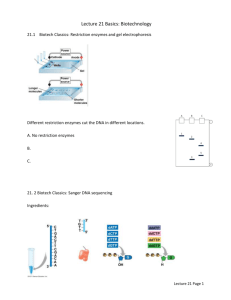
Lecture 21 Class: Biotechnology Starter: Fragmenting DNA or RNA
advertisement
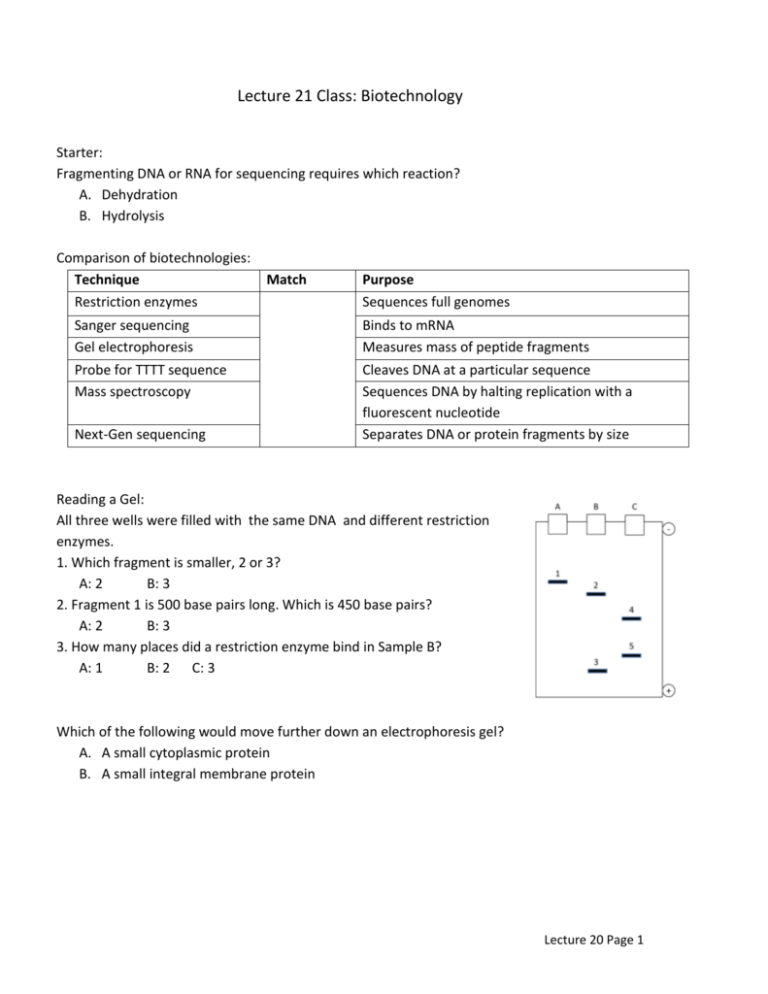
Lecture 21 Class: Biotechnology Starter: Fragmenting DNA or RNA for sequencing requires which reaction? A. Dehydration B. Hydrolysis Comparison of biotechnologies: Technique Restriction enzymes Sanger sequencing Gel electrophoresis Probe for TTTT sequence Mass spectroscopy Next-Gen sequencing Match Purpose Sequences full genomes Binds to mRNA Measures mass of peptide fragments Cleaves DNA at a particular sequence Sequences DNA by halting replication with a fluorescent nucleotide Separates DNA or protein fragments by size Reading a Gel: All three wells were filled with the same DNA and different restriction enzymes. 1. Which fragment is smaller, 2 or 3? A: 2 B: 3 2. Fragment 1 is 500 base pairs long. Which is 450 base pairs? A: 2 B: 3 3. How many places did a restriction enzyme bind in Sample B? A: 1 B: 2 C: 3 Which of the following would move further down an electrophoresis gel? A. A small cytoplasmic protein B. A small integral membrane protein Lecture 20 Page 1 Current research using restriction enzymes: Kitano, K., et al. (2011), CpG island methylation of microRNAs is associated with tumor size and recurrence of non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Science, 102: 2126–2131. Background: Methods: Amount of miRNA methylation was measured in patients with different cancer severities Restriction enzymes chop up chromosomes, kept DNA bands associated with miRNA that breaks down mitosis “go” mRNA. Measured methylation quantity with electrophoresis. Lecture 20 Page 2 Results: Representative combined bisulfite restriction analysis results of non-small-cell lung carcinoma tissue samples. Arrows, unmethylated alleles; arrowheads, methylated alleles; L, DNA size markers; numbers on top, tissue samples; stars, samples with significant restricted fragments from methylated alleles. Current research using DNA sequencing: Ramagopalan, SR et al. 2010. A ChIP-seq defined genome-wide map of vitamin D receptor binding: Associations with disease and evolution Genome Res. 20: 1352:1360. Background: Vitamin D is able to cross the membrane and binds to a complex that activates transcription. Lecture 20 Page 3 Methods: Findings: • __________ binding sites for Vitamin D • • Over ___________ genes change expression Affected genes include those associated with multiple sclerosis and Crohn’s disease Sample Problems: When might a transcriptome indicate that a mRNA is present, but a proteome not find any evidence of the protein? A. RNA was alternatively spliced B. Protein was immediately ubiquitinated C. Transcription was not regulated by a transcription factor You are interested in whether a family of three who all have irritable bowel syndrome have the same mutation in a regulatory gene. Which is necessary for restriction enzymes to be a useful tool? A. The mutation must produce a changed protein B. The mutation must be within a restriction site C. The mutation must produce a different mRNA molecule Formaldehyde is a chemical that binds protein to DNA. A good use of this chemical would be to: A. Compare restriction fragments of hemoglobin alleles B. Look for genes that are associated with a transcription factor C. Compare proteins that are expressed in patients who are being treated for cystic fibrosis Lecture 20 Page 4