Alpha particle scattering
advertisement

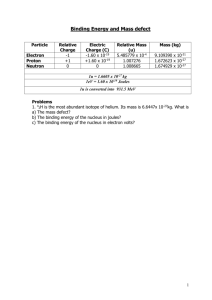
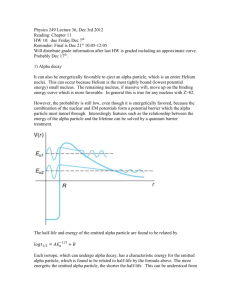
Distance of closest approach between an alpha particle to a gold nucleus Alpha particle (+2e) Gold nucleus (+79e) d If an alpha particle with a kinetic energy E is fired directly towards a gold nucleus it will feel a repulsion which increases as it gets closer - climbing the potential hill surrounding the nucleus. When all the kinetic energy has been converted to potential energy the alpha particle (charge q) has reached its distance of closest approach (dc) and comes to rest. At that point : Eα = qVE =(1/4πεo)qQ/dc so therefore dc = (1/4πεo)qQ/Eα Alpha particle scattering The diagram shows the paths of other alpha particles that were not travelling directly towards the centre of the nucleus. These are scattered. Example problem Calculate the distance of closest approach between an alpha particle of energy 5.5 MeV (5.5x106x1.6x10-19) if the charge on the gold nucleus is +79e = +79x1.6x10-19 C and the charge on the alpha particle is +2e = 2x1.6x10-19 C Using dc = (1/4πεo)qQ/Eα we have dc = [9x109x(2x1.6x10-19x79x1.6x10-19)]/8.8x10-13 = 4.125x10-14 m. This is well inside the atom but some eight nuclear diameters from the centre of the gold nucleus.