Particles of Matter
advertisement
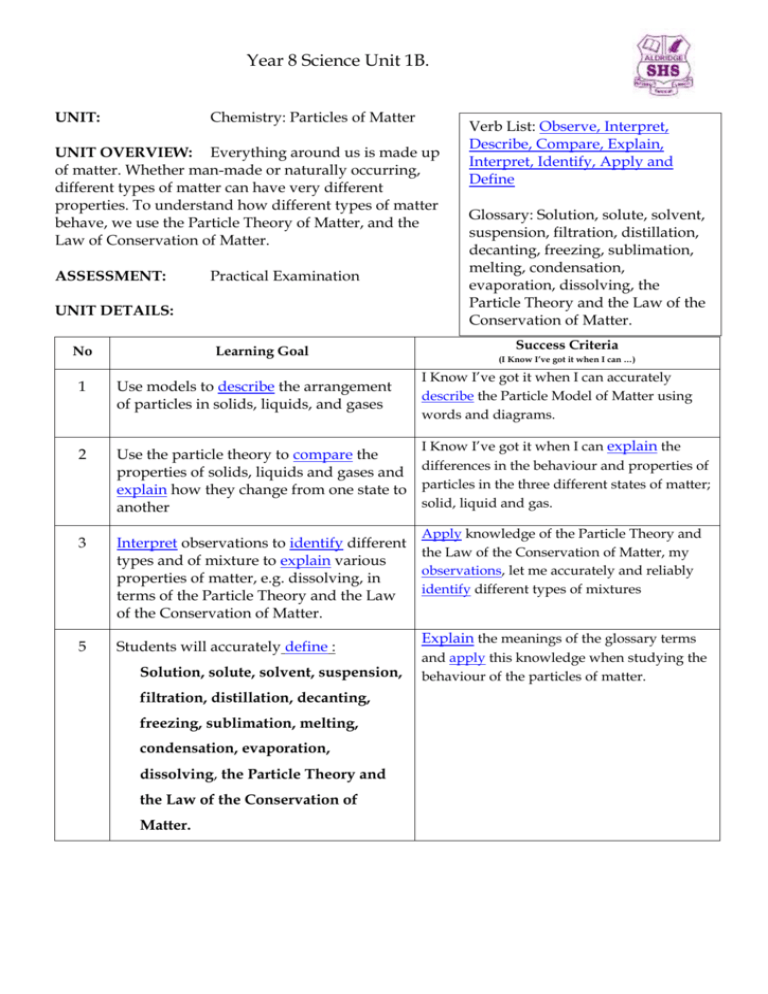
Year 8 Science Unit 1B. UNIT: Chemistry: Particles of Matter UNIT OVERVIEW: Everything around us is made up of matter. Whether man-made or naturally occurring, different types of matter can have very different properties. To understand how different types of matter behave, we use the Particle Theory of Matter, and the Law of Conservation of Matter. ASSESSMENT: Practical Examination UNIT DETAILS: No 1 2 Learning Goal Use models to describe the arrangement of particles in solids, liquids, and gases Verb List: Observe, Interpret, Describe, Compare, Explain, Interpret, Identify, Apply and Define Glossary: Solution, solute, solvent, suspension, filtration, distillation, decanting, freezing, sublimation, melting, condensation, evaporation, dissolving, the Particle Theory and the Law of the Conservation of Matter. Success Criteria (I Know I’ve got it when I can …) I Know I’ve got it when I can accurately describe the Particle Model of Matter using words and diagrams. I Know I’ve got it when I can explain the Use the particle theory to compare the properties of solids, liquids and gases and differences in the behaviour and properties of explain how they change from one state to particles in the three different states of matter; solid, liquid and gas. another Apply knowledge of the Particle Theory and 3 Interpret observations to identify different the Law of the Conservation of Matter, my types and of mixture to explain various observations, let me accurately and reliably properties of matter, e.g. dissolving, in identify different types of mixtures terms of the Particle Theory and the Law of the Conservation of Matter. 5 Students will accurately define : Solution, solute, solvent, suspension, filtration, distillation, decanting, freezing, sublimation, melting, condensation, evaporation, dissolving, the Particle Theory and the Law of the Conservation of Matter. Explain the meanings of the glossary terms and apply this knowledge when studying the behaviour of the particles of matter.