LONG TERM PLAN Year 12
advertisement

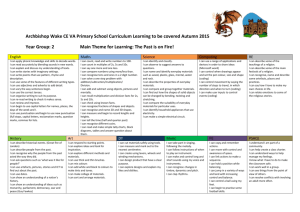
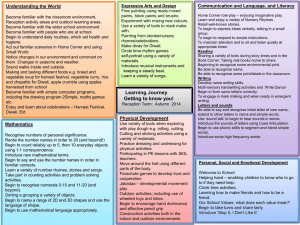
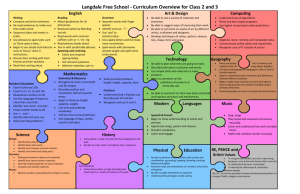
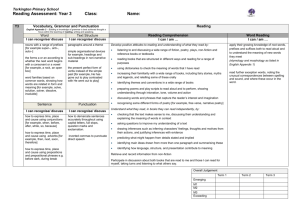
GEOGRAPHY HISTORY LONG TERM PLAN – 2015/16 – MRS CHELL - BEES - YEAR 1/2 AUTUTMN 1 AUTUMN 2 SPRING 1 VICTORIAN CHILDREN AT PLAY Changes within living memory To show their emerging sense of chronology by placing a few events and objects in order, and by using everyday terms about the passing of time. To find answers to some simple questions about the past from sources of information. BONFIRE NIGHT AND CHRISTMAS Events beyond living memory Pupils recognise the distinction between present and past in their own and other people's lives. To show their emerging sense of chronology by placing a few events and objects in order, and by using everyday terms about the passing of time To know and recount episodes from stories about the past. To find answers to some simple questions about the past from sources of information. UP, UP AND AWAY Locational knowledge • To name, locate and identify characteristics of the four countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom and its surrounding seas. Human and physical geography • To use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key physical features and key human features. Geographical skills and fieldwork • To use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries. • To use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features. THE GREAT FIRE OF LONDON Events beyond living memory Pupils recognise the distinction between present and past in their own and other people's lives. To show their emerging sense of chronology by placing a few events and objects in order, and by using everyday terms about the passing of time. To know and recount episodes from stories about the past. To find answers to some simple questions about the past from sources of information. FOLK STORIES AND CASTLES Places in their own locality Events beyond living memory To show their emerging sense of chronology by placing a few events and objects in order, and by using everyday terms about the passing of time. To know and recount episodes from stories about the past. To find answers to some simple questions about the past from sources of information. POLAR BEAR OR PENGUINS! Locational knowledge • To name and locate the world’s five oceans. Human and physical geography • To identify the location of cold areas of the world in relation to the North and South Poles; to identify seasonal weather patterns in relation to the North and South Poles; to use basic geographical vocabulary for key physical features and key human features. Geographical skills and fieldwork • To use world maps, atlases and globes to identify continents and oceans studied at this key stage. Place knowledge • To understand geographical similarities and differences. SUN HATS OR UMBRELLAS! Human and physical geography • To identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the United Kingdom; to use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key physical features and key human features; to use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key physical features, including stream, river, reservoir, sea, ocean; to identify the location of hot and cold areas of the world in relation to the equator and the North and South Poles. Place knowledge • To understand similarities and differences through studying human and physical geography. HAVE YOU EVER BEEN LOST? Geographical skills and fieldwork The location of features and routes on a map. To use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of their school. To use plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; and use basic symbols in a key. To use simple compass directions (N, S, E, W) and locational and directional language to describe the location of features and routes on a map. Human and physical geography To use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key physical features and key human features. SPRING 2 SUMMER 1 SUMMER 2 Josiah Wedgewood Pottery / Canals The lives of significant people in our own locality Pupils recognise the distinction between present and past in their own and other people's lives To show their emerging sense of chronology by placing a few events and objects in order, and by using everyday terms about the passing of time. To find answers to some simple questions about the past from sources of information. WHAT IF I LIVE IN….. Place knowledge • To understand similarities and differences through studying human and physical geography; to understand similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography of a small area of the United Kingdom. Human and physical geography • To use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key physical features and key human features. SEASIDE / PAST –PRESENTRESCUE Lives of significant individuals Pupils recognise the distinction between present and past in their own and other people's lives To show their emerging sense of chronology by placing a few events and objects in order, and by using everyday terms about the passing of time. To know and recount episodes from stories about the past. To find answers to some simple questions about the past from sources of information. WHAT IF I LIVE IN….. Place knowledge • To understand similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography of a small area of the United Kingdom. Human and physical geography • To use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key physical features and key human features. SCIENCE SEASONAL CHANGES Observe changes across the four seasons Observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies. ANIMALS INCLUDING HUMANS Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are carnivores, herbivores and omnivores Describe and compare the structure of a variety of common animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, including pets) Identify, name, draw and label the basic parts of the human body and say which part of the body is associated with each sense. EVERYDAY MATERIALS Distinguish between an object and the material from which it is made Identify and name a variety of everyday materials, including wood, plastic, glass, metal, water, and rock Describe the simple physical properties of a variety of everyday materials Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of their simple physical properties. PLANTS Identify and name a variety of common wild and garden plants, including deciduous and evergreen trees Identify and describe the basic structure of a variety of common flowering plants, including trees. ART D & T RE DRAWING – LINE AND SHAPE Use drawing as a medium to develop and share ideas. Incorporate known experiences. Focus on using lines and known geometric shapes to create. Primary and secondary colours. Artists – Making links to their own workLOWRY PAINTING COLOUR – SPACE Use painting as a medium to develop and share ideas. Involve experiences and imagination. Focus on using colour and space for effect. Artists – Making links to their own workJACKSON POLLOCK SCULPTING – TEXTURE AND FORM Use painting as a medium to develop and share ideas. Create using imagination. Develop and use a texture for effect. Incorporate known experiences or imagination. Artists – Making links to their own work TOYS Textiles: To shape textiles using templates. To colour and decorate textiles CHRISTMAS DECORATIONS Textiles: To shape textiles using templates. To colour and decorate textiles Materials: I can cut materials safely using tools provided. I can demonstrate a range of cutting and shaping techniques (such as tearing, cutting, folding and curling). LEARNING ABOUT RELIGIONS (WHAT PEOPLE D0) Knowledge and understanding of practices and lifestyles recognise features of religious life and practice FOOD To cut ingredients safely and hygienically. To assemble or cook ingredients. TRADITIONAL TALES ALGORRITHMS AND PROGRAMMING Understand what algorithms are; how they are implemented as programs on digital devices; and that programs execute by following precise and unambiguous instructions Create and debug simple programs Use logical reasoning to predict the behaviour of simple programs COMPUTERS IN EVERYDAY LIVES HOW COMPUTERS WORK Recognise common uses of information technology beyond school LEARNING ABOUT RELIGIONS (WHAT PEOPLE BELIEVE) Knowledge and understanding of beliefs and teachings recount outlines of some religious stories COMPUTING DINOSAURS DATA AND INFORMATION Use technology purposefully to create, organise, store, manipulate and retrieve digital content LEARNING ABOUT RELIGIONS (HOW PEOPLE EXPRESS THEMSELVES) Knowledge and understanding of expression and language recognise some religious symbols and words PAINTING COLOUR – SPACE Use painting as a medium to develop and share ideas. Involve experiences and imagination. Focus on using colour and space for effect. Artists – Making links to their own work- CLAUDE MONET CASTLE Construction: I can use materials to practise drilling, screwing, gluing and nailing to make and strengthen products. Mechanics: I can create products using levers and wheels.gt MATERIALS – PATTERN Use a range of materials creatively to design and make products. Use a wide range of patterns. Artists – Making links to their own work- CLARICE CLIFFE AND MODRIAN DRAWING – LINE AND SHAPE PAINTING COLOUR – SPACE Use drawing as a medium to develop and share ideas. Incorporate known experiences. Focus on using lines and known geometric shapes to create. Artists – Making links to their own work- ALFRED WALLIS CLAY SCULPTURES Materials: I can cut materials safely using tools provided. I can demonstrate a range of cutting and shaping techniques (such as tearing, cutting, folding and curling). LIGHTHOUSES Electricals and electronics: I can recognise if a battery operated device works or not. Construction: I can use materials to practise drilling, screwing, gluing and nailing to make and strengthen products LEARNING FROM RELIGION (MAKING SENSE OF WHO WE ARE) Response, evaluation and application of questions of: identity and experience identify aspects of own experience and feelings, in religious material studied PLANTS AND ANIMALS ALGORRITHMS AND PROGRAMMING Understand what algorithms are; how they are implemented as programs on digital devices; and that programs execute by following precise and unambiguous instructions Create and debug simple programs Use logical reasoning to predict the behaviour of simple programs LEARNING FROM RELIGION (MAKING SENSE OF LIFE) Response, evaluation and application of questions of: meaning and purpose identify things they find interesting or puzzling, in religious materials studied LEARNING FROM RELIGION (MAKING SENSE OF RIGHT AND WRONG) Response, evaluation and application of questions of: values and commitments identify what is of value and concern to themselves, in religious material studied HANDA’S SURPRISE DATA AND INFORMATION Use technology purposefully to create, organise, store, manipulate and retrieve digital content SEA AND COAST COMMUNICATION AND SAFETY Use technology safely and respectfully, keeping personal information private; identify where to go for help and support when they have concerns about content or contact on the internet or other online technologies MUSIC LISTENING AND APPLYING KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING Listen for different types of sounds. Know how sounds are made and changed. Make sounds with a slight difference, with help. Use voice in different ways to create different effects. CREATING AND DEVELOPING MUSICAL IDEAS (COMPOSING) Make a sequence of long and short sounds with help (duration). Clap longer rhythms with help. Make different sounds (high and low– pitch; loud and quiet– dynamics; fast and slow-tempo; quality of the sound- smooth, crisp, scratchy, rattling, tinkling etc. timbre). PSHE PE GYMNASTICS Acquiring and developing skills. Explore gymnastics actions and still shapes. Move confidently and safely in their own and general space, using change of speed and direction. Selecting and applying skills, Tactics and compositional ideas. Copy or create and link movement phrases with beginnings, middles and ends. Perform movement phrases using a range of body actions and body parts. Knowledge and understanding of fitness and health. Know how to carry and place equipment recognise how their body feels when still and when exercising Evaluating and improving performance. Watch, copy and describe what they and others have done CONTROLLING SOUNDS THROUGH SINGING AND PLAYING (PERFORMING) Take part in singing. Follow instructions on how and when to sing/play an instrument. Take notice of others when performing. Make and control long and short sounds (duration). Imitate changes in pitch– high and low. DANCE Acquiring and developing skills Explore movement ideas and respond imaginatively to a range of stimuli. Move confidently and safely in their own and general space, using changes of speed, level and direction Selecting and applying skills, tactics and compositional ideas Compose and link movement to make simple dances with clear beginnings, middles and ends Perform movement phrases using a range of body actions and body parts Knowledge and understanding of fitness and health Recognise how their body feels when still and exercising Evaluating and improving performance Talk about dance ideas inspired by different stimuli Copy, watch and describe dance movement ATHLETICS ACTIVITIES Acquiring and developing skills Remember, repeat and link combinations of actions. Use their bodies and a variety of equipment with greater control and coordination Selecting and applying skills, tactics and compositional ideas Use their bodies and a variety of equipment with greater control and coordination Knowledge and understanding of fitness and health Recognise and describe what their bodies feel like during different types of activity Evaluating and improving performance Watch, copy and describe what they and others have done RESPONDING AND REVIEWING (APPRAISING) Hear the pulse in music. Hear different moods in music. Identify texture– one sound or several sounds? Choose sounds to represent different things (ideas, thoughts, feelings, moods etc.). OUTDOOR AND ADENTUROUS ACTIVITIES Acquiring and developing skills Recognise their own space. Explore finding different places Selecting and applying skills, tactics and compositional ideas Follow simple routes and trails, orientating themselves successfully. Solve simple challenges and problems successfully Knowledge and understanding of fitness and health Recognise and describe how their body feels during exercise Evaluating and improving performance Observe what they and others have done and use their observations to GAMES Acquiring and developing skills Be confident and safe in the spaces used to play games Explore and use skills, actions and ideas individually and in combination to suit the game they are playing Selecting and applying skills, tactics and compositional ideas choose and use skills effectively for particular games Knowledge and understanding of fitness and health Know that being active is good for them and fun Evaluating and improving performance Watch, copy and describe what others are doing describe what they are doing PHONICS MATHS Phase 3 Phase 4 Phase 5 Phase 6 Develops children's knowledge of GPCs, Develops children's knowledge of GPCs, Develops children's knowledge of GPCs, their skills of blending and Develops children's knowledge of GPCs, their skills of blending and their skills of blending and segmenting their skills of blending and segmenting segmenting with letters and recognition of high frequency words segmenting with letters and recognition of high frequency words with letters and recognition of high with letters and recognition of high containing GPCs not taught at that phase. Children learn more containing GPCs not taught at that phase. Increases fluency of the frequency words containing GPCs not frequency words containing GPCs not graphemes for the 40+ phonemes taught in Phases Two and Three blending of words encountered for the first time in reading and taught at that phase. Develops children's taught at that phase. There are no new and more ways of pronouncing graphemes introduced in Phases accuracy of spelling choices. knowledge of the seven remaining letters GPCs to be learnt in this phase. Develops Two and Three. Teaches and practices the skills of blending and of the alphabet and graphemes to cover children's knowledge and skills of segmenting using all GPCs taught. most of the phonemes represented by blending and segmenting words with more than one letter. Teaches and adjacent consonants. practises the skills of blending and segmenting sounds represented by single letters and graphemes of more than one letter. Number and place count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number value count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples of twos, fives and tens given a number, identify one more and one less identify and represent numbers using objects and pictorial representations including numberlines, and use the language of: equal to, more than, less than (fewer), most, least read and write numbers from 1 to 20 in numerals and words. recognise and create repeating patterns with objects and practise counting (1, 2, 3…), ordering (first, second, third…), and to indicate a quantity (3 apples, 2 centimetres), including solving simple concrete problems, until fluent begin to recognise place value in numbers beyond 20 by reading, writing, counting and comparing numbers up to 100, supported by objects and pictorial representations practise counting as reciting numbers and counting as enumerating objects, and counting in twos, fives and tens from different multiples including varied and frequent practice through increasingly complex questions. use the terms odd and even Addition and read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (–) and equals (=) signs subtraction represent and use number bonds and related subtraction facts within 20 add and subtract one-digit and two-digit numbers to 20, including zero solve one-step problems that involve addition and subtraction, using concrete objects and pictorial representations, and missing number problems such as 7 = – 9. memorise and reason with number bonds to 10 and 20 in several forms (for example, 9 + 7 = 16; 16 – 7 = 9; 7 = 16 – 9). realise the effect of adding or subtracting zero to establish addition and subtraction as related operations. combine and increase numbers, counting forwards and backwards. discuss and solve problems in familiar practical contexts, including using quantities and include the terms: put together, add, altogether, total, take away, distance between, difference between, more than and less than, to develop the concept of addition and subtraction and use these operations flexibly. Multiplication and solve one-step problems involving multiplication and division, by calculating the answer using concrete objects, pictorial representations and arrays with support division begin to understand: multiplication and division through grouping and sharing small quantities; doubling numbers and quantities; finding simple fractions of objects, numbers and quantities. make connections between arrays, number patterns, and counting in twos, fives and tens. Fractions recognise, find and name a half as one of two equal parts of an object, shape or quantity recognise, find and name a quarter as one of four equal parts of an object, shape or quantity. recognise and find half of a length, quantity, set of objects or shape. connect halves and quarters to the equal sharing and grouping of sets of objects and to measures, as well as recognising and combining halves and quarters as parts of a whole. Measurement compare, describe and solve practical problems for: lengths and heights [Eg. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half]; mass/weight [Eg. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than]; capacity and volume [Eg. full/empty, more than, less than, half, half full, quarter]; time [Eg. quicker, slower, earlier, later] measure and begin to record: lengths and heights mass/weight capacity and volume time (hours, minutes, seconds) recognise and know the value of different denominations of coins and notes sequence events in chronological order using language [for example, before, after, next, first, today, yesterday, tomorrow, morning, afternoon, evening] recognise and use language relating to dates: days of the week, weeks, months, years tell the time to the hour and half past the hour and draw the hands on a clock face to show these times. move from using and comparing different types of quantities and measures using non-standard units, including discrete (Eg. counting) and continuous (Eg. liquid) measurement, to using manageable common standard units (cm, m, l, kg). begin to use measuring tools such as a ruler, weighing scales and containers. use the language of time, including telling the time throughout the day, first using o’clock and then half past. recognise and name common 2-D and 3-D shapes, including: 2-D shapes [rectangle, square, circle triangle] 3-D shapes [cuboid, cube, pyramid sphere]. handle common 2-D and 3-D shapes, naming these and related everyday objects fluently. recognise common 2-D and 3-D shapes in different orientations and sizes, and know that rectangles, triangles, cuboids and pyramids are not always similar to each other. apply phonic knowledge to decode words speedily read all 40+ letters/groups for 40+ phonemes read accurately by blending taught GPC read common exception words read common suffixes (-s, -es, -ing, -ed, etc.) read multisyllable words containing taught GPCs read contractions and understanding use of apostrophe read aloud phonically-decodable texts listening to and discussing a wide range of poems, stories and non-fiction at a level beyond that at which they can read independently being encouraged to link what they read or hear read to their own experiences becoming very familiar with key stories, fairy stories and traditional tales, retelling them and considering their particular characteristics recognising and joining in with predictable phrases learning to appreciate rhymes and poems, and to recite some by heart discussing word meanings, linking new meanings to those already known Prediction drawing on what they already know or on background information and vocabulary provided by the teacher checking that the text makes sense to them as they read and correcting inaccurate reading discussing the significance of the title and events making inferences on the basis of what is being said and done predicting what might happen on the basis of what has been read so far Non-fiction being introduced to non-fiction books that are structured in different ways Discussing reading participate in discussion about what is read to them, taking turns and listening to what others say explain clearly their understanding of what is read to them words containing each of the 40+ phonemes taught common exception words • the days of the week name the letters of the alphabet in order using letter names to distinguish between alternative spellings of the same sound Geometry – properties of shapes ENGLISH - READING Decoding Range of Reading Familiarity with texts Poetry & Performance Word meanings Understanding Inference ENGLIS H – WRITI NG Phonic & Whole word spelling Other word building spelling using the spelling rule for adding –s or –es as the plural marker for nouns and the third person singular marker for verbs using the prefix un– • using –ing, –ed, –er and –est where no change is needed in the spelling of root words apply simple spelling rules and guidance from Appendix 1 write from memory simple sentences dictated by the teacher that include words using the GPCs and common exception words taught so far Editing Writing sit correctly at a table, holding a pencil comfortably and correctly begin to form lower-case letters in the correct direction, starting and finishing in the right place form capital letters • form digits 0-9 understand which letters belong to which handwriting ‘families’ and to practise these saying out loud what they are going to write about composing a sentence orally before writing it sequencing sentences to form short narratives re-reading what they have written to check that it makes sense discuss what they have written with the teacher or other pupils Performing Writing read their writing aloud clearly enough to be heard by their peers and the teacher. Vocabulary leaving spaces between words • joining words and joining clauses using "and Grammar regular plural noun suffixes (-s, -es) verb suffixes where root word is unchanged (-ing, -ed, -er) un- prefix to change meaning of adjectives/adverbs to combine words to make sentences, including using and Sequencing sentences to form short narratives separation of words with spaces sentence demarcation (. ! ?) capital letters for names and pronoun 'I') beginning to punctuate sentences using a capital letter and a full stop, question mark or exclamation mark using a capital letter for names of people, places, the days of the week, and the personal pronoun ‘I’ letter, capital letter, word, singular, plural , sentence punctuation, full stop, question mark, exclamation mark Transcription Handwriting Planning Writing Drafting Writing Punctuation Grammatical Terminology