- Female Reproductive System

Anatomy and Physiology 34B
Chapter 27 - Female Reproductive System
I.
Overview
A.
Introduction to the Female Reproductive Sys.
B.
Structure & Function of the Ovaries
C.
Secondary Sex Organs
D.
Mammary Glands
E.
Puberty & Menopause
F.
Female Sexual Response
II. Introduction to the Female Reproductive Sys.
A.
Female Reproductive System - includes the _________ (gonads), uterine (Fallopian) tubes, uterus, vagina, vulva, & mammary glands
B.
Female & male reproductive systems are ______________ in that:
1.
Most reproductive organs develop from similar embryonic tissues (______________)
2.
Both systems have ___________ that produce gametes & sex hormones
3.
Reproductive organs of both become functional during _____________ as a result of sex hormones secreted by the gonads
C.
_________________ between the male & female reproductive systems are:
1.
Mature male gonads produce _________ continuously throughout life
2.
Female gonads contain ____ her ova, in an immature state, at birth. After puberty,
____ ova is ovulated per month until menopause
D.
_______________ of the female reproductive system are:
1.
Produce _________
2.
Secrete sex ___________
3.
Receive sperm from the male during _________
4.
Provide sites for ________________, implantation, embryonic & fetal development
5.
Provide nourishment for the baby via the ____________ glands
E.
__________ of the female reproductive system are:
1.
Primary sex organs - gonads ( _________ ) produce gametes ( _____ ) and secrete steroid sex hormones (estrogen & progesterone)
2.
_______________ sex organs - structures needed for ovum fertilization, blastocyst implantation, embryonic & fetal development, & parturition. These organs include: a.
___________ - copulatory organ and birth canal b.
____________ - external genitalia that protect the vaginal opening c.
Uterine (______________) tubes - transport ovulated ova and where fertilization takes place d.
_____________ - implantation & development take place here e.
_______________ glands - secrete milk to nourish child after birth
2
3.
Secondary sex characteristics - develop at ____________ in response to increased gonadotropic & sex hormone secretion a.
Distribution of _____ to breasts, abdomen, mons pubis, & hips b.
Axillary & pubic _______ c.
Broad ________
III.
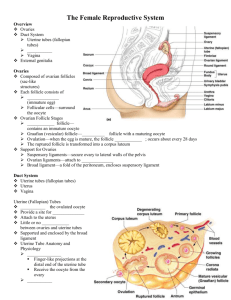
Structure & Function of the _________
A.
Position & Structure of the Ovaries
1.
Ovaries - paired organs in the upper dorsal pelvic cavity _________ fossa , lateral to the uterus, that produce ova and the sex hormones estrogen & progesterone
2.
_____ on the medial side of each ovary is the entry point for ovarian vessels & nerves
3.
Ovaries are secured by several membranous ____________ a.
_______ ligament - parietal peritoneum that supports the uterine tubes and uterus b.
_________ - posterior extension of the broad ligament that attaches to the ovaries c.
_________ ligament - anchors each ovary to the uterus d.
___________ ligament - attaches ovaries to the pelvic wall
4.
Each ovary consists of 4 _______: a.
__________ epithelium - thin outermost layer composed of simple cuboidal epithelium b.
Tunica _____________ - fibrous CT layer below epithelium c.
Ovarian _______ - outer layer of ovary; houses developing oocytes in follicles d.
Ovarian ________ - inner loose CT layer containing blood & lymph vessels and nerves
B.
The ________________ is a monthly cycle that includes the ovarian cycle in the ovaries and the menstrual cycle in the uterus
1.
At about 5 months, the female fetus’ ovaries contain about 6-7 million __________
(immature egg cells).
2.
Toward the end of gestation, the oogonia complete prophase, meiosis I and form diploid __________ ___________
3.
When a girl enters puberty, she has about 300 - 400 thousand primary ________; only about ____ will eventually be ovulated
4.
____________ follicles in the ovary cortex contain primary oocytes surrounded by follicular cells
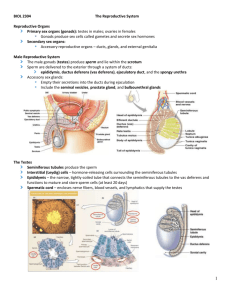
C. The ________ cycle lasts about 28 days, with day 1 being the first day of menstruation; it consists of a follicular phase, ovulation, and a postovulatory phase
1. The ___________ phase includes the menstrual phase (days 1-5) and preovulatory phase (days 6-14)
2. During the ____________ phase, the endometrial stratum functionalis is shed
3. During the ____________ phase, FSH stimulates some primordial follicles to progress to primary follicles, then secondary follicles, then a single Graafian follicle
3 a. Follicular cells divide to produce _________ epithelium that surrounds the oocyte and fills the follicle; this forms the __________ follicle, surrounded by granulosa cells (the former follicle cells) b. Some primary follicles continue to grow and form __________ follicles , which contain:
1) ________- fluid filled cavity surrounded by granulosa cells
2) Corona ________ - follicular epithelium surrounding the secondary oocyte
3) Zona ___________ - thin layer of glycoproteins between the corona radiata & oocyte c. Influenced by ___, the follicular cells secrete increased ____________ from androgens secreted by the theca folliculi cell layer just outside the follicle d. As the follicle develops, the primary oocyte completes meiosis I, forming one haploid ________ oocyte with most of the cytoplasm and one smaller _______ body that dissolves e. The secondary oocyte begins meiosis II, but stops at ___________ II until it is fertilized by a sperm
C.
____________ –about 14 days after day 1 of menstruation, the large __________ follicle bursts, releasing its oocyte into the peritoneal cavity near the opening of the uterine tube
1.
The secondary __________, surrounded by the zona pellucida & corona radiata, is swept by fimbria into the uterine tube and moved along by cilia lining the tube
2.
If not fertilized, the oocyte ___________ in a couple of days
3.
If a sperm enters the oocyte, it completes meiosis II forming one large _______ and a smaller ________ body that dissolves
4.
Sperm & ovum nuclei unite to form a diploid _________
D. The __________________ phase is divided into the luteal phase (days 15-26) and premenstrual phase (days 27-28).
1. _________ phase involves the follicle remnant after ovulation a. Influenced by ___, the empty follicle becomes a corpus __________ , which secretes ______________ to maintain the endometrial lining of the uterus b. If the oocyte is not fertilized, the corpus luteum atrophys to a nonfunctional corpus
_________
2. _____________ phase is marked by ischemia and necrosis of the stratum functionalis
E. The _________ cycle is divided into proliferative, secretory, premenstrual, and menstrual phases
1. ___________ phase (days 6-14) – stratum functionalis is rebuilt by mitosis, influenced by ___________ from the ovaries
2. ____________ phase (days 15-26) – endometrium thickens by secretion of mucus and glycogen, influenced by ____________ from the corpus luteum
3. _________________ phase is triggered by the decay of the corpus luteum and lack of
___________; uterine arteries deprive the endometrium of blood, which causes tissue necrosis and the
4. _____________ phase – sloughing off of the stratum ___________
IV.
Secondary Sex Organs
A.
Uterine (__________) tubes - about 4 in. long, extend laterally from the superior uterus; transport oocytes from the ovaries to the uterus
1.
____________ expanded middle region of the uterine tube that leads to the
2.
_______________ - the funnel-shaped, open end of the tube, close to the ovary
3.
______________ - fingerlike extensions of the infundibulum that sweep the ovulated oocyte into the tube
4.
___________ – superior margin of the broad ligament that surrounds the uterine tube
5.
The uterine tube consists of 3 _________: a.
_________ lines the lumen and is composed of ciliated columnar epithelium b.
___________ - middle layer of circular and longitudinal layers of smooth muscle c.
_________ - outer layer that is part of the visceral peritoneum
6. Pelvic inflammatory disease (____), an inflammation of the uterine tubes and associated structures, can result if pathogens enter the tubes
7. ____________ pregnancy results if a developing embryo (blastocyst) implants in the uterine tube or abdominal wall, rather than in the uterus.
8. Tubal ___________ involves severing the uterine tubes so sperm cannot contact ova
B.
_________ - hollow, thick-walled, inverted pear-shaped organ anterior to the rectum and posterosuperior to the urinary bladder; site of implantation & development of embryo & fetus
1.
__________ of the Uterus a.
________ - dome-shaped region superior to the uterine tube entry b.
________ (corpus) - enlarged main portion between fundus & cervix c.
Uterine __________ - space within the fundus & body d.
__________ - inferior constricted area opening into the vagina e.
Cervical _______ - extends through the cervix and opens into the vaginal lumen f.
Cervical _______ – secrete mucus that blocks the passage of microbes from the vagina into the uterus; the mucus becomes thinner near the time of ovulation g.
_________ - junction of the uterine cavity & cervical canal h.
Uterine _________ - opening of the cervical canal into the vagina i.
During a _____ smear , cervical cells are scraped off, then examined microscopically for abnormalities
2.
____________ of the Uterus a.
The uterus is held in place by _________ of the pelvic floor and ligaments that extend from it to the pelvic girdle or body wall b.
Four paired ____________ support the uterus
1)
___________ - folds of the broad ligament that extend from the pelvic walls
& floor to the lateral walls of the uterus; also support the ovaries & uterine tubes
2)
Rectouterine folds (uterosacral ligament) - part of peritoneum that curves along the lateral pelvic wall on both sides of the ________ to connect uterus to the sacrum
4
5
3)
Cardinal (lateral cervical) ligaments - fibrous bands in the broad ligament that extend from _______ & vagina and attach to the lateral pelvic walls; also contain some vessels, smooth muscle, & nerves
4)
________ ligaments - continuations of the ovarian ligaments; extend from the uterus’ lateral border, through the inguinal canal, & attach to the labia majora
3.
Uterine Wall - composed of 3 _________: a.
_____metrium - outermost serosal layer, consists of the thin visceral peritoneum
1)
Lateral portion is continuous with the _______ ligament
2)
________uterine pouch is formed by the peritoneum between the uterus and urinary bladder
3)
________uterine pouch is formed by the peritoneum between the uterus and the rectum b.
_______metrium - thick middle layer composed of 3 layers of smooth muscle arranged in longitudinal, circular, & spiral patterns c.
_______metrium - inner mucosal lining, consists of 2 layers
1) Stratum _________ of columnar epithelium and containing secretory glands; this layer is shed during menstruation
2) Stratum _________ - vascular layer that regenerates the stratum functionalis after each menstruation
C.
_________ - tubular, fibromuscular organ that extends from the cervix to vestibule; it receives sperm from the penis during coitus, serves as the birth canal and passageway for menses
1.
__________ - deep recess surrounding the protrusion of the cervix into the vagina
2.
Vaginal __________ - opening of the vagina into the vestibule
3.
_______ - thin fold of mucous membrane that may partially cover the vaginal orifice
4.
The vaginal wall is composed of 3 _________ a.
Mucosal layer - consists of nonketatinized _________ squamous epithelium that forms transverse folds ( vaginal _______ ) b.
___________ layer - longitudinal & circular bands of smooth muscle interlaced with CT c.
__________ layer - dense regular CT + elastic fibers that covers the vagina and attaches it to surrounding pelvic organs
D.
_________ (pudendum) - external genitalia of the female, include:
1.
________________ - adipose CT covering the pubic symphysis
2.
Labia ________ - 2 thickened longitudinal skin folds that contain loose CT, adipose, smooth muscle, sweat & sebaceous glands; homologous to male scrotum
3.
Pudendal ______ - groove that separates the labia majora
4.
Labia _________ - smaller longitudinal folds between the labia majora; also contain sebaceous glands and unite anteriorly to form the ___________ covering the clitoris
5.
____________ - small rounded projection at the anterior junction of the labia minora; homologous to the male ________
6 a.
________ clitoris contains erectile tissue, sensitive nerves, and is covered by a prepuce b.
Corpora _________ diverge posteriorly to form the crura and attach to the sides of the pubic arch
6.
Vaginal ______________ - longitudinal cleft enclosed by the labia minora; contains a.
Urethral & vaginal __________ b.
Major & minor vestibular (____________) glands inside the vaginal orifice secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina during coitus c.
Vestibular _______ - bodies of vascular erectile tissue under the skin forming the lateral walls of the vestibule; contribute to labial swelling during coitus d.
______________ (Skene) glands, homologous to the _________ gland, open into the vestibule near the external urethral orifice; also secrete mucus
7. _____________ – surgical incision through the posterior end of the vestibule to widen the vaginal orifice during childbirth
V.
_____________ Glands - modified sweat glands composed of secretory alveoli & ducts; glands develop at puberty and function in lactation after childbirth
A.
Each mammary gland is composed of 15-20 ______ , each with its own passage way to the outside; the lobes are separated by ___________ tissue
1.
Each lobe is divided into ___________ that contain the glandular mammary alveoli
2.
Mammary ____________ produce milk in a lactating female
3.
Mammary ducts from mammary alveoli converge to form ______________ ducts, which expand near the nipple to form a lactiferous ________ where milk is stored
4.
Suspensory (___________) ligaments between the lobules extend from the skin to the deep fascia over the pectoralis major muscle and support the breasts
B.
_____________ features of the breast include:
1.
_________ - cylindrical projection from the breast that contains some smooth muscle that contracts in response to cold, touch, and sexual arousal
2.
___________ - circular pigmented area surrounding the nipple
3.
Areolar _________ - sebaceous glands near the surface of the areola; secretions keep the areola pliable
C. Breast ____________ occurs in one of nine women, and is one of the leading causes of female mortality
1. Breast ________ begin with cells of the mammary ducts and may _______________ to other organs via the lymphatic system
2. ___________ include a palpable lump, puckering of the skin, changes in skin texture, and fluid discharge from the nipple
3. Risk factors include long-term _________ exposure, x-rays, carcinogenic chemicals, excess alcohol and _____ intake, and _________
4. Early detection involves breast self-examination (BSE) and routine _____________
5. Treatment may be by lumpectomy, simple ______________, or radical mastectomy, as well as radiation and chemotherapy
7
VI. Puberty & Menopause
A. ___________ begins at ages 9-10 for most girls in the USA, triggered by rising levels of
__________, FSH, and LH
1. _____ stimulates development of ovarian follicles, which secrete ___________, progesterone, inhibin, and a small amount of androgen
2. Breast development ( ________ ) is the earliest sign of puberty, stimulated by estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, glucocorticoids, and growth hormone
3. _________ is the development of pubic and axillary hair, sebaceous and axillary sweat glands. _____________ induce this and activate the female libido
4. _____________ is a girl’s first menstrual period, occurring at an average age of 12 in the USA
5. ___________ induces the development of ovaries and secondary sex organs, as well as secondary sex characteristics and bone growth
6. ______________ acts mainly on the uterus, and inhibin modulates FSH secretion
B. Climacteric & Menopause
1. With age, the number of ovarian follicles ___________, along with estrogen and progesterone secretion
2. The decline of steroids brings on a transitional period of climacteric (_____________) for a few years, leading to
3. _______________ – the cessation of ovulation and menstruation
VII. Female Sexual ____________ is similar to that of the male, including excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution phases, but has some differences
A. _______________ and plateau phases
1. _______________ occurs in the labia minora, labia majora, clitoris, and breasts
2. Lubrication of the vulva and vagina occurs via secretions of the greater __________ glands and glands in the vaginal canal
3. The inner vagina dilates and its lower end constricts to form a narrow passage, the
_________ ____________
4. The uterus rises from its forward-tilted position to a nearly vertical one (the ________ effect)
B. ___________
1. _________________ glands secrete into the vulva
2. The orgasmic platform of the vagina ____________ repeatedly
3. The __________ plunges into the vaginal canal (into the semen, if present)
C. ____________
1. The __________ returns to its forward tilt
2. The orgasmic platform __________
3. ____________ become less congested
4. Unlike men, women lack a ___________ period and may experience multiple _______ in succession