Lecture 21 Basics: Biotechnology 21.1 Biotech Classics: Restriction
advertisement
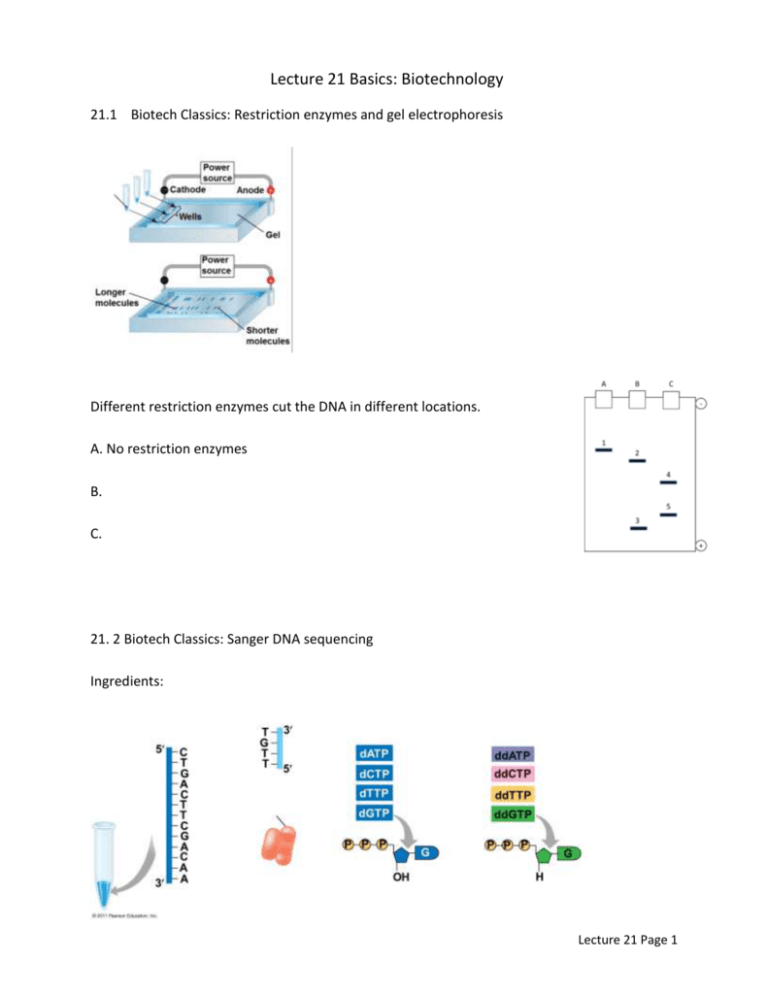
Lecture 21 Basics: Biotechnology 21.1 Biotech Classics: Restriction enzymes and gel electrophoresis Different restriction enzymes cut the DNA in different locations. A. No restriction enzymes B. C. 21. 2 Biotech Classics: Sanger DNA sequencing Ingredients: Lecture 21 Page 1 Steps: 1. 2. 3. Lecture 21 Page 2 21.3: Modern Biotechnology: Genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics Genomics: Transcriptomics Proteomics: 21.4 Genomics: Next-Generation DNA Sequencing (Watch “sales pitch” video http://youtu.be/v8p4ph2MAvI) What are the two “proprietary” technologies this company says they provide? a. b. Where is the fluorescent tag bound to the nucleotide? Why does this provide an improvement over Sanger sequencing? The sellers of this technology claim three improvements: Faster sequencing, longer read length, and high fidelity. a. What does “longer read length” likely mean? B. What does “high fidelity” likely mean? What is a ZMW? How would you describe it to a friend? How many bases per second can the DNA polymerase add to the template? Lecture 21 Page 3 How many ZMWs can run simultaneously? Circle on: (Dozens, Hundreds, Thousands, Millions) The makers claim that eventually a researcher can sequence an entire genome in: Time: ______________________ for Cost: _____________________ (Instructor disclaimer – This is one of many types of DNA sequencers. I’ve included it because the biology is most relevant to our class – not because it is the best or cheapest. No need to rush out and use this particular type). 21.5 Transcriptomics Types of RNA: Removal of rRNA: Lecture 21 Page 4 Isolation of mRNA: Sequencing of nucleotides: 21.6 Proteomics Not all of the genome Presence of mRNA… Lecture 21 Page 5 Protein Mass Spectroscopy: The spectrum of the molecule masses in graph is matched by computer to a database, to produce a reading of most likely amino acids. The sequence is matched to likely known proteins in a database for a final list of proteins found in the cell. Lecture 21 Page 6