Vocabulary Acids and Bases
advertisement
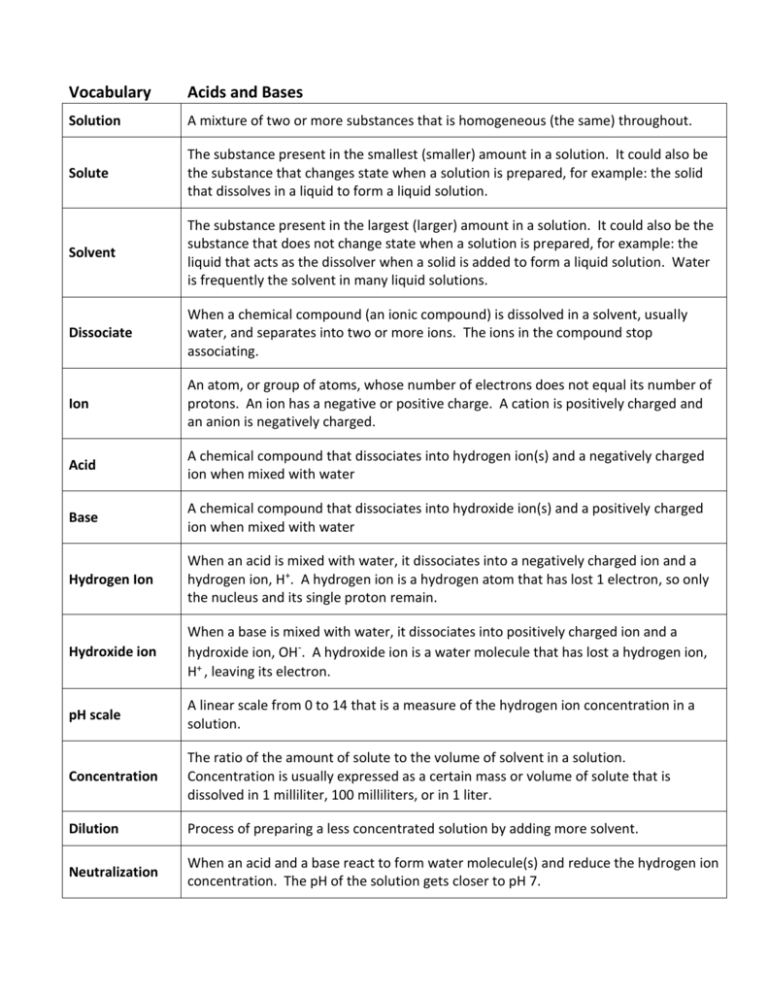
Vocabulary Acids and Bases Solution A mixture of two or more substances that is homogeneous (the same) throughout. Solute The substance present in the smallest (smaller) amount in a solution. It could also be the substance that changes state when a solution is prepared, for example: the solid that dissolves in a liquid to form a liquid solution. Solvent The substance present in the largest (larger) amount in a solution. It could also be the substance that does not change state when a solution is prepared, for example: the liquid that acts as the dissolver when a solid is added to form a liquid solution. Water is frequently the solvent in many liquid solutions. Dissociate When a chemical compound (an ionic compound) is dissolved in a solvent, usually water, and separates into two or more ions. The ions in the compound stop associating. Ion An atom, or group of atoms, whose number of electrons does not equal its number of protons. An ion has a negative or positive charge. A cation is positively charged and an anion is negatively charged. Acid A chemical compound that dissociates into hydrogen ion(s) and a negatively charged ion when mixed with water Base A chemical compound that dissociates into hydroxide ion(s) and a positively charged ion when mixed with water Hydrogen Ion When an acid is mixed with water, it dissociates into a negatively charged ion and a hydrogen ion, H+. A hydrogen ion is a hydrogen atom that has lost 1 electron, so only the nucleus and its single proton remain. Hydroxide ion When a base is mixed with water, it dissociates into positively charged ion and a hydroxide ion, OH-. A hydroxide ion is a water molecule that has lost a hydrogen ion, H+ , leaving its electron. pH scale A linear scale from 0 to 14 that is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution. Concentration The ratio of the amount of solute to the volume of solvent in a solution. Concentration is usually expressed as a certain mass or volume of solute that is dissolved in 1 milliliter, 100 milliliters, or in 1 liter. Dilution Process of preparing a less concentrated solution by adding more solvent. Neutralization When an acid and a base react to form water molecule(s) and reduce the hydrogen ion concentration. The pH of the solution gets closer to pH 7.










