Answer
advertisement
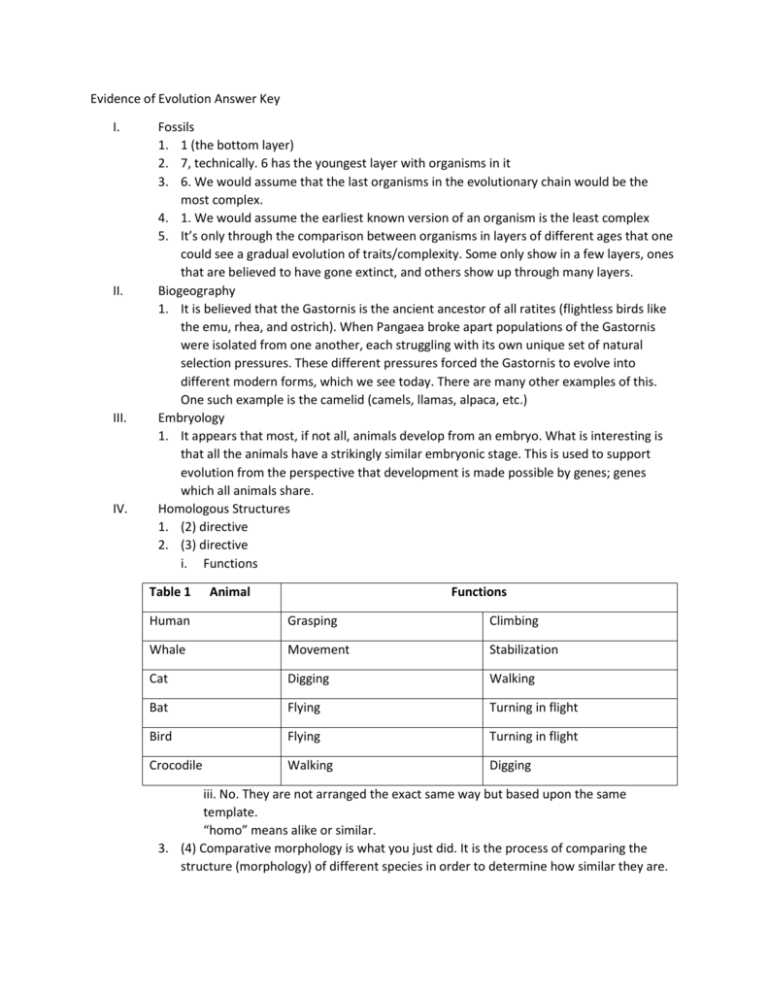
Evidence of Evolution Answer Key I. II. III. IV. Fossils 1. 1 (the bottom layer) 2. 7, technically. 6 has the youngest layer with organisms in it 3. 6. We would assume that the last organisms in the evolutionary chain would be the most complex. 4. 1. We would assume the earliest known version of an organism is the least complex 5. It’s only through the comparison between organisms in layers of different ages that one could see a gradual evolution of traits/complexity. Some only show in a few layers, ones that are believed to have gone extinct, and others show up through many layers. Biogeography 1. It is believed that the Gastornis is the ancient ancestor of all ratites (flightless birds like the emu, rhea, and ostrich). When Pangaea broke apart populations of the Gastornis were isolated from one another, each struggling with its own unique set of natural selection pressures. These different pressures forced the Gastornis to evolve into different modern forms, which we see today. There are many other examples of this. One such example is the camelid (camels, llamas, alpaca, etc.) Embryology 1. It appears that most, if not all, animals develop from an embryo. What is interesting is that all the animals have a strikingly similar embryonic stage. This is used to support evolution from the perspective that development is made possible by genes; genes which all animals share. Homologous Structures 1. (2) directive 2. (3) directive i. Functions Table 1 Animal Functions Human Grasping Climbing Whale Movement Stabilization Cat Digging Walking Bat Flying Turning in flight Bird Flying Turning in flight Crocodile Walking Digging iii. No. They are not arranged the exact same way but based upon the same template. “homo” means alike or similar. 3. (4) Comparative morphology is what you just did. It is the process of comparing the structure (morphology) of different species in order to determine how similar they are. IV. IV. Analogous Structures: Structures that do not show evolutionary relationships even though they perform the same function. a. Flight b. Internally, the bird wing is supported by bones whereas the butterfly wing is not. Externally, bird wings are covered in feathers and butterfly wings are made of chitin. Bird wings are one structure whereas butterfly wings are two. Others? c. Not really. There structures are very different from one another. The goal here is to understand that structure is more important for determining evolutionary relationships than function. d. There are many. Platypus, alligator, frog, and duck webbed feet. Webbed feet are better for swimming that toed or hooved feet. You find that organisms that spend a significant amount of time in the water have them where land animals do not. e. Convergent evolution (evolution that leads very distant relatives to reach similar adaptations because they live similar lives). Vestigial Structures a. There is no light so a light gathering organ like an eye is not necessary. b. They are built very similarly so yes. Structure Possible Function(s) Why it is considered vestigial Muscles that make hair stand up Create more depth for warmth We accommodate cold by wearing clothes. Besides, we don’t have enough hair for this function to work. Coccyx (tail bone) Once was a tail We no longer have tails. No it’s merely a nuisance when we fall on them! Muscles that move ears Hear predators from different angles. We no longer need to hear predators in the same way. We move our heads instead, if even needed at all. V. VI. Natural Selection Observed. 1. Ones that have the genetic material that confers (gives) the bug resistances. 2. Over time (many generations) the passing of the resistance genes has changed the genetic makeup of the bug populations forming new versions (some could argue species) that are different, genetically, from the originals. Biochemistry 1. Mammals: Dog, chimpanzee, mouse 2. Dog (81%), chimpanzee (98%), mouse (79%) 3. Mine are exactly the same. Hopefully yours are too. If not, why? What made your list in number 1 different? What was the criteria you used to make the list? 1. Cytochrome c 2. The larger the gap in organisms evolutionary relationships the larger the difference in amino acid sequences that give rise to the trait. 3. Biochemistry allows scientists a new perspective on evolution. What is found is that mutations accumulate and occur at a predictable rate. Since mutations are the source of variation that natural selection acts of then more differences in genetics naturally gives rise to different species. Analysis and Interpretations 1. Fossils are created by organisms getting trapped in some sort of material (amber, mud, ash) that freezes them in time. They are protected from erosion or other degrading influences. Fossils are created in a variety of ways, which gives rise to the various types of fossils found. Some are impressions left behind, like casts. Some organisms go through chemical replacement steps that replace their organic remains with more permanent compounds, like silica or minerals. Fossils are useful though because one can date the ground around the fossil, creating an age for the fossil itself. Be examining the fossils of organisms in different ages it has been repeated found that there is a progression in complexity over time. 2. Homologous structure, or being built similarly, is a string piece of evidence. It strongly suggests that the common ancestor to organisms that are built similarly had an older more primitive form. Because the different organisms had different natural selection working on them, they evolved into different species but they are still dependent upon the original frame. 3. Fish fins and whale flippers are both homologues to an extent but more analogous as the actual structure of a fin is much different than the flipper of a whale. 4. Embryology tells us that that organisms that evolved from a common ancestor develop in similar away to the original ancestor. This homology suggest evolution from a specific source ancestor. 5. The list above really summarizes this but there are others. Tonsils, wisdom teeth, body hair these are all examples of structures that are not needed by modern man. They are left overs that evolution hasn’t eliminated from our current structure. 6. You would expect that their genetics would be similar as well, considering genetics determines structure. We have two arms because our genetics says so.