2.0 Light behaves in predictable ways.
advertisement
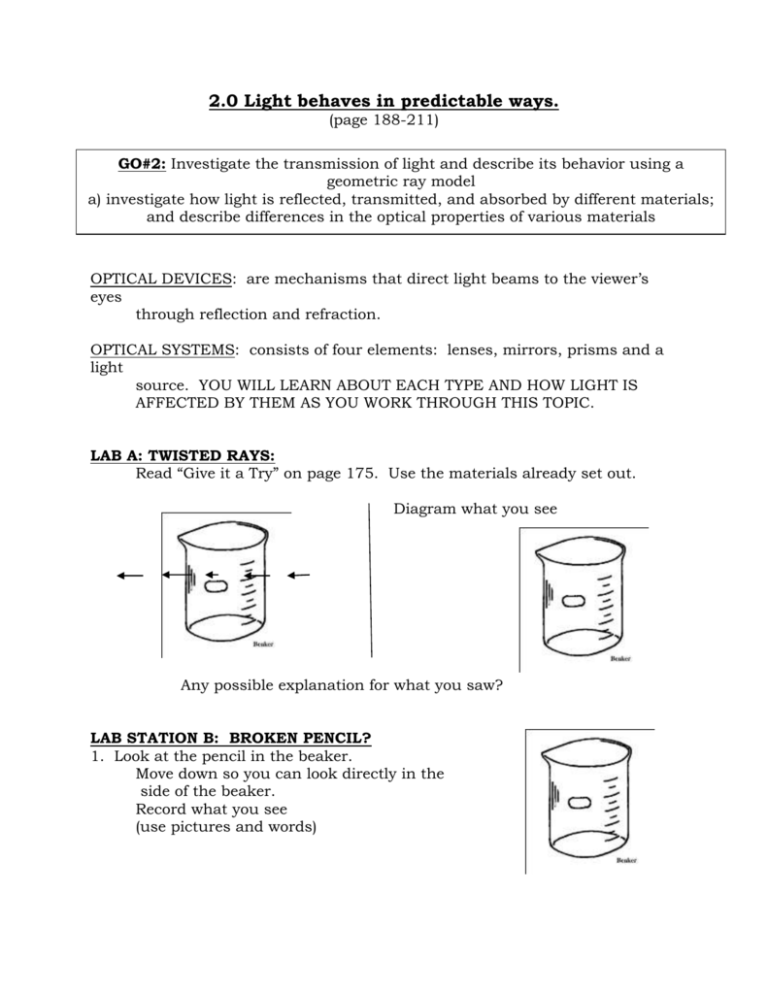
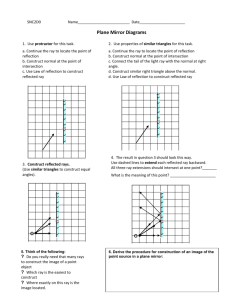
2.0 Light behaves in predictable ways. (page 188-211) GO#2: Investigate the transmission of light and describe its behavior using a geometric ray model a) investigate how light is reflected, transmitted, and absorbed by different materials; and describe differences in the optical properties of various materials OPTICAL DEVICES: are mechanisms that direct light beams to the viewer’s eyes through reflection and refraction. OPTICAL SYSTEMS: consists of four elements: lenses, mirrors, prisms and a light source. YOU WILL LEARN ABOUT EACH TYPE AND HOW LIGHT IS AFFECTED BY THEM AS YOU WORK THROUGH THIS TOPIC. LAB A: TWISTED RAYS: Read “Give it a Try” on page 175. Use the materials already set out. Diagram what you see Any possible explanation for what you saw? LAB STATION B: BROKEN PENCIL? 1. Look at the pencil in the beaker. Move down so you can look directly in the side of the beaker. Record what you see (use pictures and words) 2. Look at the pencil in the beaker half full of water. View it from the side again and record what you see. (use pictures and words) Any possible explanation for what you saw? LAB C: MAKE A PINHOLE CAMERA Read the directions on page 185. Make your own camera or use one already made to save time. Diagram what you saw of the light bulb when you looked through the camera. Wax paper Any possible explanation for what you saw? LAB D: DESK DUTY: 2.1 LIGHT TRAVELS IN RAYS AND INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS (page 190) RAY DIAGRAMS: 1. Define what predictable means. 2. A ________ _____________________ shows how light travels. The rays are drawn in ___________________ lines from the source of light. 3. Why are ray diagrams incomplete? 4. Draw two pictures below showing how ray diagrams can help explain why light intensity (brightness) changes with distance from the source. high intensity _____ of light rays reaching the eye. low intensity _____ light rays reaching the eye. 5. Draw a ray diagram below to show how shadows are created. 6. Where would you have to stand in relationship to the light source to create a very large shadow compared to a small one? LAB E: LIGHT INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS: 1. Shine a light source (light bulb) through the three different objects at this station. 2. What happened to the light rays for each material? LAB F: LIGHT INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS: 1. Shine a light source (light bulb) through the three different objects at this station. 2. What happened to the light rays for each material? LAB G: LIGHT INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS: 1. Shine a light source (light bulb) through the three different objects at this station. 2. What happened to the light rays for each material? 3. Read page 191. Material in LAB E would be considered ________________________. Material in LAB F would be considered _____________________________. Material in LAB G would be considered _____________________________. Complete the chart below based on your findings. Type of Material Interaction with Light Examples of Material Ray Diagram TRANSPARENT TRANSLUCENT OPAQUE Match the following examples of objects as to whether they are transparent, translucent or opaque. 1. 2. 3. 4. Desk _______________________ Leaf _____________________ Camera lens ___________________ Ice cube ______________________ _____________ 5. Stained glass ________________ ____________________________ 6. 7. 8. 9. Water _____________________ Mirror ____________________ Rainbow ______________________ Solid color shower curtain 10. Poster LAB H: DESK DUTY: LUMINOUS vs. NON-LUMINOUS Read page 191 1. A pencil or other opaque objects are called ______ ___________________________, meaning they ______ _____________ produce _________________. 2. Where does the light come from in order for you to see an opaque object? 3. An object that produces its own light is considered _______________________. LAB I: LIGHT REFLECTION LAB: page 192 QUESTION: What type of material makes the best reflector? HYPOTHESIS: I think because VARIABLES: manipulated: ___________________________________________ responding: _____________________________________________ 2-controlled: __________________________________________________ MATERIALS & PROCEDURES: see page 192 OBSERVATIONS: Material Description Transparent Translucent, or Opaque Surface type (smooth or rough) ANALYSIS: page 192 #6. #7. CONCLUSION TO LIGHT REFLECTION LAB: Color (shiny or dull) Qualitative Measurement Predict (good, ave, poor) Quantitative Measurement (mA) Ranking 1st, 2nd, etc.. APPLICATIONS: LAB J: TYPES OF REFLECTION: Read page 193 to complete the chart below, then go to Station J to complete the second chart. Type of Reflection Ray Diagram Interaction with Light type of surface: _______________ regular bounce off in the _______ ____________ reflected rays stay _______________ to each other image is ________________ type of surface: _____________________ diffuse each ray is reflected at a ____________ angle the light is _________________ Classify each of the following objects (found at station J) as to whether they would give a regular reflection or a diffuse reflection. OBJECT: describe it WHAT TYPE OF REFLECTION WOULD YOU GET? (diffuse or regular) LAB K:: Read “Give it a Try” on page 194 1. When you wink your right eye, the ________________ eye in the mirror winks back. 2. With 2 mirrors 90º to each other, when you wink your right eye the ____________ eye in the mirror winks back. 3. Any possible explanation for this? GO#2: b) measure and describe angles of reflection LAB L: 2.2: The Law of Reflection read page 194-196 1. The _________________ ray is the ray that goes into an object and bounces off as a ________________ beam, giving regular reflection. 2. What type of surface gives the best reflections? 3. Examples of objects that allow you to see your image are: still _____________, ____________________, __________________, or even _____________ ______________. The one that gives you the clearest reflection is a _____________ (flat) __________. QUESTION: What rule can you make that described how light reflects off a flat mirror? HYPOTHESIS: VARIABLES: manipulated: ______________________________________ responding: _______________________________________ controlled: ________________________________________ MATERIAL AND PROCEDURE: SEE PAGE 195 OBSERVATION DRAWING Top view of Mirror ANAYLYSIS QUESTIONS: a. Label the diagram above using these words: incident ray, angle of incidence, reflecting surface, normal, angle of reflection and reflected ray. b. Using a protractor measure the angle of incidence= _______° c. Using a protractor measure the angle of reflection= _______° d. Explain how the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection compare. Keep in mind instrumental errors. CONCLUSION: The “LAW OF REFLECTION” states that…. ERRORS & CHANGES: