygous and homozygous recessive. 1 out of 4 will show the recessive trait Describe the complex patterns of inheritance. Incomplete dominance is when one allele is only partially dominant. An example is when red and white flowers produce pink flowers. Codominance is when both alleles are expressed equally. An example is when red and white flowers produced checkered flowers with each color represented. Multiple alleles are when there are many allele choices but we still only get two from each parent. One example is fur color in rabbits or cats. Polygenic inheritance is when many genes control one trait. Human height is an example. Describe how sex cells are different from body cells; including what happens during meiosis. Sex cells have half the chromosomes of body cells. In humans, sex cells (egg and sperm) have 23 chromosomes and body cells have 46 chromosomes. Explain the structure and function of DNA including how DNA is replicated. DNA is composed of sugars, phosphates, and nitrogen bases. The nitrogen bases pair up (A with T and T with A) (C with G and G with C). In DNA replication, an enzyme unzips the DNA, free nitrogen bases with sugars and phosphates attached find their match, and an enzyme zips them back up. The result is two identical strands of DNA Explain how mutations occur and if they can be inherited. Mutations are changes in DNA. They can only be inherited if they are on the DNA of a sex cell. Mutations on body cells cannot be passed down to offspring. Describe how cancer is formed and any treatments that can occur. Cancer is formed when mutated cells divide and reproduce in the body. The cells can group together to form tumors. Cells entering the bloodstream can spread throughout the body. Treatments include chemotherapy, surgery, radiation, and natural treatments. Be able to answer the Big Question with evidence from classwork, labs, readings, and discussion: o Why don’t offspring always look like their parents? Use page 90-91 to help answer this questions. Answers can include dominant/recessive traits, mutations, patterns of inheritance, environmental factors, acquired traits, and other factors. Be sure to include evidence and explanations when answering this question.