Phase Changes & Diagrams Worksheet: Chemistry Practice
advertisement

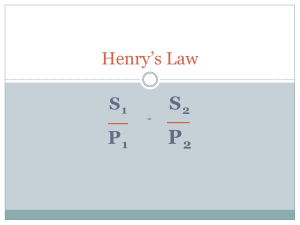
Name:__________________________________________________________________________________ Phase Changes and Phase Change Diagrams (Unit 2.3) PHASE CHANGES Important pieces of information to remember from the chart below: the name of each phase change, whether energy is added or released from the phase account, what happens to the attraction between particles. PHASE CHANGE DIAGRAMS A phase diagram is a graph of pressure versus temperature that shows the conditions necessary for a substance to be a solid, liquid, or a gas. Each substance has a unique phase diagram. Notice that in the diagram to the right, there are three regions (solid, liquid, gas) separated by three curved lines. These lines represent the pressure and temperature conditions at which two phases of a substance can coexist. The point labeled T is the triple point. This is the pressure and temperature at which all three phases of matter can exist at the same time. On the graph to the right label all six phase changes. gas Directions: For each labeled point on the graph to the right, determine the phase(s) of matter that exist. A)______________________________________ C B A B)______________________________________ D C)______________________________________ D)______________________________________ E)______________________________________ E Name:__________________________________________________________________________________ Directions: Look at the phase diagram below to answer each question. 1) If the pressure is normally 1.00 atm, what is the normal freezing point of this substance? 2) If the pressure is normally 1.00 atm, what is the normal boiling point of this substance? 3) What is the phase of a substance at 2.0 atm and 100 °C? 4) What is the phase of a substance at 0.75 atm and 100 °C? 5) What is the phase of a substance at 0.5 atm and 100 °C? 6) What is the phase of a substance at 1.5 atm and 50 °C? 7) What is the phase of a substance at 1.5 atm and 200 °C? 8) What is the phase of a substance at 1.5 atm and 800 °C? 9) What is the condition of the triple point of this substance? T= ________, P= _______ 10) If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 1.25 atm and a temperature of 3000C and lowered the pressure to 0.25 atm, what phase change would happen? 11)If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 0.75 atm and a temperature of -1000C, what phase change(s) would occur if I increased the temperature to 6000C 12) If this substance was at a pressure of 2.0 atm, at what temperature would it melt? 13) If this substance was at a pressure of 2.0 atm, at what temperature would it boil? 14) If this substance was at a pressure of 0.75 atm, at what temperature would it melt? 15) If this substance was at a pressure of 0.75 atm, at what temperature would it boil? 16) If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 1.00 atm and a temperature of -1000 C, what phase change(s) would occur if I increased the temperature to 6000 C? At what temperature(s) would they occur? (NOTE: multiple answers needed for this question)