File
advertisement

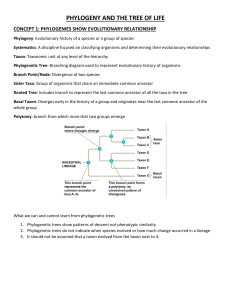
A.P.Biology – Reading Preview: Chapter 20: Phylogeny I. Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species (shows evolutionary relationships) II. Systematics: classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships a. phylogenetic tree represents a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships i. Each branch point represents the divergence of two taxa from a common ancestor; sister taxa share immediate common ancestor b. Phylogenies are inferred from morphological and molecular data III. IV. Taxonomy: the ordered division and naming of organisms V. Homology vs. analogy a. Homology is similarity due to shared ancestry b. Analogy is similarity due to convergent evolution VI. Cladistics: classifies organisms by common descent a. A clade is a group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants i. paraphyletic grouping: ancestral species and some, but not all, of the descendants ii. polyphyletic: various taxa with different ancestors iii. An outgroup is a species or group of species that is closely related to the ingroup, the various species being studied; outgroup diverged before the ingroup iv. In some trees, the length of a branch can reflect the number of genetic changes and/or time VII. molecular clock: constant rates of evolution in some genes can be used to estimate the absolute time of evolutionary change Binomial nomenclature: Linnaeus a. two-part names for species (binomial: genus, species. First letter of genus is capitalized, entire species name italicized) b. hierarchical classification – grouping species in increasingly broad categories: species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain a. The number of nucleotide substitutions in related genes is assumed to be proportional to the time since they last shared a common ancestor VIII. The three-domain system a. Domains Bacteria and Archaea are single-celled prokaryotes b. domain Eukarya: dominated bymulticellular organisms in three lineages: kingdoms Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia IX. Horizontal gene transfer: there have been substantial interchanges of genes between organisms in different domains (exchange of transposable elements and plasmids, viral infection, and fusion of organisms) a. Horizontal gene transfer complicates efforts to build a phylogenetic tree